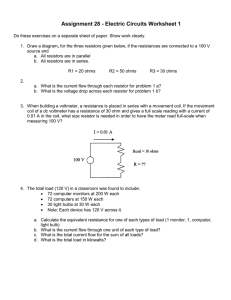
Activity 1 Voltage Divider Bias Configuration Name: Reggie Boy R. Sebarios Course: BSEE-5 Subject: Objectives: To calculate and to show the schematic diagram. To analyze the voltage-divider bias configuration. To get the actual voltage of the VCE and IC. Materials: AC Power Supply (0-20v) Multi-tester BC547 Wires Schematic Diagram: Results & Calculations: Icsat = Vcc / Rc+RE Rc+RE = Vcc / Icsat = 20v / 10mA = 2000 ohms VE = 1/10 * Vcc = 1/10 * 20v = 2v @ CE Loop where Ic = IE Vcc – IcRc – VCE – IERE = 0 IcQ = Vcc – VCE / Rc+RE = 20v – 15v / 2000ohms = 2.5 mA VE = IERE RE = VE / IE = 2v / 2.5 mA = 800 ohms Rc = 2000 ohms – 800 ohms = 1.2 k.ohms VBE = VB – VE VB = VBE + VE = 0.7v + 2v = 2.7 v BRE = 10R2 where B = 294.3 R2 = BRE / 10 = 294.3 * 800 ohms = 23.54 k.ohms VB = Vcc R2 / R1 + R2 R1 = Vcc R2 / VB - R2 = 20v * 23.524v / 2.7v – 23.54kohms = 150.83k.ohms Actual Results: R1 : R2 : RC: VCE: R E: IC: Conclusion: I conclude that by merely changing the value of the resistor the base current can be adjusted to the desired value. And by using the beta (B) relationship, IC can also be found out accordingly. Hence the Q point can be adjusted just by changing the value of the resistor connected to the base.