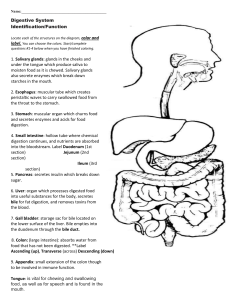
Biology & Nutrition Worksheet: Cell Division, Genetics, Digestion
advertisement

I. Identification ______________________________ 1. A point at which paired chromosomes remain in contact during the first metaphase of meiosis, and at which crossing over and exchange of genetic material occur between the strands. ______________________________ 2. Spread of cancer to new location in the body. ______________________________ 3. Phase in interphase for primary cell growth. ______________________________ 4. Organelles needed for cell movement in cell division. ______________________________ 5. Thin, fibrous form of DNA that make up a chromosome. ______________________________ 6. Serves as a guide in choosing the right foods. ______________________________ 7. The involuntary wavelike contraction of muscles of the digestive tube. ______________________________ 8. Process where the tongue mixes food with saliva and pushes it down the pharynx. ______________________________ 9. Transfat can raise this type of cholesterol known to be "bad," putting your heart at risk. ______________________________ 10. The center of the tooth. II. Multiple Choice 1. Passing on of traits from parents to their offspring, either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction. a. Heredity b. Paternity c. Crossing-over d. Mutation 2. The large surface area of the small intestine in contact with food results in: I. the long length of the small intestine II. the folds and creases in its lining III. presence of villi IV. high production of bile a. I only b. I and II c. I, II, III d. I, II, III, IV 3. Describes the overall appearance or behavior of an organism and is the physical expression of a character trait. a. Genotype b. Phenotype c. Allele d. Gene 4. Which of the following is NOT a macronutrient? a. Protein b. Nucleic acids c. Carbohydrates d. Vitamin K 5. Branch of science that researches and studies molecules and organelles to understand cell functions and organization. a. Molecular biology b. Biotechnology c. Taxonomy d. Cell biology 6. What is caused by the buildup of gas in the abdomen when you eat quickly and swallow large chunks of food without properly chewing it? a. Indigestion b. Ingestion c. Constipation d. Flatulence 7. Stage at which chromosomes pair with their homologues during prophase 1. a. Crossing-over b. Mutation c. Synapsis d. Cell division 8. Which of the following are not a source of proteins? a. Fish b. Chicken c. Cheese d. Rice 9. Father of Modern Genetics. a. Francis Crick b. Gregor Mendel c. James Watson d. Marie Curie 10. Process that produces 4 new cells. a. Mitosis b. Meiosis c. Mutation d. Cellular respiration 11. Small, vestigial sac located in the lower right side of the abdomen, attached to the large intestine close to the junction of the large and small intestines. a. Appendix b. Pancreas c. Kidney d. Gallbladder 12. Chromosome number of somatic (body) cells. a. 23 b. 46 c. 48 d. 28 13. The ______ is a part of the digestive tube that serves as a storage organ of food. a. Esophagus b. Pharynx c. Stomach d. Small intestine 14. Starter cells that produce sperm egg cells. a. Spermatogonium b. Oocyte c. Oogonium d. Spermatocyte 15. ________ is a secretory substance produced by liver and helps emulsify fats. a. Amylase b. Bile c. Trypsinogen d. Insulin 16. Hormones that are important for sexual and reproductive development, mainly in women. a. Testosterone b. Progesterone c. Androgen d. Estrogen 17. _______ is found in the gastric juice that helps digest food and kill microorganisms in food. a. Nitric acid b. Sulfuric acid c. Bile d. Hydrochloric acid 18. Rule which states that each pair of alleles behave independently of each other during gametogenesis. a. Law of Segregation b. Law of Dominance c. Law of Independent Assortment d. Law of Recession 19. Enzyme in saliva that initiates the digestion of starch. a. Amylase b. Pepsin c. Rennin d. Trypsinogen 20. The equal division of one nucleus into 2 genetically identical nuclei. a. Cytokinesis b. Karyokinesis c. Neucleokinesis d. Chromokinesis 21. ____________ is the organ that aids in reabsorption of water, minerals, and ions. a. Small intestine b. Large intestine c. Stomach d. Esophagus 22. Region that is equidistant from the spindle's two poles, where chromosomes gather and are aligned with one another. a. Cell plate b. Anaphase plate c. Metaphase plate d. Cytoplasm plate III. Modified true or false. ______________________________ 1. Plant cells pinch off at cytokinesis, forming the cell plate between the 2 new nuclei. ______________________________ 2. Saturated fats are found in canola, corn, and olive oil. ______________________________ 3. Karyotyping is used in neonatal tests or newborn screening to detect possible genetic disorders among newborn babies. ______________________________ 4. Digestion is always 100% efficient. ______________________________ 5. Synapsis is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. ______________________________ 6. Maltose is the most basic sugar in carbohydrates. ______________________________ 7. It is possible for an allele for height to have two forms, one for tall and another for short. ______________________________ 8. Nucleic acids are the building blocks of proteins. ______________________________ 9. The nucleus is a small, round complex consisting of a portion of a DNA molecule coiled around a cluster of 8-histone protein molecules. ______________________________ 10. An endoscopy enables the examination of internal organs of the body, specifically the digestive organs. ______________________________ 11. Homologues form a pair in mitosis. ______________________________ 12. Lipase is an enzyme of the salivary glands that readily digests fat. ______________________________ 13. Fraternal twins could also be of the same sex. ______________________________ 14. Bolus is a semi-fluid mass which is formed when gastric juice is mixed with food. ______________________________ 15. Paired homologous chromosomes are called quadruples. ______________________________ 16. If there were no fats in your diet, your body would have difficulty absorbing fat-soluble vitamins and antioxidants. ______________________________ 17. In peas, the tallness is dominant over shortness. If a short pea plant is crossed with a tall pea plant, all offspring will be short in appearance. IV. Enumeration A. Stages of Interphase. 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ B. Parts involved in the mechanical digestion of food. 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ C. Parts involved in the chemical digestion of food. 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ D. Accessory Glands I. Three kinds of salivary glands 1. _________________________ 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ 3. _________________________ E. Main parts of the Oral Cavity 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ F. Four types of teeth 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ 4. _________________________ G. Stages of Mitosis 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________ 4. _________________________ H. Three types of papillae 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 3. _________________________