mercantilism-and-british-north-american-colonies presentation
advertisement

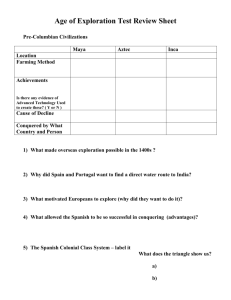
FROM RAW MATERIALS TO RICHES: MERCANTILISM AND THE COLONIES OF BRITISH NORTH AMERICA OBJECTIVES Define key terms such as mercantilism, market, raw materials, finished goods, exports, imports, trade barriers, balance of trade, Navigation Acts, tariffs, imperialism. Simulate trade in a free market economy. Simulate the mercantilist system that existed between Britain and the North American colonies. Compare and contrast the trade in a free market with trade under the mercantilist system. Explain how the mercantilist system worked and why some European powers pursued these policies. Read and interpret a variety of primary sources on the topic of mercantilism. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of mercantilism as an economic system. Describe how markets are affected by changes in government trade policies. MONEY MARKETS CAPITAL GAME ROLES ROUND 1 Households have RESOURCES—— they want GOODS. Trade resources for money and buy goods! Businesses have MONEY—they want MORE MONEY than they had at the start. Buy resources, make goods, sell goods for a profit! DEBRIEF Which businesses were successful? Why? Which households were successful? Why? What caused some households and businesses to be less successful than others? How well did everyone follow the rules? Did anyone have to go to jail? Why did the markets work even though there were few rules to follow? T-CHART FOR MERCANTILISM Dividing the world’s resources IS like dividing a cookie because: Dividing the world’s resources IS NOT like dividing a cookie because: MAP OF EUROPEAN COLONIES CIRCA 1700 MERCANTILISM POLITICAL CARTOON This cartoon may be under copyright. Please access it from the following URL: http://www.historyhub.us/14-study-notes.html TRADE RESTRICTIONS Act/Regulation Date Significance/Features Favored British ships and sailors Limited Dutch trade Required all colonial trade to be on English ships Master and three-quarters of crew must be English "enumerated goods" 1663 Land in England first Plantation Duty Act 1673 English customs house in colonies Courts to enforce trade regulations and punish smugglers Right to board ships Navigation Act Navigation Act Staple Act Navigation Act 1651 1660 1696 ROLES ROUND 2 Households have RESOURCES—they want GOODS. Trade resources for money and buy goods! Businesses have MONEY—they want MORE MONEY than they had at the start. Buy resources, make goods, sell goods for a profit! All businesses, except the British, must pay a tax to get a manufactured good. DEBRIEF Which businesses were successful? Why? Which businesses were hurt the most? Why? Which households were successful? Why? Which households were hurt the most? Why? How do you think these experiences affected how people felt about Great Britain? MERCANTILISM ASSESSMENT PIECE You will read informational text about British North America and the mercantilist system. You will use your simulation experience as well as the informational text to decide whether a person from the time period in the role you played in the simulation would have supported or opposed mercantilism. You must support your position using evidence from the reading and the simulation experience. ECONOMICS STANDARDS AND BENCHMARKS National Standards for Economic Education Content Standard 5: Trade Students will understand that: Voluntary exchange occurs only when all participating parties expect to gain. This is true for trade among individuals or organizations within a nation, and among individuals or organizations in different nations. Students will be able to use this knowledge to: Negotiate exchanges and identify the gains to themselves and others. Compare the benefits and costs of policies that alter trade barriers between nations such as tariffs and quotas. Content Standard 7: Markets and Prices Students will understand that: Markets exist when buyers and sellers interact. This interaction determines market prices and thereby allocates scarce goods and services. Students will be able to use this knowledge to: Identify markets in which they have participated as a buyer and seller and describe how the interaction of all buyers and sellers influences prices. Also, predict how prices change when there is either a shortage or surplus of the product available. Content Standard 13: Income Students will understand that: Income for most people is determined by the market value of the productive resources they sell. What workers earn primarily depends on the market value of what they produce. HISTORY AND COMMON CORE STANDARDS National U.S. History Content Standards Content Standard 3A: Economic Life in British North America •The student will explain mercantilism and evaluate how it influenced patterns of economic activity. Common Core Standards Grades 9-10 students Comprehension and Collaboration 1c. Propel conversations by posing and responding to questions that relate the current discussion to broader themes or larger ideas; actively incorporate others into the discussion; and clarify, verify, or challenge ideas and conclusions. Grades 11-12 students 1c. Propel conversations by posing and responding to questions that probe reasoning and evidence; ensure a hearing for a full range of positions on a topic or issue; clarify, verify, or challenge ideas and conclusions; and promote divergent and creative perspectives.