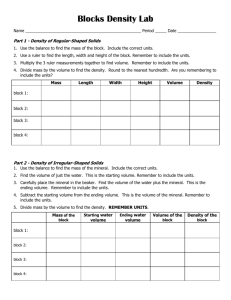
1 1.0: PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1.2: DENSITY ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain density: 1.1. Define density. 1.2. Solve simple problem on density. 2. Carry out an experiment to differentiate the density of regular and irregular shaped solids and liquids. 1 2 1.0: PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1.2: DENSITY DENSITY. • Density of a substance is defined as its mass per unit volume. Density mass volume m v where = density of a substance m = mass of the substance v = volume of the substance • S.I. Unit: kgm-3. • Other unit: gcm-3. INVESTIGATING THE DENSITY OF SOLIDS Regular-shaped solids. • The volume of a substance of regular shape (rectangular bar, cylinder or sphere) may be calculated from measurements made by venier calipers or micrometer screw gauge. Irregular-shaped solids. • The volume of an irregular shape solid (stone) may be determined by using the displacement method. 2 3 1.0: PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1.2: DENSITY To determine the density of regular-shaped solid. Apparatus: Vernier calipers, ruler and electronic balance. Procedure: 1) Find the mass, m, using the electronic balance. 2) Determine the volume by taking appropriate measurements and then calculating the volume as follows: cuboid – measure the length, breadth and height by using a metre rule or venier calipers. V l b h d 2 l cylinder – measure the diameter and the length. V 4 sphere – measure the diameter with a pair of venier calipers together with a metre 3 4 d rule. V 3 2 To determine the density of irregular-shaped solid. Apparatus: Measuring cylinder, thread, irregular-shaped solids. Procedure: 1) Weigh and record the mass of the irregular-shaped solids. 2) Pour water into the measuring cylinder up to a certain level, e. g. 50 cm3. 3) Place the irregular-shaped solids into the measuring cylinder. 4) Record the new reading on the measuring cylinder. 5) Calculate the densities of each of the irregular-shaped solids. 6) Calculate the densities of each object. 3 4 1.0: PROPERTIES OF MATTER 1.2: DENSITY INVESTIGATING THE DENSITY OF LIQUIDS To determine the density of a liquid. Apparatus: Burette, beaker, balance, retort stand. Procedure: 1) Find the mass of a clean, dry beaker (m1). 2) Run a volume (V) of the liquid from the burette into the beaker. 3) Find the mass of the beaker and the liquid (m2). 4