Acid-Base Titration Lab: NaOH Concentration Determination
advertisement
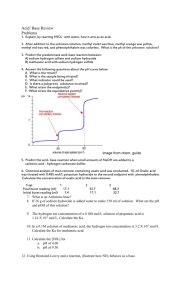
Physical Science Experiment Grade 12 Acids and Bases Titration/volumetric analysis Name :....................................... School :....................................... Date :....................................... Acid Base titration of oxalic acid sodium hydroxide to determine the concentration of a sodium hydroxide solution. To determine the concentration of a supplied sodium hydroxide solution using a standard of oxalic acid. Investigative question: Formulate an investigative question for this investigation. (2) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………........ …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Hypothesis: Formulate a hypothesis for this investigation: (2) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Variables: Dependent…………………………………………………………… (1) Independent :………………………………………………………..( 1) Control :…………………………………………………………………( 1) Apparatus 250 or 500 ml Volumetric Filter paper flasks 50ml Burette. spatula 25ml Pipette. Medicine dropper Erlenmeyer flasks Mass meter Beaker Retort stand White tile clamp Chemicals Oxalic Acid Sodium hydroxide phenolphthalein Distilled water Wash bottle Safety Precautions: The acid, base and indicator should not come into contact with the skin or eyes. In case of such incident immediately flush contaminated area with running tap water. Safety goggles and gloves are recommended. Method: Part 1: Preparing a Standard solution of oxalic acid Acid Base titration of oxalic acid sodium hydroxide to determine the concentration of a sodium hydroxide solution. To determine the concentration of a supplied sodium hydroxide solution using a standard of oxalic acid. Investigative question: Formulate an investigative question for this investigation. (2) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………........ …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Hypothesis: Formulate a hypothesis for this investigation: (2) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Variables: Dependent……………………………………………………………(1) Independent:………………………………………………………..(1) Control:…………………………………………………………………(1) Apparatus 250 or 500 ml Volumetric Filter paper flasks 50ml Burette. spatula 25ml Pipette. Medicine dropper Erlenmeyer flasks Mass meter Beaker Retort stand White tile clamp Chemicals Oxalic Acid Sodium hydroxide phenolphthalein Distilled water Wash bottle Safety Precautions: The acid, base and indicator should not come into contact with the skin or eyes. In case of such incident immediately flush contaminated area with running tap water. Safety goggles and gloves are recommended. Method: Part 1: Preparing a Standard solution of oxalic acid 1. The chemical formula of oxalic acid is (COOH)2.2H2O. Calculate the formula mass of oxalic acid. (2) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. What mass do you need to make 500ml of 0,1M solution of oxalic acid? (3) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. What mass do you require to make 250 ml of 0.1 M solution of oxalic acid. (1) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. Measure out this mass of oxalic acid accurately to one decimal place using a filter paper. Tare the balance to correct the mass of the filter paper. 5. Carefully pour the measured amount of oxalic acid into the 250 ml volumetric flask. 6. Add some water to the volumetric flask until half full. Close the flask with a stopper and shake the content to dissolve oxalic acid. Continue adding water with the wash bottle, very slowly at end, until the bottom of the meniscus of the liquid lines up with the mark on the neck/stem of the flask. Replace the stopper and give a final shake to ensure even mixing. Label the flask. 7. This is your standard solution. What is the meaning of this statement? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Part 2 Finding the concentration of a solution of sodium hydroxide by titrating it against a standard solution of oxalic acid. 1. Fit the burette into the clamp on the retort stand. 2. Use the funnel to pour the sodium hydroxide solution into the burette. 3. Place a beaker under the tap of the burette and open the tap just long enough to remove the air in the bottom of the burette. Fill the burette to the zero mark. 4. Pipette 25 ml of the standard oxalic acid solution into the Erlenmeyer /conical flask. 5. Add 2or3 drops of phenolphthalein in to the conical flask and swirl it gently to evenly distribute the indicator. 6. Place the flask under the tap of the burette and then [place the white tile underneath the flask to enhance visibility of any colour change during titration. 7. Slowly open the tap and allow sodium hydroxide solution from the burette into the conical flask. Control the tap with your left hand and use your right hand to swirl the flask. 8. When you get near the end point, add the solution from the burette drop by drop, until the solution turns pale pink and holds this colour for approximately 10 – 15 seconds. 9. Close the tap and record the volume of sodium hydroxide used in the table provided below. 10. Refill the burette to zero mark and repeat this procedure from 2 – 9 two more times so that you have a total of three readings. Take the average of these reading which will be considered as the volume of NaOH (aq) needed to neutralize 25 ml of (COOH)2.2H2O. Results: Titration ( Runs) Volume of oxalic acid Volume of Sodium Hydroxide 1 25 59 2 3 Average (4) Interpretation of results: 1. Write down a balanced equation for the reaction between oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………(3) 2. How many moles of sodium hydroxide will react with one mole of oxalic acid? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………(1) 3. Calculate the number of moles of oxalic acid in the Erlenmeyer flask. (3) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4. Calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide used to neutralize 25 ml of oxalic acid in the flask. (3) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 5. Calculate the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution. (3) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 6. How does the experimental value of sodium hydroxide solution compare to the estimated value of 0.2 mol.dm-3? (3) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 7. List two factors that could give rise to experimental error. (2) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 8. Briefly explain why phenolphthalein is the chosen indicator? (2) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 9. What colour is phenolphthalein in and acid medium? (1) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 10. What colour does this indicator display when titration reaches the end point? (1) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 11. Conclusion: ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (Total marks=40) 8.