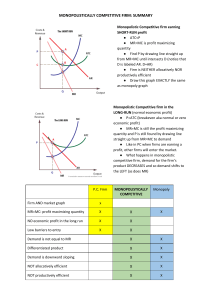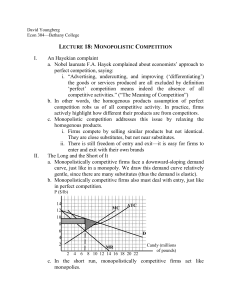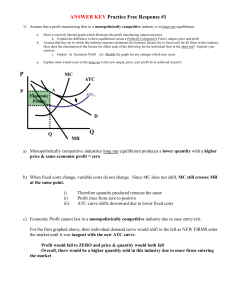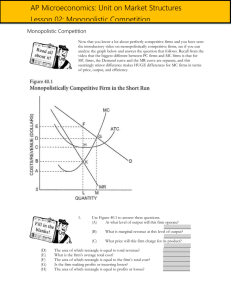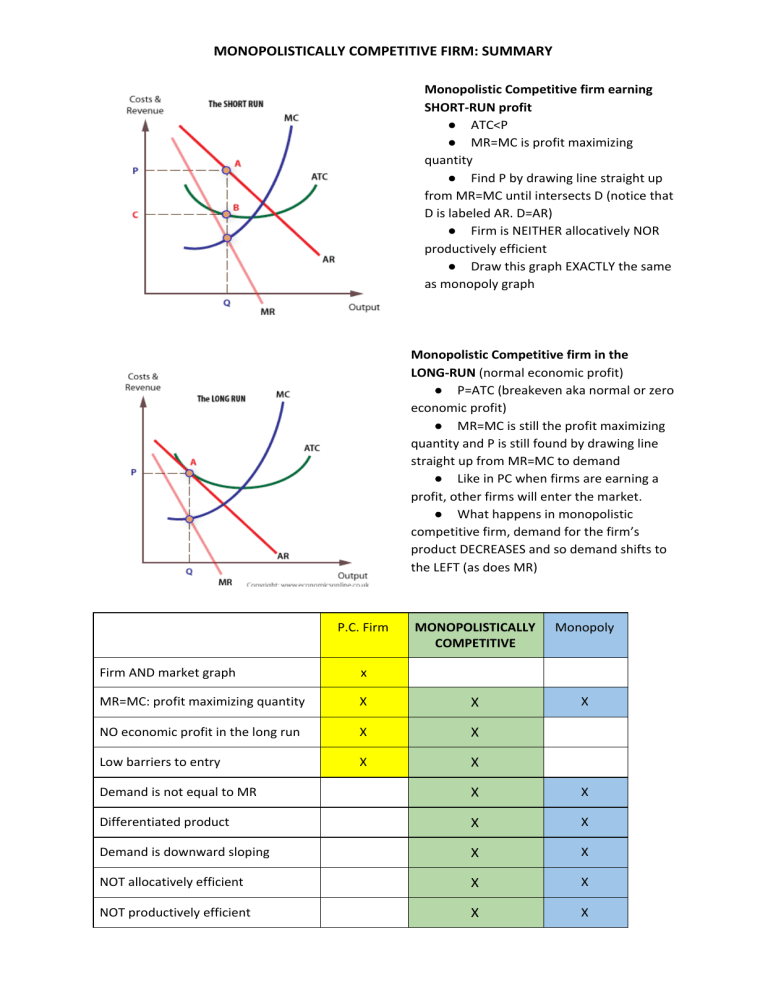
MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE FIRM: SUMMARY Monopolistic Competitive firm earning SHORT-RUN profit ● ATC<P ● MR=MC is profit maximizing quantity ● Find P by drawing line straight up from MR=MC until intersects D (notice that D is labeled AR. D=AR) ● Firm is NEITHER allocatively NOR productively efficient ● Draw this graph EXACTLY the same as monopoly graph Monopolistic Competitive firm in the LONG-RUN (normal economic profit) ● P=ATC (breakeven aka normal or zero economic profit) ● MR=MC is still the profit maximizing quantity and P is still found by drawing line straight up from MR=MC to demand ● Like in PC when firms are earning a profit, other firms will enter the market. ● What happens in monopolistic competitive firm, demand for the firm’s product DECREASES and so demand shifts to the LEFT (as does MR) P.C. Firm MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE Monopoly X Firm AND market graph x MR=MC: profit maximizing quantity X X NO economic profit in the long run X X Low barriers to entry X X Demand is not equal to MR X X Differentiated product X X Demand is downward sloping X X NOT allocatively efficient X X NOT productively efficient X X MONOPOLISTICALLY COMPETITIVE FIRM: SUMMARY Allocatively efficient(Ae): D(AR)=MC Productively Efficient (Pe): minimum of ATC Role of Advertising Firms operating under monopolistic competition usually have to engage in advertising because they offer similar products. Demand curve for monopolistic firm is more elastic than monopoly. Monopolistically competitive firms try to DIFFERENTIATE their product via one or more: price, quality, size, color, packaging, performance (e.g, features), design, distribution and many times through a perceived difference (e.g, emotional appeal to consumer). Most firms are either monopolistically competitive or oligopolies. Examples of industries that are monopolistically competitive: beverages, fast food, hotels, retailers, personal care products and many more.