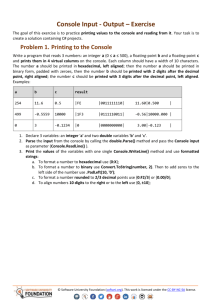
Intro to Computer Programming: Concepts & Languages
advertisement

ITC 112
Computer Programming 1
Programming
2
COMPUTER
▰
▰
▰
▰
▰
Electronic device that can manipulate data
is a device that computes, especially a programmable electronic machine that
performs high-speed mathematical or logical operations or that assembles,
stores, correlates, or otherwise processes information.
is a device that accepts data and manipulates it
is a machine for manipulating data according to a list of instructions.
the term usually refers to an electronic device that can perform automatically a
series of tasks according to a precise set of instructions
3
Problem Solving Concept with Computer
▰ Computer Fundamental
❑ CPU – where all the processing take place
❑ Memory – store all data currently processed, before program can be
execute, program must be loaded into memory
❑ Input Device – Device use to input data to be processed into
computer
❑ Output Device – Device use to display processed data (output)
❑ Secondary Memory – Store permanent data (can be as output
device.
CPU
Output Device
Input Device
Main Memory
Secondary Memory
4
COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEMS
▰ Hardware - refers to the part of the computer that you
can touch (tangible). It consists of interconnected
devices that control everything the computer does
▰ Peopleware - refers to the person who uses the
computer.
▰ Data - refers to the raw facts the computer can
manipulate. Data can consist of letters, numbers,
sounds, or images
5
Components (cont…)
▰ Software - refers to set of electronic instructions that
tell the hardware what to do.
These sets of
instructions are also known as programs, and each of
them has a specific purpose
▰ In computer science software are classified into :
❑ System software
❑ Application software
6
Software
▰
System software : software manages the
computer and its peripheral devices
(hardware)
❑
❑
❑
❑
❑
❑
E.g. Operating systems(OS)
Text editor
Preprocessor
Language translator
Linker
Loader
7
Software
▰ Application software : performs specific tasks
▰ E.g word processor, desktop publishing software,
spreadsheets, database, graphics, communication,
program perform a specific task such as
accounting, scientific, engineering, education etc.
8
Programming Languages
▰
Programming language is divided into
three categories:
❑
Machine Language
❑
Assembly/Low-Level Language
❑
High-Level Language
9
Machine Language
▰ Language understood by the computer
▰ Bunch of 0’s and 1’s
▰ Program written in machine language can be executed
without being translated
▰ Nevertheless, hard to learn because it is written in 0’s and
1’s
▰ Program is too long to solve simple problem
▰ Machine-dependant and not portable
▰ E.g. 0101 1000 0101 1001 1100 0111
▻ 0101 0001 1100 0100 1011 1000
10
Assembly Language
▰ It is a low level programming language.
▰ To make it easier for the programmer, the strings of
0’s and 1’s are replaced into instructions which
resembles English language to represent computer
operation element
▰ So easier to understand and written
▰ E.g
LOAD
MULT
STOR
rate
hour
wages
11
Assembly Language
▰ Nevertheless,
need language translator called
Assembler to change Assembly Language to
Machine Code for execution purpose
▰ Assembler is a type of system software, that we use
to translate our assembly code into binary code
(understand by computer.
12
High-Level Language
▰ Example of high level programming language are COBOL, Fortran,
PASCAL, C - Language, C++, C#, Java, Visual Basic etc
▰ One instruction of it, consist several instructions in machine level or
assembly language.
▻ E.g. Grosspay := Hourswork * Payrate;
▰ Before it can be executed by computer, the program must be changed to
machine code before executed. For high level language compiler will
translate the coding into assembly code and binary code.
▰ Compiler is a type of system software that we use to compile our C
code.
13
COMPILER AND INTERPRETER
▰ Compiler: A compiler is program that converts the instruction of a high
level language into machine language as a whole. A program written in
high level language is called source program. After the source program
is converted into machine language by the compiler, it is called an object
program.
