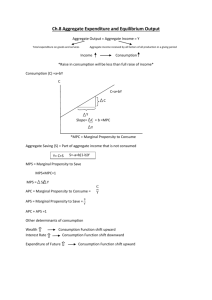
Econ 98-Chiu Aggregate Expenditure Worksheet Name & SID: Spring 2004 Date: Assumptions are critical in macroeconomics. Different assumptions change dramatically your answers. Assume the following conditions for the following questions: • • • • • • No government spending (G=0) Closed economy (NX=0) Prices are fixed (inflation=0) Nominal and real interest rates are fixed Planned investment is autonomous of interest rates Y refers to real GDP (not nominal) 1. What is the difference between an identity, behavioral relationship, and equilibrium relationship? Give an example of each. 2. What is the difference between aggregate output and aggregate income? 3. What are the two components of investment spending? 4. What is the major determinant of consumption spending (C)? 5. What are the components of consumption spending? Page 1 of 4 Econ 98-Chiu Aggregate Expenditure Worksheet Name & SID: Spring 2004 Date: 6. Define marginal propensity to consume (mpc). 7. What is planned aggregate expenditure? 8. How is planned aggregate expenditure different from aggregate expenditure? 9. Define the equilibrium relationship between aggregate output and planned aggregate expenditure. 10. Draw the Keynesian-cross (Y=AE) model. Label your aggregate output line, Y=AE. Label your planned aggregate expenditure line, AE. Label the equilibrium GDP, Y1. Page 2 of 4 Econ 98-Chiu Aggregate Expenditure Worksheet Name & SID: Spring 2004 Date: 11. What happens when Y2>Y1? 12. What happens when Y3<Y1? 13. What is controversial about these adjustment mechanisms? 14. Assume full-employment aggregate output (Y*) is above Y1. Why is Y* not sustainable in equilibrium? Is Y1 desirable for an economy? 15. What is Keynes’ major argument about full-employment output and equilibrium output? 16. Define the multiplier in words. 17. Define the multiplier as an equation. Page 3 of 4 Econ 98-Chiu Aggregate Expenditure Worksheet Name & SID: Spring 2004 Date: 18. What is the multiplier effect? 19. Suppose the marginal propensity to consume is .95. And suppose planned investment increases by $2. How much does equilibrium output increase? [ Hint: Y=C+I ] 20. Generalize the change in equilibrium output as a function of the multiplier and the change in planned investment (as an equation). Page 4 of 4