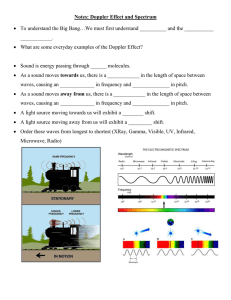
Sound Chapter 24 24-1 What is Sound? I can explain how sound waves are produced. I can describe how sound waves are transmitted. I can compare the phases of matter as to their ability to transmit sound I can describe how the speed of sound is affected by the density of the medium through which it travels. How sounds are made… Sound is produced when matter vibrates. As an object vibrates, it gives energy to the particles of matter around it. Sound is a longitudinal wave. It moves with a series of compression and rarefactions. Sound Waves Molecules in the air vibrate about some average position creating the compressions and rarefactions. We call the frequency of sound the pitch. Anything that vibrates produces sound. When you speak, your vocal cords vibrate. Particles of air simply move back and forth. A radio would NOT work in outer space because there is not any medium for sound to travel through. “If a tree falls in the forest and no one is present to hear it, is there a sound?” Speed of Sound Determined by the temperature, elasticity, and density of the medium. Temperature Sound travels slower in lower temperature Sound travels faster in higher temperature Average speed of sound in air = 340 m/s Medium Speed (m/s) Air 343 Helium 972 Water 1500 Steel 5600 Elasticity & Density Sound can travel through any medium. Greatest speed in solids, slowest speed in gases. Fastest in more elastic mediums, solids are more elastic. In materials of the same phase, the more dense the slower the waves travel. 24-1 What is Sound? I can explain how sound waves are produced. I can describe how sound waves are transmitted. I can compare the phases of matter as to their ability to transmit sound I can describe how the speed of sound is affected by the density of the medium through which it travels. Book Work 24-1 Section Review Page 618 #1-4 Section 24-1 Worksheet 24-2 Properties of Sound I can describe the properties of sound waves. I can explain how frequency and pitch are related. I can describe the Doppler effect. Frequency & Pitch Sounds can be described by high or low pitches. Pitch depends on how fast the particles of the medium vibrate. Pitch is the number of waves in a given amount of time, also known frequency. Meaning the pitch depends on the frequency. Pitch A measure of how high or low a sound is Pitch depends on the frequency of a sound wave For example, - Low pitch - High pitch - Low frequency - High frequency - Longer wavelength - Shorter wavelength Doppler Effect Police car speeding by: Higher pitch as approached, lower pitch as moving away. Change in pitch is referred to as the Doppler effect. Occurs whenever there is motion between the source of a sound and its receiver. Source or receiver must be in motion. Doppler Effect Police car moving towards you, pushing waves together causing: Shorter wavelengths, higher freq., higher pitch. Police car moving away from you, spreading waves out: Longer wavelengths, lower freq., lower pitch Loudness Chart Loudness is related to the amount of energy carried by a wave. 24-2 Properties of Sound I can describe the properties of sound waves. I can explain how frequency and pitch are related. I can describe the Doppler effect. Terms to Know Pitch Doppler Effect Book Work 24-2 Section Review •Page 623 • #1-4 • Name that Sound Worksheet 24-6 How You Hear I can identify the parts that make up the ear. I can explain how vibrations are converted into electrical signals. For Sound to be heard… You need 3 things: 1. a source that produces the sound 2. a medium to transmit the sound 3. an organ of the body that detects the sound Sound enters the outer ear, vibrates eardrum, enters middle ear and vibrates liquid-filled inner ear. Human Ear Outer Ear The outer ear acts as funnel for the waves. The waves travel through the ear canal and hit the lightly stretched membrane called the eardrum causing it to vibrate. The vibrations then enter the middle ear. Middle Ear The middle ear contains the 3 smallest bones in the body. hammer, anvil, stirrup The vibrations travel through the 3 bones and are transmitted to a liquid-filled inner ear. Inner Ear The inner ear contains the cochlea. Cochlea is snail shaped Contains liquid and hundreds of cell attached to nerve fibers The nerve fibers form one larger nerve that travels to the brain where they are interpreted as sound Human Ear 24-6 How You Hear I can identify the parts that make up the ear. I can explain how vibrations are converted into electrical signals. Chapter Review Pg 638 Multiple Choice #2-5, 9-10 True or False #1-4, 6 After Chapter Review is turned in… - Study vocabulary words Concept Mastery #1-4