▰ Interpreter: An interpreter is a program that converts one statement of a
program at a time. It executes this statement before translating the next
statement of the source program. If there is an error in the statement, the
interpreter will stop working and displays an error message.
▰ The advantage of interpreters over compilers is that an error is found
immediately. So the programmer can make corrections during program
development.
14
PROGRAMMING CYCLE
❑People make decisions
every day that affect
their lives.
Documentation
Defining the
problem
Checking out
the program
Planning the
solution
Coding the
solution
15
PROGRAMMING CYCLE
▰ Generally there are five (5) steps in Programming Cycle.
o Defining the problem – defining what has to be done or
what problem has to be solved
o Planning the solution – select the best method for solving
the problem
o Coding the solution – prepare the set of instructions for
the computer to execute
o Checking out the program – perform debugging and
testing the program using representative input data
o Documentation – write up the full specifications for other
program users
16
Types of Problems
▰ Algorithmic Solution – problem can be solved with a
series of actions. So once we eliminate the
alternatives and have chosen one best methods,
these steps are called algorithm.
▰ Heuristic Solution – Problem with solutions require
reasoning built on knowledge and experience, and a
process of trial and error. Usually use in the Artificial
Intelligent software or Expert system software.
17
Problem Solving with Computer
▰ Solution means the instructions that must follow to
produce the best results.
▰ Results mean the outcome or completed computer –
assisted answer.
▰ Program means the set of instructions that make up
the solution after they have been coded into a
particular computer language.
18
Problem Solving Concept For Computer
▰
Problem that can be solve with
computers generally consist of three:
❑ Computational – problem with mathematical processing
❑ Logical – problem involving with relational or logical
processing. This is kind of processing involve in decision
making.
❑ Repetitive – problem involving repeating a set of
mathematical or logical instructions.
19
Algorithm
▰ A specific and step-by-step set of instructions for carrying
out a procedure or solving a problem, usually with the
requirement that the procedure terminate at some point
▰ 2 types of algorithm representation will be explained:
❑ Flowchart
❑ Pseudocode
▰ Structured Method (will be explained later)
❑ A method of designing problem solution
20
Algorithm
Knowledge:
Understand algorithm representation using flowchart
and pseudocode
Skill:
Map problem to solution in flowchart and pseudocode
forms
21
Algorithms
▰ List of instruction for carrying out some process step by step
▰ Organizing the solution where programmer develop a set of
instruction for the computer and this is call algorithm.
▰ Pseudo code may be use, it is close to the actual programming
language that the programmer will used later.
▰ To complete it, the programmer will write another separate set of
instruction (coding/program) that will be understand by the
computer.
▰ Instead of Pseudo code, we can also represent the set of
instruction in term of Flowchart ( a graphic presentation of the
algorithm.
22
‘Divide and Conquer’ Strategy in Algorithm
Problem: Prepare a Breakfast
1. Start
2. Prepare
a Breakfast
3. End
23
“Divide and Conquer” Strategy in Algorithm
1. Start
2. Prepare a Breakfast
2.1 Prepare a tuna sandwich
2.2 Prepare some chips
2.3 Make a cup of coffee
3. End
24
“Divide and Conquer” Strategy in Algorithm
1. Start
2. Prepare a Breakfast
2.1 Prepare a tuna sandwich
2.1.1 Take 2 slices of bread
2.1.2 Prepare tuna paste
2.2 Prepare some chips
2.3 Make a cup of coffee
3. End
25
“Divide and Conquer” Strategy in Algorithm
1. Start
2. Prepare a Breakfast
2.1 Prepare a tuna sandwich
2.1.1 Take 2 slices of bread
2.1.2 Prepare tuna paste
2.2 Prepare some chips
2.2.1 Cut potatoes into slices
2.2.2 Fry the potatoes
2.3 Make a cup of coffee
3. End
26
“Divide and Conquer” Strategy in Algorithm
1. Start
2. Prepare a Breakfast
2.1. Prepare a tuna sandwich
2.1.1 Take 2 slices of bread
2.1.2 Prepare tuna paste
2.2. Prepare some chips
2.2.1 Cut potatoes into slices
2.2.2 Fry the potatoes
2.3. Make a cup of coffee
2.3.1 Boil water
2.3.2 Add water with sugar and coffee
3. End
27
Something to ponder…
▰
What is the connection
between these real life
processes and
algorithm?
