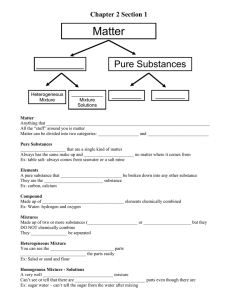
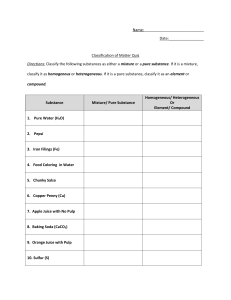
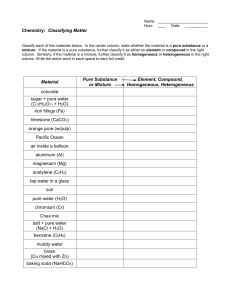
Name_______________________________ Period _____ Date ___/___/___ 1 Introduction to Chemistry CLASSIFYING MATTER & SEPARATION OF MIXTURES Part 1: Classify each of the materials below. In the center column, state whether the material is a pure substance or a mixture. If the material is a pure substance, further classify it as either an element or compound in the right column. Similarly, if the material is a mixture, further classify it as a solution (homogeneous mixture) or a heterogeneous mixture in the right column. Material 1. concrete 2. sugar + pure water (C12H22O11 + H2O) 3. iron filings (Fe) 4. limestone (CaCO3) 5. Pacific Ocean 6. magnesium (Mg) 7. acetylene (C2H2) 8. tap water in a glass 9. soil 10. chromium (Cr) 11. Chex mix 12. salt + pure water (NaCl + H2O) 13. benzene (C6H6) 14. muddy water 15. brass (Cu mixed with Zn) Pure Substance or Mixture Element, Compound, Solution, Heterogeneous Mixture Part 2: Complete the following sentences by filling in the appropriate word(s) from the list below. Each word can be used once, more than once, or not at all. filtration crystallization chromatography distillation 16. Heterogeneous mixtures are often separated by ______________________. 17. Separating sand from water can be done by _________________________. 18. The sugar in sugar water can be removed by _________________________. 19. The separation technique that takes advantage of different boiling points is called _________________________. 20. Removing chlorophyll pigment from leaves might be done by ______________________. 21. Crude oil is broken down by heat, vaporized, and allowed to condense into various liquids such as gasoline. This process is called ________________________.