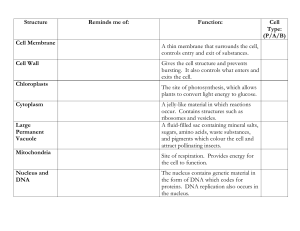
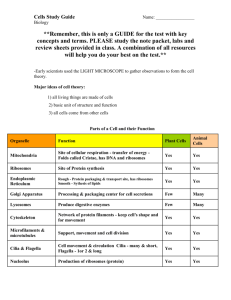
1. Eukaryotic cells 2. Prokaryotic cells What are prokaryotic cells? • PRO NO Bacteria OR What are eukaryotic cells? • EU YOU have and more Comparing Cell Types What are some main differences between these two cells? • Stores and protects genetic information • Makes sure the DNA is available for use at al times • Enclosed in a double membrane called the nuclear envelope • Inside the nucleus is the nucleolus – the site where ribosomes are housed for making protein Smooth ER – No Ribosomes Rough ER Studded with Ribosomes which gives it a bumpy look Ribosomes – made of protein and RNA site of protein synthesis Found in the ER and suspended in the cytoplasm • Consists of closely layered stacks of membrane-enclosed spaces • Processes, sorts and delivers proteins • Supplies energy to the cell by converting the food you eat into useable energy • Has its own ribosomes and DNA just like the nucleus • Contain enzymes • Can engulf and digest targets molecules: This helps the cell: 1. Defend cells from invading bacteria and viruses 2. Break down damaged or worn-out cell parts • Small region of the cytoplasm that produces microtubules • Contains centrioles • Cylinder-shaped organelles made up of microtubules arranged in a circle • Divide DNA during cell division Chloroplasts: Cell walls: • Provide rigid support and give the cell its shape • Carry out photosynthesis • Made up of sacs that contain chlorophyll – a light absorbing molecule that gives plants their green color • Have their own DNA and Ribosomes like the nucleus and mitochondria in animal cells How are Living Things Organized?