Continental Drift: Pangaea, Wegener, Plate Tectonics
advertisement

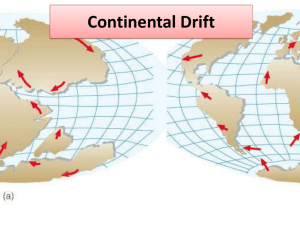
Continental Drift Pangaea Continental Drift Seafloor Spreading Plate Tectonics Plate Lithosphere Asthenosphere Convection Currents Alfred Wegener German meteorologist who proposed the theory of Continental Drift He thought that the puzzle like fit of the continents was not just a coincidence Continental Drift According to Wegener’s hypothesis, the continents have moved slowly to their current locations Wegener suggested that all continents once were connected as one landmass that broke apart about 200 million years ago He called this large landmass Pangaea A Controversial Idea Wegener’s ideas of continental drift were controversial. It wasn’t until long after his death that his basic ideas about continental drift were accepted. Other scientists of that time disagreed with Wegener’s hypothesis. They said that continental drift would not be necessary to explain Wegener’s observations. A Controversial Idea Why? He was unable to explain exactly how the continents drift apart. His theory was that the continents plowed through the ocean floor and were driven by the spin of the Earth. How could continents drift? Although Wegener provided evidence to support his hypothesis of continental drift, he couldn’t explain how, when, or why these changes took place. Because other scientists could not provide explanations either, Wegener’s idea of continental drift was initially rejected. Rock, fossil, and climate clues were the main types of evidence for continental drift. How could continents drift? After Wegener’s death, more clues were found, largely because of advances in technology, and new ideas that related to continental drift were developed. Play first 4 minutes of Eye of Nye (play youtube.com of Alfred Wegener song) Quick Questions What are some things that make the theory of Continental drift difficult to accept? As you read, see how your ideas compare with people who first heard the theory. Why was the scientific community dissatisfied with the theory of continental drift? A Closer Look at Evidence Activity Get Worksheet with the Five Continents detached. FIRST STEP: Need 5 colors to color the 5 different Fossil Record Evidence found on each continent. SECOND STEP: Color the Coast Lines(dotted) a shade of Blue THIRD STEP: Color the continent land a shade of green. FOURTH STEP: Cut out continents (LEAVE COASTLINE ATTACHED) and fit it together like a puzzle. The fossil records should fit together! Glue down on page 13 if you know it is correct! Evidence: Animal Fossils Fossils found in different parts of the world supported continental drift. Fossils of the reptile Mesosaurus have been found in South America and Africa. Evidence: Plant Fossils Fossils of plants also support continental drift. The plant Glossopteris has been found on 5 separate land masses (Africa, Australia, India, South America, and Antarctica). The appearance of this plant on so many different continents also support Wegener’s idea that were once connected and had similar climates Evidence: Climate Glacial deposits and rock surfaces scoured and polished by glaciers are found in several land masses. (South America, Africa, India, and Australia). This shows that parts of these continents were covered with glaciers in the past. PAGE 184 Evidence: Rock Sequences Similar rock structures are found on different continents. Parts of the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States are similar to those found in Greenland and western Europe. PAGE 184 YouTube Video “Continental Drift” Michael Sammartano 11:56 Afterwards: Cloze Activity Fill in blank worksheet. “Continental Drift” Exit Slip 1. Who was the person who came up with the hypothesis of Continental Drift? 2. What was the large landmass called? 3. Name three different types of evidence that supports Continental Drift. 4. Why was the theory controversial in its time? What question do we still have after all of Alfred Wegener’s Evidence? HOW did the Continents Drift? HOW do continents drift? Plates move due to 1. Sea-Floor Spreading and because of 2. Convection Currents in the mantle. Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-Floor Spreading Discovered by Harry Hess Harry Hess 1906–1969 American Geologist While on duty with the US Naval Reserve, he discovered flat-topped seamounts using echo sounders on his ship. He described the oceans as young and with constant renewal by magma flowing into the mid-ocean ridges. In this he described the seafloor spreading process. Discovered Sea-Floor Spreading by using: Sonar - a device that bounces sound waves off under-water objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. *The time it takes for the echo to arrive indicates the distance to the object. Harry Hess Princeton grad. Geologist Navy Captain during WWII Conducted sonar mapping of sea floor while traveling from battle to battle during the Island-hopping campaign in the Pacific during World War II. Sonar is Sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor, and then back to the sonar recording device on the ship to tell seafloor depth. Ocean Floor Map In 1952, Marie Tharp developed the first chart of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge System. Later, with Bruce Hoezen, they complied a map of the Global Ridge System. Advances in SONAR and SUBMARINE technology in the 1950's and 1960's allowed scientists to understand what was happening on the Ocean Floor. The Mid-Ocean Ridge System R Above: The Global Mid-Oceanic Ridge System (Analogy: The Mid-Ocean Ridges are like the seams on a baseball.) The Mid-Atlantic Ridge Mid-Atlantic Ridge – the longest chain of mountains in the world---these are divergent plate boundaries. Harry Hess after studying the maps of the ocean floor, he developed a theory that new ocean crust forming and spreading laterally at Mid-ocean ridge called SEA FLOOR SPREADING Sea-Floor Spreading Ocean floor moves like a conveyor belt carrying continents with it. New ocean floor forms along cracks in the ocean crust as molten material erupts from the mantle spreading out and pushing older rocks to the sides of the crack. Sea-Floor Spreading * the process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor while pushing older rocks away from the ridge The Eye of Nye (11 minutes) 4 minutes on Alfred Wegener end Harry Hess YouTube Video 4:19 Alfred Wegener vs. The Fixists (Continental Drift) – Science History Battle Rap Sea-Floor Spreading Evidence 1.Molten Rock Material – Rocks shaped like pillows(rock pillows) show that molten material has erupted again and again from cracks along the mid-ocean ridge and cooled quickly Sea-Floor Spreading Evidence 2. Magnetic Strips – Rocks that make up the ocean floor lie in a pattern of magnetized stripes which hold a record of the reversals in Earth’s magnetic field Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-Floor Spreading Evidence 3. Drilling Rock Core Samples – Core samples from the ocean floor show that older rocks are found farther from the ridge; youngest rocks are in the center of the ridge Sea-Floor Spreading Evidence 4. Iceland Growing larger every year due to volcanic activity. Iceland Landscape Iceland Landscape Iceland Landscape Iceland Landscape If the Sea-Floor is Spreading..Why doesn’t Planet Earth Get Bigger? Subduction – Process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle; allows part of the ocean floor to sink back into the mantle Why is the sea floor spreading apart? Answer: Convection Currents in the Mantle are causing Oceanic Crust to Separate. Continents Adrift Video 26 minutes Needs to be after SeaFloor Spreading and Convergent and Divergent Boundaries!! Continents Adrift Video Quiz Number your paper to 9 1. Which of these is NOT used as evidence that Earth’s surface consists of plates that are in continuous motion? A. B. C. D. Earthquakes Blizzards Mountains Volcanoes 2. What did scientist Alfred Wegener call the largest supercontinent that once existed? A. B. C. D. Eurasia Panamerica Pangaea Ring of Fire 3. Which of these pieces of evidence did Wegener use to support his theory of continental drift? A. B. C. D. Subduction Zones Divergent Boundaries Seafloor Spreading Fossils from Different Countries 4. Seafloor spreading explains why….? A. Materials circulate within the Earth’s Mantle. B. The ocean has high and low tides. C. One portion of the Earth’s crust dives beneath another portion. D. The oldest part of the ocean floor is found farthest from the mid-ocean ridge. 5. Scientists think that tectonic plates can move when…..? A. Materials circulate in the Earth’s mantle. B. High tide occurs. C. Magma is released from the mid-ocean ridge. D. The lithosphere begins to melt. 6. The rock outer layer of the Earth is called the? A. B. C. D. Mantle Atmosphere Hydrosphere Lithosphere 7. Energy released during an earthquake creates? A. B. C. D. An overheated inner core. A mid-ocean ridge An eruption of molten lava A seismic wave 8. The Ring of Fire refers to? A. An active erupting volcano. B. The volcanoes surrounding the Pacific Ocean. C. The spreading that takes place on the ocean floor. D. The land once known as Pangaea. 9. Mountains on the Earth’s surface form in random locations, with no relation to the Earth’s Plates? A. TRUE B. FALSE