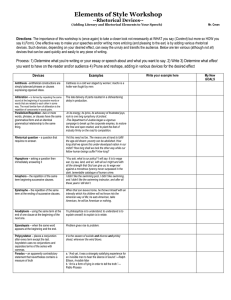
LANGUAGE, LANGUAGE, LANGUAGE Language Feature Definition and Purpose Emotive Language that appeals to the emotions and aims to provoke an emotional response. This kind of language is common in the media and is a powerful tool for persuading the audience to buy a product or accept a particular point of view. Sensational Language that aims to provoke a sharp and immediate response, capture attention and amplify a topic or situation. Persuasive Language that is designed to persuade or convince the audience of a particular point of view. Advertising relies on persuasive language to engage and appeal to the audience. Closed ended or Allow a limited range of response from the control questions audience and generally require complicity with the speaker’s views and opinions. Analogy Refers to the comparison between two things that share a similarity but are otherwise different. An analogy relies on comparison in order to establish, highlight or infer a relationship between two things and thereby shed light on one or both things more fully. Metaphor A figure of speech that compares two things or ideas that are apparently unrelated but are linked linguistically in such a way that a point of similarity is created, producing a vivid image. Used to precisely capture the feelings, mood, object or essence of one thing by associating it directly with another. Much more forceful and compelling than an analogy. Amplification A language device used to emphasise, highlight and magnify for effect. It may involve the repetition of particular words to attain impact on the audience. - Anaphora refers to the repetition of words at the beginning of clauses. - Epiphora refers to the repetition of words at the end of clauses. Alliteration Refers to the repetition of consonants in neighbouring words, particularly at the beginning of words, or stressed syllables. Alliteration is a common language device used for special effect in poetry, speech, advertising and occasionally in prose. Alliteration is beneficial in persuasive texts to grab the attention of the audience. Assonance Refers to when two or more words, close to one another, repeat the same vowel sound, but start with different consonant sounds. This enhances the musical effect in the text by creating an internal rhyme. In addition, it develops a particular mood in the text that corresponds with its subject matter. Examples