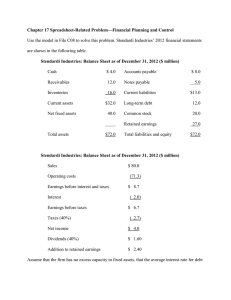
Prospectus Review and Fundamental Analysis Prepared December 3, 2009 CRITIQUE CONTENT The prospectus provides sufficient information to make an investment decision. There is comprehensive information provided on the industry as a whole, an enormous amount of information on the corporation itself including its structure, history, strengths and competition. The Growth strategy is helpful; however it would be useful to see a strategic plan in the prospectus detailing how the company plans to reduce its considerably high long term debt. PRESENTATION The material presented in the prospectus is generally readable and understandable for most people. Aside from the financials, the information is presented in a manner that most laypeople would understand. Although the prospectus is 183 pages long, making use of the table of contents will allow a prospective investor the ability to find the specific information they are looking for quickly. STRENGTHS OF THE PROSPECTUS Comprehensive – the information provided is very complete. Easy to read – written in a manner that many investors will be able to understand. Benchmark analysis There is an excellent history of the company including the current structure and management style. There appears to be full, true and plain disclosure of the material facts relating to the security. Many levels of due diligence confirming the information presented. There is confirmation from Price Waterhouse Coopers (the auditor), the many underwriters as well as the management and board of directors from Dollarama. Increased Prestige – For Dollarama, the fact that the company is not public gives it more visibility and enables them to obtain a larger market for their goods. WEAKNESSES OF THE PROSPECTUS Length -The sheer size of the document may dissuade the average investor from buying as it may seem overly complicated or may leave too much room of “fine print” that may not benefit the investor. 12 pages of risks may scare off some investors. The notes to the financial statements are not always written in plain English with many prospective investors having to “look around” the document to find what they are looking for. This however seems to be common among many initial public offerings and is not exclusive to Dollarama. An investor may feel that management’s business decisions will be affected by the market price of the shares and the feeling that they must get market recognition for the shares rather than making key strategic business decisions in a timely manner. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS Overall, the prospectus provides sufficient information for a potential investor to make a decision. The material provided appears to be complete, true and generally written in plain language. The layers of due diligence presented in the prospectus will make an investor feel confident that the information presented is accurate. Lastly, the strengths and weaknesses of the prospectus appear to correlate with those of many initial public offerings, not just the Dollarama prospectus. ANALYSIS RISKS Business Risk -As a dollar store, they are vulnerable to increases in operating and merchandise costs. Business Risk – There are no guarantees that the customer will continue to pay for products at a dollar store that cost more than a dollar (as per their strategy to introduce price points between $1 and $2) Merchandise levels per store may not be able to be refreshed as often as when they were a smaller organization Political and Country Risk - An increase in the cost or a disruption in the flow of their imported goods may significantly affect the sales and profits and have an adverse impact on cash flows. Economic Risk – World and local economies could potentially have adverse effects both on sales as well as cost of goods sold. Credit Risk – Dollarama’s level of indebtedness could adversely affect their ability to raise additional capital to fund operations, limit their ability to react to changes in the economy or industry and prevent them from meeting their debt obligations. The organization is highly leveraged with long term debt excluding financing costs of $838.4 million. This could result in reorganization, refinancing or sale of assets to meet obligations. Credit Risk – Despite current leveraging, Dollarama may continue to take on more debt, further compounding the risk effect. Interest Rate Risk – The Company has much of its debt in variable rate debt agreements. Business Risk – The Company produces much of its own private brands, which may not sell as well as other substitutes , thus negatively affecting gross margins as the cost of goods sold for private brands is much less than others. Storage – Dollarama may be unsuccessful in procuring additional warehouse space for much of its inventory. Costs in a hard real estate market may also make this unpalatable. Competition could limit growth opportunities and reduce profitability. Technology Risk – Experiencing significant disruptions in their IT systems could result in business and financial disruptions. Regulatory Risk – Dollarama is subject to environmental regulations, and compliance with such regulations could require them to make expenditures. Market Risk - Failure to attract and retain qualified employees while controlling labour costs, as well as other labour issues, could adversely affect business and financial results. Exchange Rate Risk - Fluctuations in the value of the Canadian dollar in relation to the U.S. dollar may impact operating and financial results and may affect the comparability of results between financial periods. Product Risk – The Company is subject to the risk of product liability claims and product recalls. Additionally, any litigation may adversely affect business and financial results. Market Risk – Value of the shares is subject to prevailing market conditions and can be volatile. IPO Risk – Securities have no prior public market and value may drop after the offering. Dividend Risk – Company has no plans to pay dividends for the foreseeable future. Therefore investment returns will be solely from capital gains or losses. Company Risk – Dollarama is a holding company. Upon completion of this Offering, the Common Shares will be effectively junior to approximately $522.6 million of indebtedness and other liabilities (including trade payables) of their subsidiaries. POSITIVE ATTRIBUTES The Canadian dollar store industry remains relatively under-penetrated relative to the U.S. dollar store industry. There is much opportunity for potentially significant growth. Current and Quick ratios are well within boundaries of acceptability. The company has the asset coverage to pay its immediate liabilities. All investment income from this stock should be in the form of investment income, with the opportunity for dividends in the future. Gains and losses can be deferred