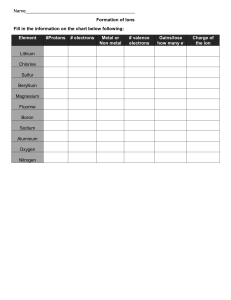
Conduction is one of the basic property of the metal. But conduction in metals differ, this difference in the conductivity can be explained using Band Theory Let us consider the metal Copper (Cu) the electronic configuration of Cu and its energy level diagram can be written as When a di atomic Cu is formed the moecular obrital diagram can be written as But in metallic Cu there are N number of atoms so molecular orbital diagram for Natoms can be given as In the molecular orbital diagram of N-atoms the bonding molecular orbitals of valence shell are collectively termed as Valance band. Similarly the anti bonding molecular orbitals of valance shell are termed as Conduction band. The difference in the energy between the valance band and conduction band is the deciding factor of the property of metal conductor During conduction the electrons jump from valance band to conduction band, lesser the energy required for the transition, higher would be the probability of electron to jump thus the conductor would be higher so metal would behave as very good conductor. But as the energy gap is relatively higher the transition would require higher energy thus the transition would be not easier, thus the resistance of metal would increase In a solid, like copper, aluminum, and steel, these atoms are arranged on a crystal lattice (yes, metals are actually crystalline!). On a microscopic level, heat is conducted via something called phonons (essentially lattice/atomic vibrations) and free electrons. For metals, the ability of a material to conduct heat is tied predominantly with how far electrons travel without being scattered. It is no coincidence metals are both good electrical and thermal conductors. Metals have free electrons, which can also carry heat. The electrons can scatter off of a variety of things like defects, impurities, or lattice vibrations The last one is what really differs between two crystalline materials like copper and aluminum, which have different bonding characters and atomic masses. Steel does worse for similar reasons, and also because it has carbon impurities, which inhibit the transfer of heat. For non-metals, heat is no longer transferred via electrons because there are no free electrons to carry the heat. Instead, they are carried by phonons.