Uploaded by
emmaknezevic02
Neurotransmitters Study Guide: Functions, Drugs, and Effects
advertisement

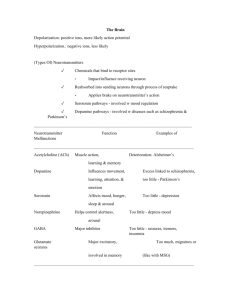
Agonist Drugs: Mimic effects of neurotransmitters naturally found in the human brain Antagonist Drugs: Block the brain’s neurotransmitters Neurotransmitter Function Effect of Deficit Effect of Surplus Agonist Drug Acetylcholine (ACh) Produces muscle contractions and is found in the motor neurons: Involved in memory formation, learning, and general intellectual functioning Paralysis, Alzheimer’s Violent Muscle Contractions Nicotine Dopamine Involved in voluntary muscle movement, attention, learning, memory, emotional arousal, and pleasurable sensations Parkinson’s Schizophrenia Cocaine Drug addiction Serotonin Involved in mood, sexual behavior, pain perception, sleep, eating behavior, and maintaining a normal body temperature Depression, Anxiety, OCD, Insomnia Autism Prozac, SSRIs Norepinephrine Involved in increasing heartbeat, arousal, learning, memory, and eating Depression Anxiety Caffeine, Amphetamines Endorphins Regulates pain perception and involved in sexuality, pregnancy, labor, and positive emotions associated with aerobic exercise Body experiences pain Body may not give adequate warning about pain, artificial highs Opiates Silly memory aids for the neurotransmitters Antagonist Drug Anti-Psychotic drugs like Thorazine Lithium ACh- Take the “A” and put it with “Alzheimer’s”, Alzheimer’s involves memory loss and ACh involves memory processing Dopamine- Too much Dopamine makes you “dopey” (as in Schizophrenic) Excess dopamine causes the brain to be over stimulated or “dopey’ Serotonin- “Sarah’s tone is very sad.” Too little serotonin causes depression as this chemical plays a role in moods. Norepinephrine- “Nora is bi-polar” Too much and too little norepinephrine causes mania and depression in folks who have bi-polar as this chemical also affects moods GABA- “Gabby” talks too much and needs to be quieted down, and made to be more “inhibited.” GABA is an inhibitory chemical that slows down neural functions. Glutamate- Glutamate sounds like glucose. Glucose is a sugar-like substance, and sugar increases energy and “excites” the body. Glutamate is an excitatory chemical that speeds up the nervous system. ACh- Acetylcholine ● Controls muscle movement and memory processing ● Alzheimers -Lack ● Uncontrollable Muscle Movement- Excess ● Nicotine- Agonist Dopamine● Controls mood ● Parkinsons- Lack ● Schizophrenia- Excess ● Cocaine- Agonist ● Antagonist- Anti-psychotic Drugs Serotonin● Affects mood ● Depression, Anxiety, OCD, Insomnia- Lack ● Autism- Excess ● SSRIs- Agonist Norepinephrine● Affects mood ● Depression- Lack ● ● ● Anxiety- Excess Caffeine, Amphetamines- Agonist Lithium- Antagonist GABA● Gabby needs to be calmed down ● Inhibiting neurotransmitter Glutamate● Excitatory neurotransmitter ● Like Sugar Endorphins● Affects mood and pleasure and pain sensitivity ● Feel immense amounts of pain- Lack ● Dangerous to not feel pain- Excess ○ Natural Highs ● Agonist- Opiates The knee jerk reflex is controlled by interneurons in the (SPINAL CORD) Action potential, electrical state of axon is (DEPOLARIZED; SLIGHTLY NEGATIVE) Endocrine gland and body growth (PITUITARY GLAND) (Spinal Cord) Action potential, electrical state of axon is (Depolarized)(less negative) Endocrine gland and body growth (Pituitary Gland) Runners high is due to the release of (endorphins) Reuptake (reabsorption of excess neurotransmitters by sending neuron) Neurons that carry info away from spinal cord (efferent neurons) S(Sensory) A(Afferent) M(Motor) E(Efferent) Opiate drugs occupy the same receptor sites as (endorphins) ~Block pain signals Hormones are chemical messengers of the (endocrine system) Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that travel across the (synaptic gap) Studies neurotransmitter abnormalities in depressed patients (biological psychologist) ACh is linked to (alzheimers) Positively charges ions across the membranes of a neuron an produce (action potential) All or none response pattern (firing a neural impulse) The selectively permeability of a neural membrane creates an (resting potential) ~Slightly negative because selectively permeability PNS to sensory neurons as CNS is to (interneurons) ~Central nervous system only has INTERNEURONS ~Brain and Spinal Cord Sequence of neural impulse transmission Dendrite Cell body Axon Terminal Branches Synapse Longest part of motor neuron is (Axon) Role of sympathetic nervous system (Preparing for fight or flight) Strengtnening of synaptic connections facilitates the formation of (Neural Networks) Simple reflex simple (sensory neuron Drug that enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter (an agonist) ~Tell the next neuron to fire Theory about bumps on skull revealing abilities and traits is (phrenology) Too much dopamine is associated with (schizophrenia) ~Not enough is (Parkinsons) -Anti psychotic works to stop dopamine firing Electrical charge that travels down the axon of a neuron is called (action potential) Dendrite function is to (Receive Signals) Depolarization of neural membrane can create a (action potential) The neuron located exclusively in the brain and spinal cord is the (interneuron) Voluntary movements, such as writing with a pencial are directed by the (Somatic Nervous System) Job of sodium pump is to (Keep axon charged by returning and keeping sodium outside) Psychoactive drugs interfere with normal neural transmission. Where does this take place? (Synapse) ~Mimics neurotransmitters Speed of a neural impulse increases when the axon is covered with (myelin sheath) Electrochemical information system is called (Nervous System) Self regulating body function are governed by the (Autonomic Nervous system) Serotonin Affects (Mood) Acetylcholine (ACh) Muscle contractions, and memory Dopamine Serotonin Sarah is in a bad tone, affects mood Alzheimers, Paralysis Norepinephrine Noradrenaline, Endorphins Pain threshold