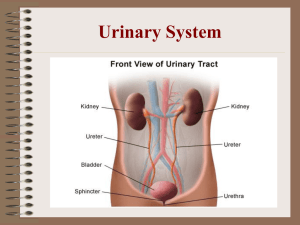
THE URINARY SYSTEM Stuctures • THE KIDNEYS • THE URETERS • THE URINARY BLADDER • THE URETHRA Kidney 1. Location and external anatomy Retroperitoneum 2. Internal anatomy E 4. Physiology Renal corpuscle Nephron Renal tubes The tubule Collecting duct => Renal papilla => Calyx => Ureter The ureters Ureterovesical valve 3. Blood supply The urinary bladder • Shaped: A Sac-like hollow organ -> store urine • Location: Along the body’s midline at the inferior end of the pelvis • Volume: Hold 600-800 milliters of urine from ureters because of the elastic walls Internal urethral sphincter External urethral sphincter Urination • 3-step process The walls of the bladder stretch when urine fills the bladder Spinal cord Relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter Sensation of needing to urinate • People can choose when to urinate because the external urethral sphincter is controlled to close and open. The urethra A tube through which urine passes from the bladder to the exterior of the body Male ( 8-10 inches and ends at the tip of the penis ) Female (2 inches, ends inferior the clitoris and superior to the vagina opening) The urethra • The flow of urine through the urethra is controlled by the internal and external urethral sphincter muscles. 1) The internal urethral sphincter + smooth muscle + open involuntarily 2) The external urethral sphincter + skeletal muscle + open voluntarily FUNCTIONS The nephrons. • Inside each kidney are around a million tiny structures called nephrons. • The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney that filters blood to produce urine. The glomerulus • Arterioles in the kidneys deliver blood to a bundle of capillaries surrounded by a capsule called a glomerulus. • As blood flows through the glomerulus, much of the blood's plasma is pushed out of the capillaries and into the capsule, leaving the blood cells and a small amount of plasma to continue flowing through the capillaries. The cells surrounding the tubules selectively absorb water and substances from the filtrate in the tubule and return it to the blood in the capillaries. At the same time, waste products present in the blood are secreted into the filtrate. By the end of this process, the filtrate in the tubule has become urine containing only water, waste products, and excess ions. The proximal convoluted tubule or PCT • The proximal convoluted tubule or PCT which is a coiled area that extends from the Bowman's capsule. Proximal convoluted tubule The loop of Henle • The loop of Henle connects the proximal convoluted tubule or PCT to the distal convoluted tubule or DCT. The loop of Henle The distal convoluted tubule or DCT. • The distal convoluted tubule which is a coiled area that extends from the loop of Henle to the collecting duct. The distal convoluted tubule The blood exiting the capillaries has reabsorbed all of the nutrients along with most of the water and ions that the body needs to function. The kidneys maintain the homeostasis of several important internal conditions by controlling the excretion of substances out of the body. Ions • Ions can control the excretion of potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, and chloride ions into urine. • When these ions reach a higher than normal concentration, the kidneys can increase their excretion out of the body to return them to a normal level. • Conversely, the kidneys can conserve these ions when they are present in lower than normal levels by allowing the ions to be reabsorbed into the blood during filtration. pH • The kidneys monitor and regulate the levels of hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions in the blood to control blood pH. • The kidneys excrete excess H+ ions into urine for elimination from the body. The kidneys also conserve bicarbonate ions, which act as important pH buffers in the blood. Osmolarity • The kidneys maintain the body’s osmotic balance: Control the amount of water that is filtered out of the blood and excreted into urine. Osmolarity • The changes in excretion of water are controlled by antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Osmolarity • The changes in excretion of water are controlled by antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Blood Pressure • The kidneys monitor the body’s blood pressure to help maintain homeostasis. Blood Pressure High blood pressure Low blood pressure Reducing the reabsorption of water into the blood Producing the enzyme renin to constrict blood vessels Producing watery, dilute urine Producing concentrated urine EXERCISES EXERCIES A. Answer the following questions. 1. What is the function of the urinary system? The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. 2. What does the urinary system consist of? The urinary system consist of the kidneys, the ureters, the urinary bladder, the urethra. 