28
Pseudocode
▰ An outline of a program, written in a form that can easily be
converted into real programming statements. It resembles the
actual program that will be implemented later. However, it
cannot be compiled nor executed.
▰ Pseudocode normally codes the following actions:
❑
❑
❑
❑
Initialization of variables
Assignment of values to the variables
Arithmetic operations
Relational operations
29
Example of Pseudocode
1. Start
2. Read quantity
3. Read price_per_kg
4. price = quantity * price_per_kg
5. Print price
6. End
30
Flowchart
Flowchart
represents
algorithm graphically. It is
intended for communication
and documentation
31
Algorithm-Basic symbols of flowchart
FLOWCHART SYMBOL
EXPLANATION
Flow Direction indicator
Flow of the direction
Terminal
A start and an end of a module. For some end for a main module and exit
for other module
Processing
Processing block, for the calculation, and other step of instructions.
Input / Output (I/O)
Input and output data to from the computer memory.
Decision
Usually has one entrance and two exit.
Process Module
Task that process in different place, module
Preparation
The number of loop execute will start with A, counter incremented by S,
and until the end value B
Connector
on page
off page
Flowchart can be sectioned, the connector will show where the section
continue
32
Flowchart – Other Syntax
Symbol
Semantic
Function call
Magnetic Disc
Stored Data
Document/File
Multiple Document/File
33
Flowchart-(ex.: from previous)
Algorithm
Main Module
1. Repeat
Process Read
Process Calc
Process Print
Until no more
employee
2. End
Algorithm
Calc Modul
2000
1. GrossPay = Hour *
payrate
2. Exit
Flowchart
Algorithm
start
Read
Read Module
1000
1. Read Hours, Payrate
2. Exit
Calc
Print
false No more
employee
True
Algorithm
start
Print Module
3000
1. Print Pay
2. Exit
exit
start
Read
Hours, Payrate
exit
end
GrossPay = Hours * Payrate
Flowchart
Flowchart
start
Print
GrossPay
exit
34
Something to ponder…
Are the steps in the
algorithm
discussed
earlier specific enough
to be executed by
computer?
35
Problem Solving Process
Input
Process
Output
36
Problem Solving Process
Calculate and display the price of a number of
apples if the quantity in kg and price per kg are
given.
Input
Process
• Quantity
• Price_per_kg
Output
Price
Price = Quantity * Price_per_kg
37
Flowchart: Calculate Price of Apples
Start
Input
Quantity
Input
Price_per_kg
Price = Quantity * Price_per_kg
Output
Price
End
38
C# Program: Calculate Price of Apples
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Enter the quantity of Apple in Kg.: ");
quantityOfApple = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter the price of Apple in Kg.: ");
priceOfApple = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Amount = quantityOfApple * priceOfApple;
Console.Write("Total Amount is {0}", Amount);
}
Start
Input
Quantity
Input
Price_per_kg
Price = Quantity * Price_per_kg
Output
Price
End
39
C# Program: Calculate Price of Apples
static void Main(string[] args)
{
It’s not complete!
