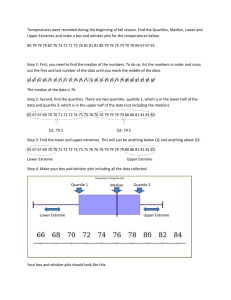
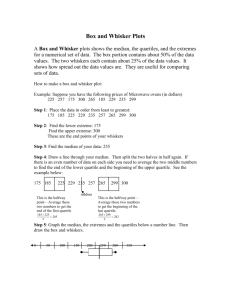
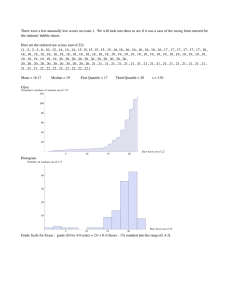
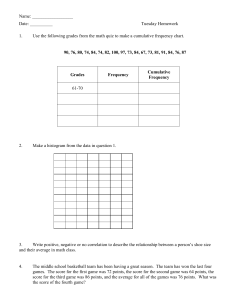
- n Second moment: ∑ (Xi ­ X )2 ; variance i=1 - n Third moment: ∑ (Xi ­ X )3 ; skewness i=1 - n Sample Coefficient of Skewness: S k = ∑ (Xi ­ X )3 / (n ­ 1)s3 i=1 Measures of Kurtosis - Indicate the concentration of data around the peak, whether it is flat or peaked Types of Kurtosis Leptokurtic Mesokurtic Platykurtic Curve More peaked Not too flat nor too peaked Less peaked Hump Narrower Same as Normal Curve Flatter Tail Thicker Same as Normal Curve Thinner Kurtosis Kurtosis < 3 Kurtosis = 3 Kurtosis > 3 - All of them symmetric, MMM Average square difference from the mean -> Variance Box and Whisker Plot - A simple graphical method used to display the median, the quartiles, and the minimum and maximum observations Boxplot Features 1. Location - It presents measures of location such as the median, the quartiles, and the extremes - Median, 1st and 3rd Quartile 2. Spread - Presents the variation of your dataset through the lengths of your boxes and whiskers - Dispersion through the length of the box and whisker - Look at the IQR, Variance (0, infinity) 3. Symmetry - The data set can be called symmetric if the length the upper half of the boxplot has the same length as the lower half - Same distance = symmetric 4. Extremes - The lowest and highest observations are the endpoints of the boxplot - Extremes that are not outliers - These are based on certain criteria 5. Outliers - Outlying observations are plotted using an asterisk or an X-mark Boxplot Steps 1. Compute for the median and the quartiles 2. Put a line across a number line where the median is. Plot the third quartile and the first quartile - increments 3. Construct a rectangle with one end at the first quartile and the other end at the third quartile 4. Compute the Interquartile Range IQR (which is the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile) 5. Compute for the lower and upper fences which are the outlier cutoffs given the following formulas: - 𝐿𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟𝑓𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 = 𝑄1 − 1.5 𝐼𝑄𝑅 - 𝑈𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑓𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 = 𝑄3 + 1.5 𝐼𝑄𝑅 - All observations that are outside the interval [Lower fence, Upper Fence] are considered to be outliers. - Do not put the whisker on the lowest / highest fence but the value that meets it 6. Excluding the outliers, identify the two values that are closest to the lower fence and upper fence, respectively. Draw a line, starting from these values up to each side of the rectangle. We refer to these lines are the whiskers 7. Plot each outlier at its corresponding value using an asterisk or an X mark