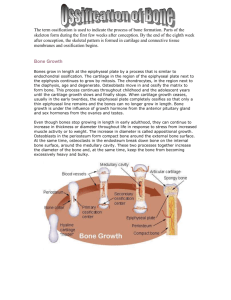
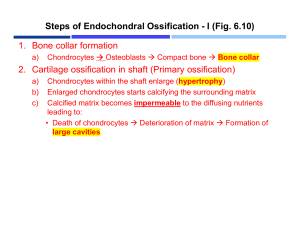
Skeletal system The skeletal system is split into two parts: - Axial - Appendicular Cartilage is also found in the skeletal system Function: - Support - Protection - Movement - Blood/platelet production - Calcium and phosphorus sites Cartilage is a resilient, semi rigid, avascular type of connective tissue. It is found on the heads of long bones and where two bones would meet. Cartilage is formed from the mesenchyme, which differentiates to chondrocytes. Bone is a connective tissue that has been ossified. There are two types of bone, compact and cancellous, spongy, trabecular bone. In long bones compact bone surrounds spongy bone, which in turn surrounds a hollow middle called the medullary. Bone is ossified in lamella that surround a Haversian canal. These canals hold blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves. The whole bone is surrounded by a Periosteum except for the cartilage. Osteoblasts are formed from the mesenchyme cell, the osteoprogenitor. Osteoblasts build the bone by depositing salts, primarily calcium hydroxyapatite. Osteoblasts evolve into osteocytes, which are trapped within the formed bone. Osteoclasts dissolve bone to release salts and help keep the bone in homeostasis. It forms by way of the pressure exerted from it. There are two types of bone formation: - Endochondral ossification - Intramembranous ossification Intramembranous ossification occurs during foetal development and is formed directly from the differentiation of the mesenchyme to osteoblasts. Endochondral ossification occurs by way of chondrocytes. The mesenchyme first differentiates into chondrocytes, which produce cartilage. The cartilage is then progressively ossified. This occurs from gestation to maturity. Long bones are formed through Endochondral ossification. At first the bone is a cartilage model which starts to ossify at the primary ossification site in the middle of the bone, diaphysis. Second ossification sites formed in the heads of the bone, epiphyses. The diaphysis and epiphysis are split by the growth plate, which disappears after maturity, the metaphysis. Joints Classified into 2 types: - Synovial - Solid o Cartilaginous o Fibrous