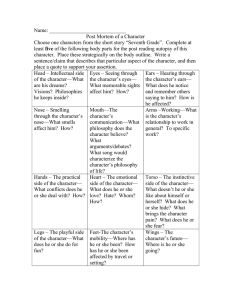
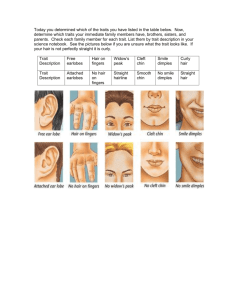
Little Monsters Aim: To produce baby monsters following Mendelian Inheritance Materials A coin for each student Access to the Little Monster Traits Table Method: Making the parent monster 1. Work through the traits one at a time 2. Flip a coin twice 3. A coin that lands heads up codes for the dominant trait e.g. M 4. A coin that lands tails up codes for the recessive trait e.g. m 5. Write down the genotype of the parent monster after flipping the coin twice e.g. Mm 6. Write down the phenotype of the monster e.g. sad mouth Example: The gene for hair can be either straight or curly. Curly is dominant (H). Both coins are flipped. The M coin has tails and so codes for h. The F coin has heads and codes for H. Write down Hh for the genotype for hair. The phenotype is Curly hair. Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes Eyebrows Chin Genotype Phenotype Draw your parent monster www.schoolscience.com.au The next generation of Little Monsters Your parent monster grows up and meets another parent monster. They have two children. It is your job to determine what their children look like. Working with another student, determine the genotype and phenotype of the children 1. If your parent monster is homozygous for a trait then it contributes the allele that it has to the offspring. 2. If your parent monster is heterozygous for a trait then you need to flip a coin to determine which allele the offspring is going to have. 3. Your partner and you contribute ONE allele for each trait. 4. Draw your monster offspring Child 1 Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes eyebrows Chin Genotype Phenotype Child 2 Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes eyebrows Chin Genotype Portraits of the children www.schoolscience.com.au Phenotype Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes Eyebrows Chin Dominant Curly (H) Upside down smile (M) One tooth (T) Small and pointy (E) Large and pointy (N) Diamond shaped (Y) Thick and curly (B) Square (S) Recessive Straight (h) Big smile (m) Lots of teeth (t) Round ears (e) Small button nose (n) Circular (y) Thin, long and droopy (b) Pointy (s) Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes Eyebrows Chin Dominant Curly (H) Upside down smile (M) One tooth (T) Small and pointy (E) Large and pointy (N) Diamond shaped (Y) Thick and curly (B) Square (S) Recessive Straight (h) Big smile (m) Lots of teeth (t) Round ears (e) Small button nose (n) Circular (y) Thin, long and droopy (b) Pointy (s) Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes Eyebrows Chin Dominant Curly (H) Upside down smile (M) One tooth (T) Small and pointy (E) Large and pointy (N) Diamond shaped (Y) Thick and curly (B) Square (S) Recessive Straight (h) Big smile (m) Lots of teeth (t) Round ears (e) Small button nose (n) Circular (y) Thin, long and droopy (b) Pointy (s) Trait Hair Mouth Teeth Ears Nose Eyes Eyebrows Chin Dominant Curly (H) Upside down smile (M) One tooth (T) Small and pointy (E) Large and pointy (N) Diamond shaped (Y) Thick and curly (B) Square (S) Recessive Straight (h) Big smile (m) Lots of teeth (t) Round ears (e) Small button nose (n) Circular (y) Thin, long and droopy (b) Pointy (s) www.schoolscience.com.au