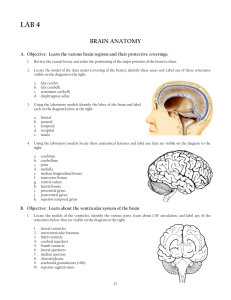
Neuroanatomy Chapter 4: Cerebral Cortex: place where consciousness arises and where voluntary action is initiated. I. General Structures and Landmarks of the Cerebral Cortex a. Cerebral hemispheres: two mirror-image halves of the cerebral cortex b. Meningeal lining: Membranes that overlay the cerebral cortex, consisting of the dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. FUNCTION: protects and supports the structure of the brain. Provides nutrients to the neurons and glial cells. i. Layers: 1. Dura mater: outermost layer. Comprised of two layers of tough connective tissue that are tightly bound together. a. The outer layer is More inelastic than the inner layer b. Epidural space is the space between the layers c. 4 infoldings that support and surround the major structures of the brain i. Falx cerebelli ii. Tentorium cerebelli iii. Diaphragma sallae d. Subdural hematoma: cerebral blood vessel is ruptured. 2. Arachnoid mater: spider like covering that’s under the dura mater which many blood vessels of the brain pass a. Lacey filamentous lining, easily disrupted during dissection. 3. Pia mater: inner most later. Delicately envelops all the sulci and gyri of the CNS. a. Contains major blood vessels that serve the surface of the cerebrum. c. Gyri: outfoldings d. Sulci: infoldings i. Major Sulci and Fissures 1. Superior longitudinal fissure: separates the right and left hemispheres. 2. Precentral gyrus: boundary between the frontal and parietal lobes 3. Lateral fissure/ lateral sulcus/ Sylvian fissure: Separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes. In swallowing, the buccal cavity. e. The Ventricles and Cerebrospinal Fluid i. Cerebrospinal Fluid: CSF: bathes the CNS, providing a cushion for the neural tissue, some nutrient delivery and an important waste removal process that occurs during sleep. 1. Consist of 4 cavities: a. Lateral Ventricles: Right lateral ventricle, Left lateral ventricle (largest ventricles) i. Choroid plexus: produce the bulk of the CSF, although all of the ventricles produce CSF. ii. Largest of the ventricles iii. Four spaces that extend into each of the lobes of the cerebral cortex. Shaped like a horseshoe 1. Anterior horn of the lateral ventricles projects into the frontal lobe to the genu of the corpus callosum. 2. Septum pellucidum: medial wall of lateral ventricle. b. Third ventricle ,Fourth ventricle