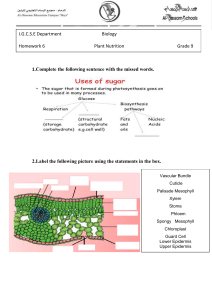
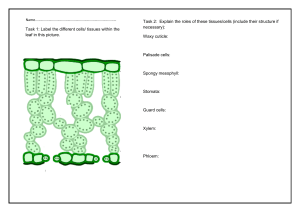
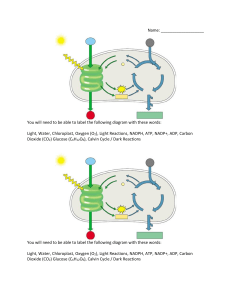
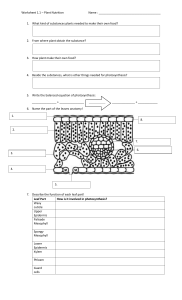
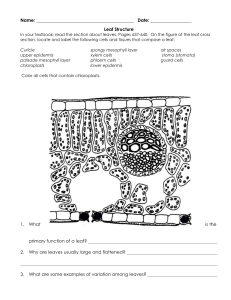
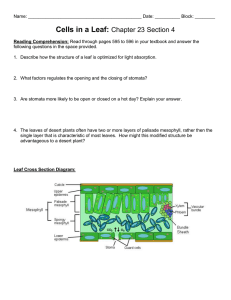
21.4 Leaves KEY CONCEPT Leaves absorb light and carry out photosynthesis. 21.4 Leaves Most leaves share some similar structures. • The blade is usually broad and flat. – collects sunlight for photosynthesis – connects to the stem by a petiole blade petiole 21.4 Leaves • Mesophyll is between the leaf’s dermal tissue layers. cuticle upper epidermis palisade mesophyll spongy mesophyll lower epidermis 21.4 Leaves • Guard cells surround each stoma. – Stomata open and close when guard cells change shape. – When stomata are open, water evaporates and gas exchanges. – Stomata close at night and when plant loses too much water. guard cells stoma 21.4 Leaves Most leaves are specialized systems for photosynthesis. (don’t memorize this, it is just background info) • There are two types of mesophyll cells. – both types contain chloroplasts – palisade mesophyll absorbs sunlight – spongy mesophyll connects to stomata cuticle upper epidermis palisade mesophyll xylem spongy mesophyll phloem lower epidermis stomata 21.4 Leaves • Leaves have many adaptations (you’ll get to this later in the year) – for extreme temperatures, ex: pine needles • . 21.4 Leaves • Leaves have many adaptations. – for extreme temperatures, ex: pine needles – for water loss, ex: cactus spines – for aquatic environments, ex: water lily 21.4 Leaves • Leaves have many adaptations. – for extreme temperatures, ex: pine needles – for water loss, ex: cactus spines – for aquatic environments, ex: water lily – for getting food, ex: Venus’ flytrap