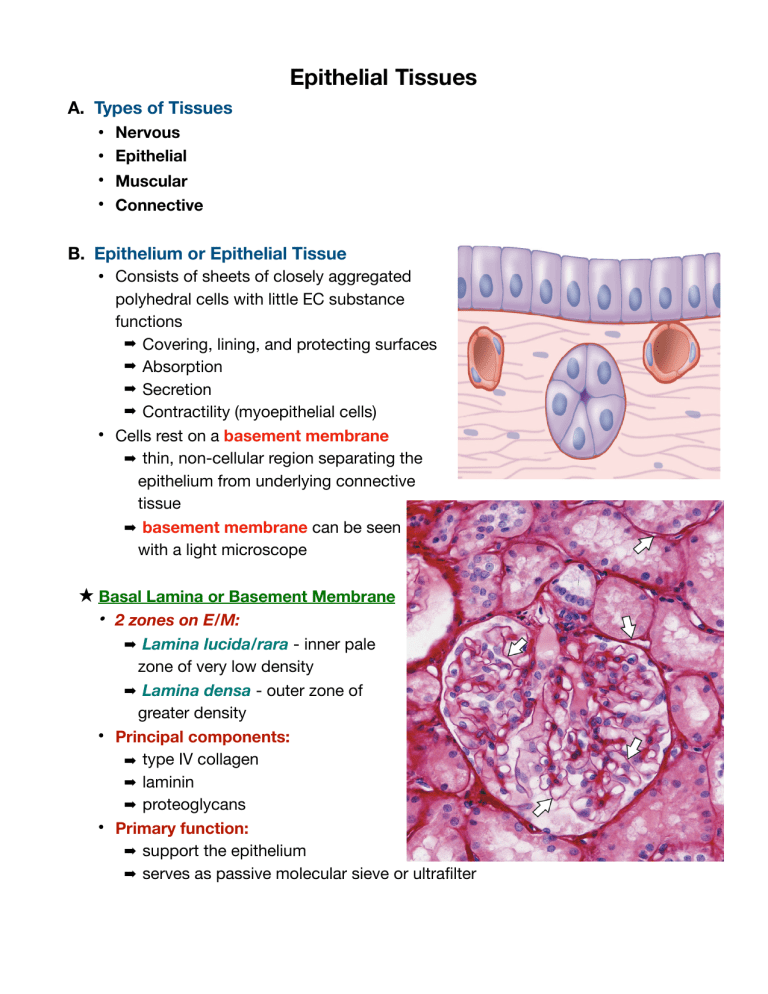
Epithelial Tissues A. Types of Tissues • • • • Nervous Epithelial Muscular Connective B. Epithelium or Epithelial Tissue • Consists of sheets of closely aggregated polyhedral cells with little EC substance functions ➡ Covering, lining, and protecting surfaces ➡ Absorption ➡ Secretion ➡ Contractility (myoepithelial cells) • Cells rest on a basement membrane ➡ thin, non-cellular region separating the epithelium from underlying connective tissue ➡ basement membrane can be seen with a light microscope ★ Basal Lamina or Basement Membrane • 2 zones on E/M: ➡ Lamina lucida/rara - inner pale zone of very low density ➡ Lamina densa - outer zone of greater density • Principal components: ➡ type IV collagen ➡ laminin ➡ proteoglycans • Primary function: ➡ support the epithelium ➡ serves as passive molecular sieve or ultrafilter ★ Germ Cell Origin • Ectoderm ➡ gives rise to the: ✓ Corneal epithelium ✓ Epidermis of the skin ✓ Glandular appendages of the skin - e.g. sweat, sebaceous and mammary glands • Mesoderm ➡ Urinary tract ➡ Male and female reproductive tracts ➡ Endothelium - cells lining the blood and lymph vessels ➡ Mesothelium - cells lining the cavities • Endoderm ➡ Intestinal glands ➡ Liver ➡ Pancreas ★ Classification of Epithelia ➡ based on the number of layers, shape of cells, specializations present on their free surface • Simple: if made up of 1 layer • Stratified: if there are multiple layers C. Simple Squamous Epithelium • • • • Alveoli Bowman’s Capsule Endothelium Mesothelium ✴ Simple Squamous Epithelium - Bowman’s capsule of glomerulus (kidney) D. Simple Cuboidal Epithelium • • • • • Thyroid follicles Surface of ovary Choroid plexus of brain Pigment epithelium of retina Ducts of many glands ✴ Simple Cuboidal Epithelium - Thyroid follicle E. Simple Columnar Epithelium • lines the digestive tract from the cardia of stomach to the anus • Uterus (endometrium) and fallopian tubes ✴ Simple Columnar Epithelium - Intestinal Epithelium F. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium • Trachea and bronchi • Excretory dust to the parotid gland • Male urethra ✴ Pseudostratified Columnar Ciliated Epithelium - Respiratory Epithelium G. Stratified Squamous Epithelium • Keratinizing Stratified Squamous Epithelium - skin • Non-keratinizing Stratified Squamous Epithelium - oral cavity, vagina, esophagus, cornea ✴ Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium - Skin ✴ Stratified Squamous Non-keratinized Epithelium - Esophagus H. Transitional Epithelium • Urothelium • Urinary tracts from the renal calyces to the urethra ✴ Transitional - Urinary Epithelium ๏ Epithelial Polarity • cells of epithelia are structurally and functionally polarized to carry out function of secretion, absorption, and regulation of trans-epithelial traffic of ions and solutes. • They have a: ✓ free or apical surface ✓ junctional specializations ✓ basal lamina ๏ Junctional Specializations 1. Zonula Occludens (ZO) or Tight Junction • Most apical forming a continuous band encircling the cell apex together with ZA • Membrane of adjoining cells fuse and close off the intercellular space • Cell attachment - strongest at the ZO • Important Function: permeability barrier 2. Zonula Adherens (ZA) or Adherent Junction • Band encircling the cell (below ZO) • Rich in actin • Important Functions: ✓ Responsible for binding of band to junctional membrane ✓ Stabilize the brush border of columnar epithelia 3. Desmosomes or Macula Adherens (D) • Do not form continuous band encircling the cell apex • Separate plagues arranged in a row around the cell • Scattered on the lateral surface of the cell (below ZA) 4. Gap Junctions or Communicating Junction (GJ) • No actual fusion of membrane • Connexons - seen bridging the gap • Permeability is affected by pH and calcium concentration • Function: permits passage of small molecules between cells (ions and amino acids)






