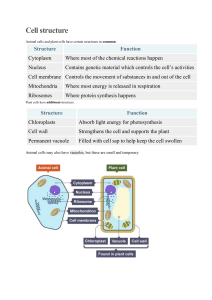
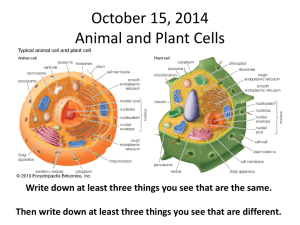
YEAR 9: CELL STRUCTURE AND ORGANISATION Cg Nizah 2017 Q1:Show and explain the structure of animal cell and plant cell Q2: Identify and describe cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm for animal cells; cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, sap vacuole and chloroplasts for plant cells) PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL CELL MEMBRANE Cell membrane: • Thin layer that surrounds the cell • It is semi-permeable membrane. (allow some substances to enter / leave cell but not others) E.g. It allows useful substances to enter but not the waste product. Oxygen Vs Carbon dioxide What do you think is the advantage of this? • Jelly like substance • Consists of water 70% to 90% and many chemical compounds • Contain many small vacuoles which contain food and water. • Many activities are carried out in the cytoplasm. Example: Food is broken down to release energy. Enzymes and other proteins CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS • Controls activities in the cytoplasm and reproduction of the cell. • Nucleus contains the threadlike material called chromosomes. • Chromosomes contain hereditary materials called GENES. • Genes control what organism looks like and how it function. CELL WALL • Cell wall is made up of cellulose • The cell wall supports and protects plant cell and gives regular shape. • The cell wall is fully permeable. • Large vacuole for plant cell and Small vacuole for animal cell. • Old plant will have one large vacuole and a young plant would have a few large vacuole VACUOLE VACUOLE • A plant vacuole contains liquid called cell sap. • Cell sap is made up of water and dissolve substances like sugar and salts • The cell sap helps to support the cell, making it turgid by taking in water. CHLOROPLAST • Chloroplast contains green pigment called chlorophyll (green colour). • Plants make food in chloroplast. • The chlorophyll traps the sunlight need to make food by a process called photosynthesis. TEST State which part of a plant cell a)Makes food? b)Contains cell sap? c) Protect and support the cell? d)Controls all activity in the cell? e) Controls the movement of substance into and out of cell? COMPARE THE VISIBLE DIFFERENCES IN STRUCTURE OF THE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS CELL WALL VACUOLES CHLOROPLAST CYTOPLASM ANIMAL CELL Animal cell do not have cell wall Animal cell has many small vacuoles Animal cell has no chloroplast Animal cell is filled with cytoplasm PLANT CELL Plant cell have cell wall Plant cell has only one/few large vacuole Plant cell has chloroplast Plant cell has a thin lining of cytoplasm SUMMARY FROM LAST CLASS 1.What does semi permeable membrane means? 2.What is the FUNCTION OF CYTOPLASM? 3. What is the FUNCTION of nucleus? 4.What does Chromosome contain? 5.What is the FUNCTION of chloroplast? Q3: State, in simple terms, the relationship between cell structure and cell function for: i). root hair cells – absorption ii) Identify these cells from diagrams and from photomicrographs MODIFICATION OF CELL STRUCTURE FOR SPECIFIC FUNCTION Why would you want to modify a car? THE ROOT HAIR CELLS • The root hair cell is found at the tip of the root. • It is specially modified so that it can absorb water easily for the plant. Root hair cells grows outwards from the root Which part of plant cell you don’t see in root hair cell? To store a lot of Itwater has in large the vacuole? Why? vacuole PHOTOMICROGRAPH OF ROOT HAIR CELL HOW DOES THE STRUCTURE OF THE ROOT HAIR CELL HELPS WITH ABSORPTION? i) Grows To increase surface area for outwards absorption of water and mineral salts from the cell ii) Large Stores as much water as possible vacuole XYLEM VESSEL Xylem is made up of a number of long tube-like structures called the xylem vessels. FORMATION OF XYLEM VESSEL Each cell wall is thicken with lignin (a tough substance) Lignin is to support the plant XYLEM VESSEL • In plants, a tissue called the xylem transport water and mineral ions from the roots to the stems and leaves. The xylem: transport water and mineral ions from the roots to the stems and leaves. PHOTOMICROGRAPH OF XYLEM VESSEL Support the plant ROOT HAIR CELLS AND XYLEM VESSEL Q: State, in simple terms, the relationship between cell structure and cell function for red blood cells – transport of oxygen Identify these cells from diagrams and from photomicrographs BLOOD VESSEL RED BLOOD CELL Yearred 8 Question: • The blood cell transport oxygen from the lungs to all What is the function of red parts the body. bloodofcell? • It contains red pigment called Haemoglobin. • Haemoglobin is the one that carries oxygen. MODIFICATION OF RED BLOOD CELL 1. BICONCAVE DISC Give large surface area to easily pick up and release oxygen 2. NO NUCLEUS So that more haemoglobin, to carry oxygen PHOTOMICROGRAPH OF HUMAN BLOOD SMEAR BRIEFLY DESCRIBE HOW THE FOLLOWING CELLS ARE MODIFIED FOR THEIR SPECIAL FUNCTION 1.Root hair cell (2) 2.Red blood cell (2) POINTERS (IA 1) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Draw and label animal cell and plant cell Functions of parts Differences between animal and plant cell Function of Root hair cell Features that help to absorb water efficiently? HOW? Function of Red blood cell; what carries the oxygen? Features that help to transport oxygen? HOW?