Human Body Systems Overview
advertisement

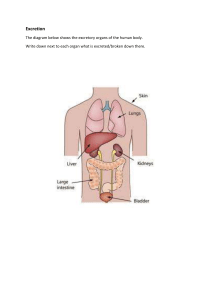
This human body system is responsible for the digestion of foods and absorbing the nutrients from foods. Its main parts include the mouth, esophogus, stomach, large and small intestine and the anus. This system performs six major functions; support, movement, protection, production of blood cells, and storage of ions and endocrine regulation. The adult body has 206 bones. This system is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person’s body weight. Each of these muscles is a discrete organ constructed of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves. This system is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. The lungs carry out this exchange of gasses as we breathe. Red blood cells collect the oxygen from the lungs and carry it to the parts of the body where it is needed. This is a system of sex organs within an organism which work together for the purpose of reproduction. This system is an organ system consisting of the skin, hair, nails, and exocrine glands. The skin is only a few millimeters thick yet is by far the largest organ in the body. Skin forms the body’s outer covering and forms a barrier to protect the body from chemicals, disease, UV light, and physical damage. This system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and all of the nerves that connect these organs with the rest of the body. Together, these organs are responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts. The brain and spinal cord form the control center that relays information to the rest of the body. This system is the collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood, among other things. Also known as the cardiovascular system. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and the approximately 5 liters of blood that the blood vessels transport. Responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and cellular waste products throughout the body, the cardiovascular system is powered by the body’s hardest-working organ — the heart This system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter the blood to remove wastes and produce urine. Besides filtering and eliminating wastes from the body, this system also maintains the homeostasis of water, ions, pH, blood and pressure.