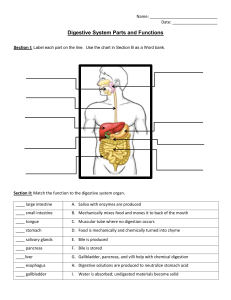
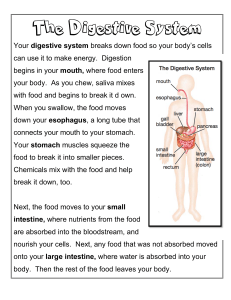
Digestive System Notes The main function of the digestive system is to: 1. breakdown foods into nutrients that can be used by the body 2. absorb nutrients that are necessary for energy, growth, and maintenance 3. rid the body of solid waste - Digestion – the process by which your body breaks down food into small nutrient molecules. 2 Kinds of Digestion 1. Mechanical – foods are physically broken down into smaller pieces. Ex. Chewing with your teeth. 2. Chemical – Chemicals produced by the body break foods into their smaller chemical building blocks. - Absorption – the process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. - Saliva – the fluid released when your mouth waters that plays an important role in mechanical and chemical digestion. Digestion Process 1. Mouth - Begins to break down food into smaller pieces through mechanical digestion. Salivary glands produce saliva; saliva in the mouth starts the process of chemical digestion. Saliva contains a chemical substance called ptyalin which is an enzyme that breaks down some starches into sugars. - enzyme- a protein that speeds up chemical reactions in the body. 2. As you swallow, a small flap of tissue called the epliglottis automatically closes over windpipe (so your food won’t go down the wrong way). 3. Esophagus – The muscular transport tube that carries chewed food to the stomach. It is lined with mucus. -mucus- a thick, slippery substance produced by the body. This makes food easier to swallow. Food stays in the esophagus about 10-12 seconds. - peristalsis – waves of muscular contractions that move food through the digestive system. 4. Stomach – J-shaped, muscular pouch located in the abdomen. It continues the process of mechanical digestion (Mostly mechanical digestion is taking place in the stomach). The stomach churns and mixes food with digestive juices continuing chemical digestion that the mouth started. An avg. adult’s stomach holds about 2 liters of food. -pepsin- is an enzyme produced by the stomach that digests proteins. Pepsin, hydrochloric acid, and mucus are secreted by cells in the stomach. After 3 to 6 hours in your stomach, muscle contractions and enzymes have changed the food into a soft, watery substance. 5. Small intestines - The organ where most of the chemical digestion of food takes place; nutrients from food are also absorbed through the small intestines. The small intestine is approx. 6 meters (21 feet) long and is named for its small diameter (23 cm wide). The pancreas, small intestine, and salivary glands are organs that secrete digestive enzymes. -liver – organ that produces bile. It is the largest and heaviest organ inside the body. - bile – a substance that breaks up fat particles. -gallbladder – the organ that stores bile. -pancreas – a triangular organ that lies between the stomach and the first part of the small intestine. It produces pancreatic juice and insulin. The enzymes produced by the pancreas move into the small intestine and help break down proteins, starches, and fats. The insulin produced is important in controlling the body’s use of sugar. - Food does not pass through the liver and pancreas – these are digestive helpers. After a period of 3 to 5 hours, most of the food that is in the small intestine is digested. -villi – fingerlike structures that line the small intestine through which food is absorbed into the bloodstream. - By the time the food is ready to leave the small intestine, it is basically free of nutrients, except for water. 6. Large intestines - The organ where water is absorbed from the food and taken into the bloodstream; prepares the remaining undigested food for elimination from the body. The large intestine is about 6.5 cm in diameter but only 1.5 meters long. Bacteria that are helpful to digestion live in the large intestine. -After spending 18 to 24 hours in the large intestine, most of the water that is contained in the undigested food is absorbed. Materials that are not absorbed in the large intestine form a solid waste. 7. Rectum and anus - The rectum is a short tube that stores solid waste until it is eliminated from the body (end of the large intestine). -anus- opening at the end of the rectum through which solid wastes are eliminated.