3. Where are the kidneys located? The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs found along the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity. 4. What is the renal medulla made up of? The renal medulla is made up of triangular areas called pyramids. 5. How many nephrons do the kidneys contain? Each kidney contains about one million nephrons. => Each kidney contains about 2 million nephrons. 6. Where is urine stored before it is eliminated from the body? Urine stored in the urinary bladder before it is eliminated from the body. 7. What is the function of the urethra in males? In males, the urethra carries sperm out of the body through the penis. 8. How do the kidneys maintain the body homeostasis? The kidneys maintain the body homeostasis by controlling the excretion of substances out of the body. 9. What is ADH and its function? ADH is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pityutary gland ADH help the body retain water. 10. What is the role of the enzyme renin? Enzyme renin constrict blood vessels and produce concentrated urine. EXERCIE B Complete the sentences with the words or phrases given kidney urinary bladder secrete renal pelvis urethra beanshaped ureter renal pelvis system urine kidney secrete ureter renal pelvis urinary bladder urethra beanshaped urinary system urine waste products kidney secrete urinary bladder urethra beanshaped 1. The _________ is a muscular tube carrying urine from a kidney to bladder. ureter renal pelvis urinary system urine waste products kidney secrete urinary bladder urethra beanshaped 2. The _______ is the place where urine accumulates, waiting for urination. renal pelvis urinary system urine waste products kidney secrete urethra beanshaped 3. _______ is waste liquid that collects in the bladder and is discharged from the body. renal pelvis urinary system urine waste products kidney secrete urethra beanshaped 4. The ________ lead urine out of the body from the bladder. renal pelvis urinary system urine kidney beanshaped secrete 5. The __________ disposes of waste products and toxins from the blood. renal pelvis urinary system urine kidney beanshaped secrete 6. A _________ is one of a pair of organs in the abdomen that separates waste liquid from the blood. renal pelvis urinary beanshaped secrete 7. The kidney is a __________ structure with a convex and concave border. renal pelvis urinary secrete 8. The tip, or papilla, of each pyramid empties urine into a minor calyx; minor calyces emty into major calyces, and major calyces emty into the ____________. renal pelvis urinary secrete 9. The kidneys excrete a variety of _________ produced by metabolism into the urine. urinary secrete 10. The kidneys ______ a variety of hormones, including erythropoietin, calcitriol, and renin. EXERCISE C. Add names of organs to the descriptions of their functions. Rearrange the descriptions of functions to reflect the actual sequence of stages in urine production and excretion. 1.Kidneys 2.The external urethral sphincter 3.The urethra 4.urine 5.The detrusor mucle 6.The urinary bladder 7. The ureters Rearrangement 1 7 6 4 5 2 3 EXERCISE D. Choose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences 1. D 2. A 3. D 4. B 5. C 6. A 7. D 8. D 9. C 10. D Exercise F 1-A 2-C 3-A 4-D 5-A 6-B 7-D 8-A EXERICISE G. Match the terms on the left with their definitions on the right. 1. Nephron A. A cluster of capillaries 2. Proximal B. Voiding 3. Distal C. Excessive urine production 4. Convoluted D. Renal system 5. Urination E. Near 6. Urinary system F. Coiled 7. Eliminate G. A person treating diseases of the urinary tract 8. Polyuria H. Far 9. A urologist I. Get rid of 10. Glomerulus J. Functional unit of the kidney EXERCISE H. Choose the correct word or phrase to complete each sentence below. • 1. The urinary bladder is a sac-like hollow organ used for the storage / production of urine. • 2. Renin causes an increase / decrease in blood volume. • 3. The ureters are a pair of tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder / exterior of the body. • 4. The internal / external urethral sphincter is made of smooth muscle and opens involuntarily when the bladder reaches a certain set level of distention. • 5. The internal / external urethral sphincter is made of skeletal muscle and may be opened to allow urine to pass through the urethra or may be held closed to delay urination. • 6. Excretion / Secretion is a term used to describe urination. • 7. Pain during urination is most likely a symptom of incontinence / urinary tract infection. • 8. The left kidney is located slightly higher / lower than the right kidney because the right side of the liver is much larger than the left side. • 9. The ureter / urethra is the tube that carriers urine to the outside of the body. • 10. The urethra is longer / shorter in males than in females. Excerise I • 1- Filter • 2- Molecular • 3- Eventually • 4- Selective • 5- Completely • 6- Secretion • 7. Tubular • 8.Excretion • 9.Called • 10. Transport Exercise J • 1-A • 2-C • 3-A • 4-C • 5-C • 6-B filter-> elimination filter-> filters enters-> entering moves-> move that-> which urinating-> to urinate