Special Education Disabilities Comparison Graphic Organizer
advertisement

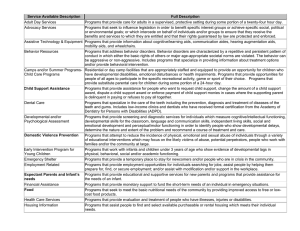
RUNNING HEAD: Comparision Graphic Organizer Category Cause 1 Definition Characteristics Prevalence Autism Developmental disability significantly affecting verbal and non-verbal communication and social interaction Some experts say that autism is caused by genetics or vaccinations The most accepted prevalence rate for autism is 10 per 10,000, a rate derived from analysis of 32 separate prevalence surveys conducted between 1966 and 2001. T Deaf-Blindness Simultaneous hearing and visual impairments causes severe communication and other developmental educational needs Individuals with autism will always have developmental differences in communicative function, social interaction skills, and behavioral characteristics that will be present to varying degrees. Down Syndromes, Trisomy 13, Usher Syndrome Deaf-Blind from birth, Maternal rubella, genetic syndromes In the 2003-2004 school year, 1,667 students were served under the category of multiple disabilities in the United States, representing 0.03% of all special education students. Deafness Hearing impairment so severe that a child is impaired in processing linguistic information genetic or hereditary factors, infections, developmental abnormalities, or environmental/trau matic factors. genetic or hereditary factors, infections, developmental abnormalities, or environmental/trau matic factors. The U.S. Department of Education reports 5,971,495 students receiving special education services in the 2003-2004 school year. Potential Impact on Learning Individuals with autism will always have developmental differences in communicative function, social interaction skills, and behavioral characteristics that will be present to varying degrees. Communication/lan guage development Movement and motor development Cognitive development and the ability to learn Emotional/social development Body image and self-concept students with auditory impairments characteristically experience significant issues with regard to social and RUNNING HEAD: Comparision Graphic Organizer 2 intellectual development, speech and language, and educational achievement. Developmental Delay A delay in either, physical, cognitive, communication social or emotional development heir characteristics vary with the disability category determined by the Admission, Review and Dismissal committee. n/a There is no data available that reflects an accurate count of children served as "NonCategorical Early Childhood." Emotional Disturbance Inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors emotional development, behavioral development, and cognitive development. Depression, Mania, Chronic Pain, Personaity Disorder 7.7%, or 461,055 students, received special education services based on a classification of emotional disturbance. Services are designed by the evaluation to meet a child's needs in physical development, cognitive development, communication, social or emotional development, and adaptive development. Students with emotional disorders can be found at every level of cognitive functioning, but the majority of these students tend to have low average intelligence. RUNNING HEAD: Comparision Graphic Organizer 3 Hearing Impairment Impairment in hearing, can be permanent, or fluctuating Conductive Hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, mixed hearing loss, central hearing disorders Genetic or Hereditary factors, infections, developmental abnormalities or environmental traumatic factors The U.S. Department of Education reports 5,971,495 students receiving special education services in the 2003-2004 school year. students with auditory impairments characteristically experience significant issues with regard to social and intellectual development, speech and language, and educational achievement. Intellectual Disability Subaverage intellect two characteristics shared in varying degrees by all individuals with intellectual disabilities are limitations in intellectual functioning and limitations in adaptive behavior. Developma delays Prevalence ratings for intellectual disabilities are inconsistent, highlighting the often hidden nature of intellectual disabilities within other disability classifications. With the appropriate supports in place, students with intellectual disabilities can achieve a high quality of life in many different aspects. Curriculum and instruction must be carefully modified to help these students reach their potential in both academics and RUNNING HEAD: Comparision Graphic Organizer Multiple Disabilities Simultaneous impairments which causes severe educational needs that are unable to be accommodated Orthopedic Impairment Severe orthopedic impairment that affects a child’s educational performance Other Health Impairment Limited strength, vitality, or alertness children with multiple disabilities will typically share deficits in five distinct areas of development: intellectual functioning, adaptive skills, motor skills, sensory functioning, and communication skills. Neuromotor Impairments, Degenerative Diseases, and Musculoskeletal Disorders Delay in development asthma, attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, diabetes, epilepsy, cardiac conditions, hemophilia, Genetics, Health issues Club foot, impairments caused by disease, bone tuberculosis, cerebral palsy 4 other functional areas such as independent living. Most of the The U.S. students served Department of Education reports under the multiple disability category 5,971,495 do have some level students of cognitive receiving special impairment, but the education specific diagnosis services in the of this impairment 2003-2004 school can often be ambiguous or year. undetermined. The U.S. Department of Education reports 5,971,495 students receiving special education services in the 2003-2004 school year. The U.S. Department of Education reports 5,971,945 students receiving special education services in the 2003-2004 school year. Many students with orthopedic impairments have no cognitive, learning, perceptual, language, or sensory issues. Students with AD/HD, no matter what subtype, can have deficits in three areas that may impact their educational performance. These RUNNING HEAD: Comparision Graphic Organizer leukemia, rheumatic fever, sickle cell anemia, and nephritis. Specific Learning Disability A disorder of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or in using language, spoken or written Academic problems Trauma Disorders of Environmental attention Influences Poor motor abilities Psychological process deficits and informationprocessing problems Lack of cognitive strategies needed for efficient learning Oral language difficulties Speech or Language Development Communication disorder such as stuttering, impaired articulation, language impairment articulation Delay development disorders, fluency disorders, and voice disorders. 5 three areas are executive functioning, intellectual functioning, and social/emotional functioning. Specific learning Learning disabilities are disabilities are considered a highhistorically incidence disability. characterized as The U.S. having a strong Department of impact on Education reports psychological that there are over processes, 2.8 million students academic being served for achievement, and specific learning social/emotional disabilities development. Speech and language impairments are considered a highincidence disability. Approximately 20% of children receiving special education services are receiving Delays and disorders may range from so subtle that they have little or no impact on daily living and socialization to the inability to produce speech or to RUNNING HEAD: Comparision Graphic Organizer Traumatic Brain Injury Acquired injury to the brain caused by external physical force Symptoms can vary greatly depending upon the extent and location of the brain injury. However, impairments in one or more areas (such as cognitive functioning, physical abilities, communication, or social/behavioral disruption) are common Open or closed head injuries resulting in impairments 6 services for speech and language disorders. About 80,000 to 90,000 of the 475,000 children who have sustained TBIs are permanently disabled from their accidents or injuries understand and use language. Students with TBI are too often inappropriately classified as having learning disabilities, emotional disturbance, or mental retardation. As a result, the needed educational and related services may not be provided within the special education program.