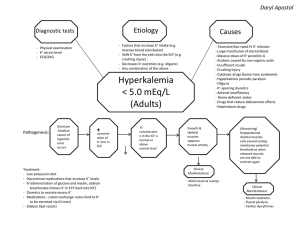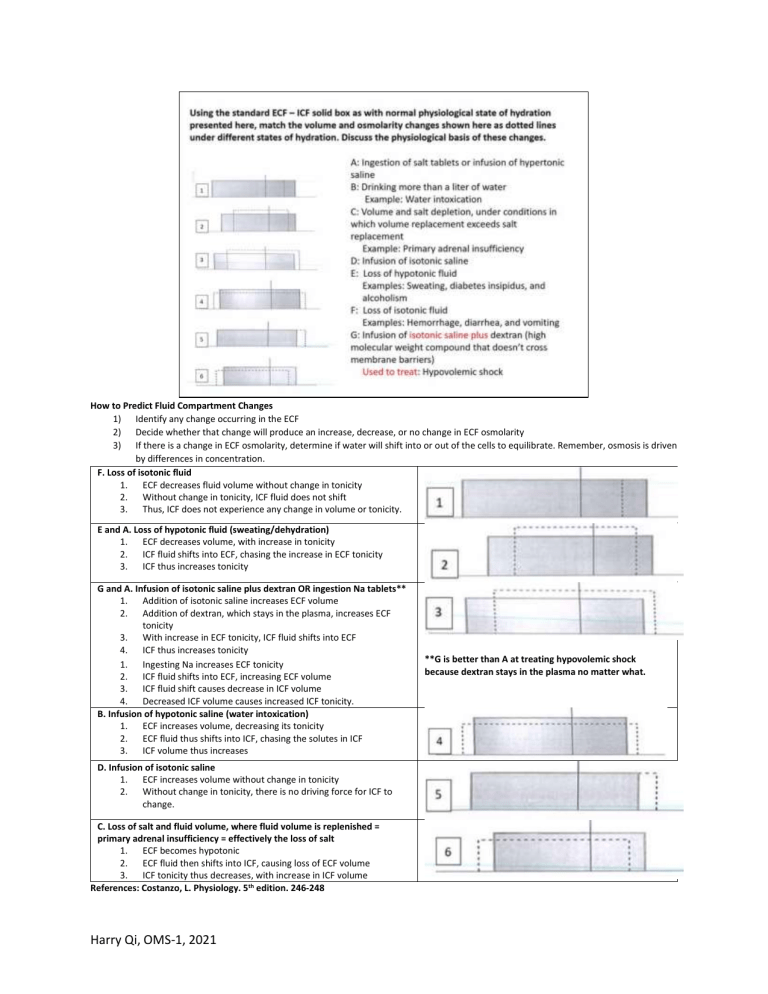
How to Predict Fluid Compartment Changes 1) Identify any change occurring in the ECF 2) Decide whether that change will produce an increase, decrease, or no change in ECF osmolarity 3) If there is a change in ECF osmolarity, determine if water will shift into or out of the cells to equilibrate. Remember, osmosis is driven by differences in concentration. F. Loss of isotonic fluid 1. ECF decreases fluid volume without change in tonicity 2. Without change in tonicity, ICF fluid does not shift 3. Thus, ICF does not experience any change in volume or tonicity. E and A. Loss of hypotonic fluid (sweating/dehydration) 1. ECF decreases volume, with increase in tonicity 2. ICF fluid shifts into ECF, chasing the increase in ECF tonicity 3. ICF thus increases tonicity G and A. Infusion of isotonic saline plus dextran OR ingestion Na tablets** 1. Addition of isotonic saline increases ECF volume 2. Addition of dextran, which stays in the plasma, increases ECF tonicity 3. With increase in ECF tonicity, ICF fluid shifts into ECF 4. ICF thus increases tonicity 1. Ingesting Na increases ECF tonicity 2. ICF fluid shifts into ECF, increasing ECF volume 3. ICF fluid shift causes decrease in ICF volume 4. Decreased ICF volume causes increased ICF tonicity. B. Infusion of hypotonic saline (water intoxication) 1. ECF increases volume, decreasing its tonicity 2. ECF fluid thus shifts into ICF, chasing the solutes in ICF 3. ICF volume thus increases D. Infusion of isotonic saline 1. ECF increases volume without change in tonicity 2. Without change in tonicity, there is no driving force for ICF to change. C. Loss of salt and fluid volume, where fluid volume is replenished = primary adrenal insufficiency = effectively the loss of salt 1. ECF becomes hypotonic 2. ECF fluid then shifts into ICF, causing loss of ECF volume 3. ICF tonicity thus decreases, with increase in ICF volume References: Costanzo, L. Physiology. 5th edition. 246-248 Harry Qi, OMS-1, 2021 **G is better than A at treating hypovolemic shock because dextran stays in the plasma no matter what.