until realized and the dividends earned in a taxation year are treated as tax preferred. NEGATIVE ATTRIBUTES No dividends to be paid for the foreseeable future. Exceptionally high level of debt to the company The relatively low retail cost of goods implies that many transactions nationwide would be required to provide adequate return of investment. Financial and economic conditions may not be ripe for an IPO following the recent credit crunch and largest financial downturn since the great depression. NEUTRAL ATTRIBUTES It appears that the industry in general is either correlated with the market or slightly on the defensive side. VALUATION 1. Dividend Discount Model The forward looking statements, the risk factors statement and the dividend policy all indicate that the Corporation does not currently anticipate paying any cash dividends on its Common Shares in the foreseeable future. The Corporation currently intends to use its earnings to finance the expansion of its business and to reduce indebtedness. That being said, I would need to assume that down the road dividends will be paid and forecast those dividends based on benchmark analysis. Dollar General, one of Dollarama’s American Competitors recently paid a special dividend of $0.43 per share. As this is in US dollars it would equate to $0.45 at an exchange rate of $0.94 Canadian to US dollars. Like Dollarama, Dollar General does not plan to pay any regular dividends. This being said, as a special dividend is separate from a typical recurring dividend cycle, we can assume the quarterly dividend could be set for $0.12 per share or $0.48 per share annually. For the following model I will also assume that beta is 1 based on competition and the assumption that it moves in concert with the market in general. Market returns by historical and industry returns of 16%. g is forecast based on 3%. K=Rf+(RM-RF) K=.25+ 1(15.75) K=16 P0 = D1/k-g P0 = 0.48/.16 -.03 P0= $3.69 per share 2. Price-Earnings Multiple Earnings per share = net earnings (before extraordinary items-preferred dividends/# of common shares outstanding EPS=$72,900,000-0/$72,691,935 EPS=$1.00 P/E = Price of Common Share/EPS P/E= 17.50/1.00 P/E= 17 times As Dollarama is currently trading at a multiple (P/E) of 17, the interpretation is that an investor is willing to pay $17 for $1 of current earnings. This shows that at a price of $17.50 the stock may be very close or slightly overvalued. However more fundamental analysis is required to make this assumption. 3. EBITDA Multiple Enterprise Value = Value of equity + Value of Debt - Cash and Cash Equivalents EV=$102,237,000 +$806,384,000 - $66,218,000 EV=$842,403,000 EV/EBITDA $842,403,000/1,614,000,000 =0.52 The main advantage of EV/EBITDA over the P/E ratio is that it is unaffected by a company's capital structure. It compares the value of a business, free of debt, to earnings before interest. OTHER FINANCIAL RATIOS Current Ratio Current Assets/Current Liabilities $356,745,000/$98,483,000 = 3.62 The current ratio measures a Dollarama’s ability to pay the liabilities that it is most likely to have to pay soon with that assets that should yield cash the quickest. A ratio of more than two is an adequate measure of Dollarama’s ability to pay. Quick Ratio Current Assets-Inventory/Current Liabilities $356,745,000-$249,644,000/$98,483,000 =1.08 The quick ratio provides a more stringent measure of overall liquidity since inventory may not be as liquid an asset as desired. Although Dollarama has a rather large inventory, it’s ratio is still above 1 giving it adequate assets to pay liabilities. Debt to Equity Ratio Short Term Debt + Long Term Debt/Book Value of Shareholder’s Equity $15,302,000+$806,304,000/$102,237,000 =8.03 This number appears very high as the long term debt is exceptionally high, primarily due to expansion and reorganization. This is identified in the risk component of the prospectus. RECOMMENDATION In making a recommendation to an individual investor, it is first important to understand their goals. An advisor must first look at the investors time horizon, risk tolerance, expected rate of return, portfolio diversification or strategic asset allocation strategy, amount of money invested and level of investment knowledge. This stock is being sold as a value stock and at a glance the price seems appropriate. I would also caution that IPO’s typically underperform the market. Academic research has shown that IPO’s that come out following a recession or bear market can do well. Aside from the exceptional long term debt, this may be a good buy provided an investor can purchase at the IPO price. As there are indications that no dividends will be paid for the foreseeable future, all investment income will be in the form of capital gains, appropriate for non-registered investing with tax preferred returns. This also increases the risk to the portfolio. Given an expected return of 16% it is conceivable that this stock could fit quite nicely into the equity portion of a certain investor’s portfolio. PASSIVE VERSUS ACTIVE INVESTING STRATEGIES Active managers will use a variety of methods to complete their task of beating a stated index. They believe that there are inefficiencies in the marketplace and that they can be exploited using a variety of methods. Many growth managers focus on current and future earnings of individual companies, particularly Earnings per Share. They will pay more for companies if they feel that the company’s higher growth potential is worth the price. For value managers, they will typically focus on specific stock selection. They look for overlooked, cheap or disliked stocks and the manager will wait for the stock’s intrinsic value to rise. This results in lower portfolio turnover and is generally a longer term management approach. Active management can take the form of sector rotation, interest rate anticipation, spread traders and asset allocation among others. Active managers can potentially reduce risk and add value. While there is limited evidence that active equity and fixed income managers can add value after accounting for additional investment management fees, the potential risk reduction benefits can often justify the use of active management strategies. Passive management is consistent with the view that securities markets are efficient – that is, securities prices at all times reflect all relevant information on expected return and risk. The passive portfolio manager does not believe that it is possible to identify stocks as underpriced or overpriced, at least to an extent that would achieve enough extra return to cover the added transactions costs. These managers use a buy-and-hold system. I believe that markets are not truly efficient and that given the upside reward of taking advantage of market inefficiencies, the additional cost of active management can be justified for a portion of an individual portfolio.