Declare the
variables…
Console.Write("Enter the quantity of Apple in Kg.: ");
quantityOfApple = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter the price of Apple in Kg.: ");
priceOfApple = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Amount = quantityOfApple * priceOfApple;
Console.Write("Total Amount is {0}", Amount);
}
40
C# Program: Calculate Price of Apples
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int quantityOfApple;
double priceOfApple;
double Amount;
Start
Declaration
Console.Write("Enter the quantity of Apple in Kg.: ");
quantityOfApple = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter the price of Apple in Kg.: ");
priceOfApple = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
} Input
Amount = quantityOfApple * priceOfApple;
Console.Write("Total Amount is {0}", Amount);
}
End
Process
Output
41
C# Program: Calculate Price of Apples
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int quantityOfApple;
double priceOfApple;
double Amount;
Chapter 4
Console.Write("Enter the quantity of Apple in Kg.: ");
quantityOfApple = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter the price of Apple in Kg.: ");
priceOfApple = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
} Chapter 6
Amount = quantityOfApple * priceOfApple;
Console.Write("Total Amount is {0}", Amount);
}
Chapter 5
Chapter 6
42
Example 2
Write a program to calculate the average
mark of three ITC112’s students.
Input
• Mark A
• Mark B
• Mark C
Process
????
Output
Average_mark
THINK!!
43
Activity
▰ Make a flowchart that will compute and print area of the
rectangle.
▰ Compute and print the area and perimeter of square.
▰ Make a flowchart that will convert the following:
❑ Kilometer into Mile (1km = 0.62mile)
❑ Inch into Meter (1inch = 0.0254meter)
❑ Temperature in Celsius into Fahrenheit C=(F−32) × 5/9
❑ Temperature in Fahrenheit into Celsius F= C × 9/5 + 32
44
Example 3
A car park has the following charges:
The 1st three hours costs ₱20.00. The subsequent
hours cost ₱5.00 per hour. Write an algorithm
based on a vehicle’s entry and exit time.
Input
• Entry_time
• Exit_time
Process
????
Output
Charge
45
Flowchart: Calculate Car Park Charge
Start
Input Entry_time
Input Exit_time
Period = Exit_time – Entry_time
Charge =20
No
If
Period > 3
Yes
Charge = 20+(Period-3) * 5
Output
Charge
End
46
C# Program: Calculate Car Park Charge
Start
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int EntryTime, ExitTime, Period, Charge;
Console.Write("Entry Time: ");
EntryTime = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Exit Time: ");
ExitTime= Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Period = ExitTime - EntryTime;
if (Period > 3)
Charge = 20 + (Period-3) * 5;
else
Charge = 20;
Charge =20
Console.Write("Total Charge is {0}", Charge);
Console.ReadLine();
}
Input Entry_time
Input Exit_time
Period = Exit_time – Entry_time
No
If
Period > 3
Yes
Charge = 20+(Period-3) * 5
Output
Charge
End
47
C# Program: Calculate Car Park Charge
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int EntryTime, ExitTime, Period, Charge;
Console.Write("Entry Time: ");
EntryTime = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Exit Time: ");
ExitTime= Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Period = ExitTime - EntryTime;
if (Period > 3)
Charge = 20 + (Period-3) * 5;
else
Charge = 20;
}
Chapter 7
Console.Write("Total Charge is {0}", Charge);
Console.ReadLine();
}
48
Activity
▰ Accept grade and print “FAILED” if grade is less than 75,
otherwise print “PASSED”.
▰ Determine if the inputted integer is positive or negative.
Print “POSITIVE” if positive, otherwise print “NEGATIVE”.
▰ Print the smaller number in two (2) inputted integers.
▰ Print the smallest number in three (3) inputted integers.
▰ Print “EVEN” if the inputted integer is even, otherwise print
“ODD”.
49
Algorithm Development Guidelines
▰ Identify the input and output of the problem.
▰ If necessary, use ‘Divide & Conquer’ strategy to
decompose the problem into smaller and
manageable sub problems. Decompose the
problem until all the sub problems can be solved to
get the required results
▰ For each sub problem, identify and list out the steps
involved in solving it
50
Something to ponder
What might be the
disadvantage of
flowchart?
51
End of Lecture 2
Yes !! That’s all?
What’s next???
INTRODUCTION TO
C# on the way …
52