Cells
advertisement
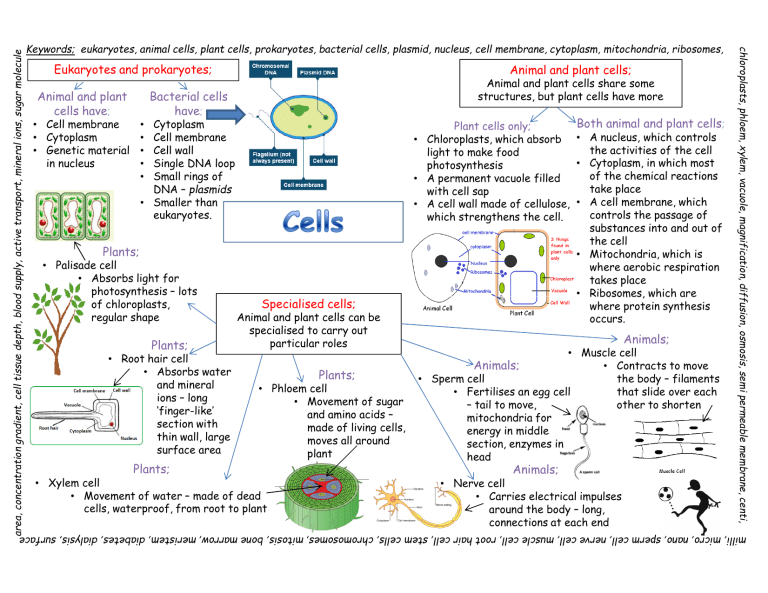
area, concentration gradient, cell tissue depth, blood supply, active transport, mineral ions, sugar molecule Eukaryotes and prokaryotes; Animal and plant cells have; Animal and plant cells; Animal and plant cells share some structures, but plant cells have more Bacterial cells have; • Cell membrane • Cytoplasm • Genetic material in nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Single DNA loop Small rings of DNA – plasmids • Smaller than eukaryotes. Plant cells only; • Chloroplasts, which absorb light to make food photosynthesis • A permanent vacuole filled with cell sap • A cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell. • • • • • Plants; • Palisade cell • Absorbs light for photosynthesis – lots of chloroplasts, regular shape Plants; • Root hair cell • Absorbs water and mineral ions – long ‘finger-like’ section with thin wall, large surface area Specialised cells; Animal and plant cells can be specialised to carry out particular roles Plants; • Phloem cell • Movement of sugar and amino acids – made of living cells, moves all around plant Plants; • Xylem cell • Movement of water – made of dead cells, waterproof, from root to plant Both animal and plant cells; • A nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell • Cytoplasm, in which most of the chemical reactions take place • A cell membrane, which controls the passage of substances into and out of the cell • Mitochondria, which is where aerobic respiration takes place • Ribosomes, which are where protein synthesis occurs. Animals; • Muscle cell • Contracts to move • Sperm cell the body – filaments • Fertilises an egg cell that slide over each – tail to move, other to shorten mitochondria for energy in middle section, enzymes in head Animals; Animals; • Nerve cell • Carries electrical impulses around the body – long, connections at each end chloroplasts, phloem, xylem, vacuole, magnification, diffu diffusion, osmosis, semi permeable membrane, centi, Keywords; eukaryotes, animal cells, plant cells, prokaryotes, bacterial cells, plasmid, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, milli, micro, nano, sperm cell, nerve cell, muscle cell, root hair cell, stem cells, chromosomes, mitosis, bone marrow, meristem, diabetes, dialysis, surface Mitosis; This is the process of making an identical copy of a cell Chromosomes; Found in the nucleus of every cell, made of DNA, contains a large number of genes, usually found in pairs Animal cells; Stem cells; • From human This is an undifferentiated cell of embryos an organism that is capable of • Can make most making more cells of the same types of human type, or make new cells cells • Adult bone Plants; marrow cells Treatment; Normal • Meristem tissue can form many • Stem cells may help to Cell; in plants can form cells including treat diabetes and any plant cell type blood paralysis DNA copies • This can happen Therapeutic cloning; itself, at any time • Embryo is made with the throughout the Diffusion is affected by; pulled to Diffusion ; same genes as the • Temperature plants life each end of Movement of patient • Concentration • Can produce plant the cell; substances from a • No rejection = medical • Surface area clones quickly and HIGH treatment economically concentration to a • May object on religious How ... Like things get oxygen LOW concentration grounds in and out and through a semi of cells... glucose. Active permeable Cytoplasm & transport; membrane – no cell membrane Movement Microscopy; energy is needed divides; 2 new AGAINST a Have lead to a better identical cells concentration understanding of cells gradient – needs Transport in cells; energy Cell differentiation; Movement of substances Both animal and plant Light: Electron; into and out of a cell across cells specialise First can magnify in a membrane developed, greater detail, basic higher Plants; Animals; understanding magnification Can continue to Most cells develop of cells differentiate during embryo Osmosis; throughout a development, in Osmosis is the diffusion of water plants life later life this is particles from a dilute solution to a repair and concentrated solution through a replacement partially permeable membrane. Down the concentration gradient