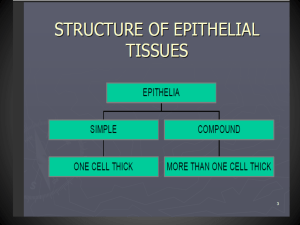
TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. Define tissue List the four major tissue types of the body and discuss the special characteristics of each tissue Define histology Describe the two criteria by which epithelial tissues are classified Define apical surface, basal surface, apical membrane, basolateral membrane and lateral membrane Describe the function and list the two layers that constitute the basement membrane Define polarity, cellularity and avascularity Be able to differentiate simple, stratified, pseudostratified - layers Be able to differentiate squamous, cuboidal, columnar, transitional – shapes Be able to recognize an example of where each cell type could be found. Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a simple squamous epithelium List one example of where a simple squamous epithelium may be located Define endothelium and mesothelium Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a simple cuboidal epithelium List one example of where a simple cuboidal epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a simple columnar epithelium List one example of where a simple columnar epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a pseudostratified columnar epithelium List one example of where a ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium may be located List one example of where a non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium List one example of where a nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium List one example of where a keratinized simple squamous epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a stratified cuboidal epithelium List one example of where a stratified cuboidal epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of a stratified columnar epithelium List one example of where a stratified columnar epithelium may be located Describe, draw and list the function(s) of transitional epithelium List one example of where transitional epithelium may be located List 6 general characteristics of epithelial tissues and explain how the characteristics relate to the function of epithelial tissues Describe the location, structure and function of microvilli Define brush border Describe the location, structure and function of cilia Describe the function of glands Compare exocrine gland to an endocrine gland Describe the structure and function of mucous, serous and cutaneous membranes Describe locations in the body where each type of membrane can be found Contrast the amount of extracellular matrix present in epithelial tissue with the amount of extracellular matrix in connective tissue proper List three fiber types that may be present in various connective tissues Describe the properties of collagen, reticular and elastic fibers 42. List a function for each of the listed connective tissue cells: fibroblast, macrophage, lymphocyte, mast cell 43. List the types of connective tissue in the category of connective tissue proper 44. List the type of fibers present in areolar connective tissue and contrast areolar connective tissue with respect to fiber density and amount of ground substance 45. List a function of areolar connective tissue 46. Describe the functional and structural differences between the two types of dense connective tissue 47. List the two types of dense connective tissue 48. Draw adipose tissue, define adipocytes, and describe the function of adipose tissue