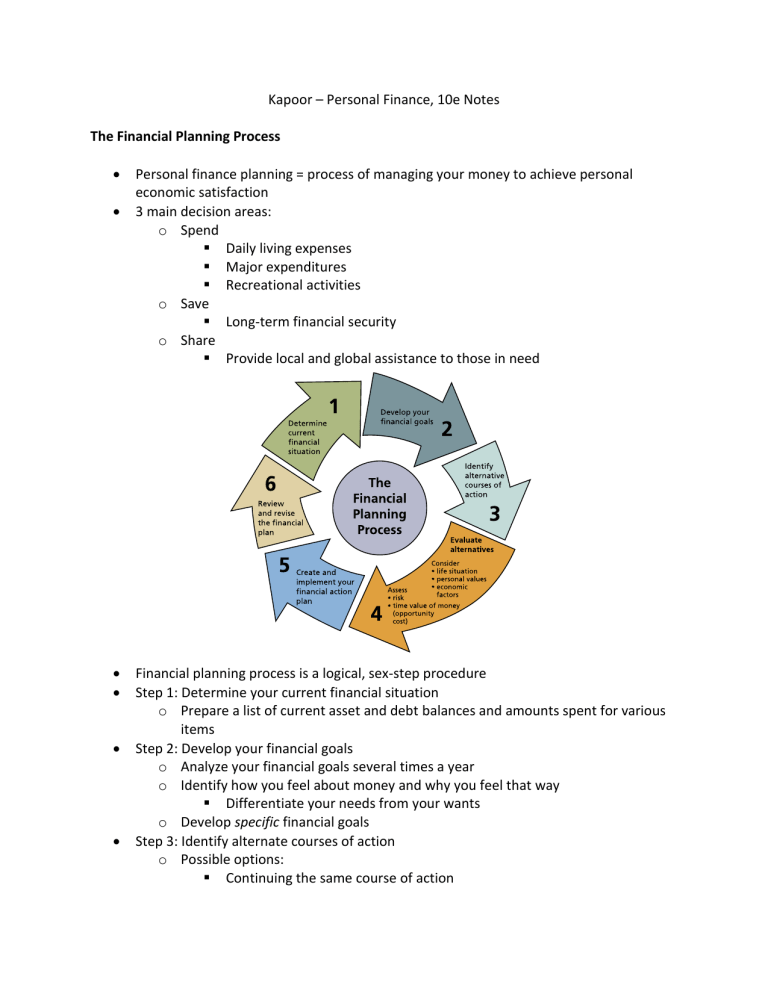
Kapoor – Personal Finance, 10e Notes The Financial Planning Process Personal finance planning = process of managing your money to achieve personal economic satisfaction 3 main decision areas: o Spend Daily living expenses Major expenditures Recreational activities o Save Long-term financial security o Share Provide local and global assistance to those in need Financial planning process is a logical, sex-step procedure Step 1: Determine your current financial situation o Prepare a list of current asset and debt balances and amounts spent for various items Step 2: Develop your financial goals o Analyze your financial goals several times a year o Identify how you feel about money and why you feel that way Differentiate your needs from your wants o Develop specific financial goals Step 3: Identify alternate courses of action o Possible options: Continuing the same course of action Expanding the current situation Change the current situation Take a new course of action Step 4: Evaluate your alternatives o Every decision closes off alternatives Opportunity cost (the trade-off of a decision) = what you give up by making a choice o Evaluating risk – types of risk Inflation risk Interest rate risk Income risk Personal risk Liquidity risk o Financial planning information sources Print and media Digital sources Financial experts Financial institutions Step 5: Create and implement your financial action plan o Develop an action plan that identifies ways to achieve your goals Step 6: Review and revise your plan o Financial planning is a dynamic process that is affected by multiple factors Developing Personal Financial Goals Types of financial goals o Two factors influence your financial aspirations for the future: Time frame in which you’d like to achieve your goals Short-term goals – within the next year Intermediate goals – from 1-5 years Long-term goals – more than 5 years off o Plan these in coordination with short-term/intermediate goals because those are the basis for achieving the longterm goals Goal frequency – small financial goals can be set often, but bigger financial goals are likely to be less frequent Type of financial need that drives your goals Consumable-product goals – occur on a periodic basis and involve items that are used up relatively quickly Durable-product goals – infrequently purchased, expensive, tangible items Intangible-purchase goals – personal relationships, health, education, leisure, etc. Goal-setting guidelines o S = specific (know exactly what your goals are so that you can create a plan designed to achieve them) o M = measurable (with a specific amount) o A = action-oriented (what are you undertaking?) o R = realistic (goals based on your income and life situation) o T = time-based (allows you to measure your progress) Influences on Personal Financial Planning 3 main elements affect financial planning activities: o Life situation – age, employment situation, marital status, number/age of household members Adult life cycle = stages in the family and financial needs of an adult o Personal values Values = ideas and principles that you consider correct, desirable, and important o Economic factors Economics = study of how wealth is created and distributed Federal Reserve System (the Fed) = U.S. central bank; maintains an adequate money supply by influencing borrowing, interest rates, and the buying/selling of government securities Global marketplace influences financial activities Economic conditions (especially consumer prices, consumer spending, and interest rates) influence financial decisions Consumer prices o Inflation = rise in the general level of prices Buying power of the dollar decreases Caused by an increase in demand without a comparable increase in supply Most harmful to people living on fixed incomes and lenders of money This is why interest rates rise in periods of high inflation o Consumer price index (CPI) = measure of the average change in the prices urban consumers pay for a fixed “basket” of goods/services; published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics o Deflation = decline in prices Consumer spending