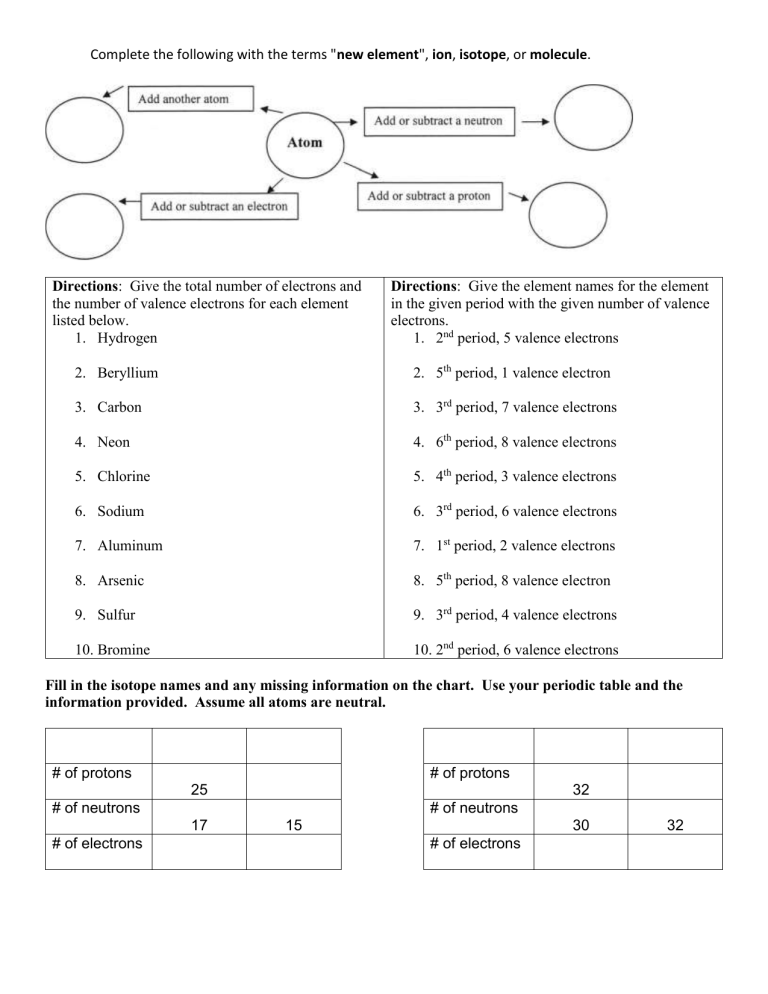
Complete the following with the terms "new element", ion, isotope, or molecule. Directions: Give the total number of electrons and the number of valence electrons for each element listed below. 1. Hydrogen Directions: Give the element names for the element in the given period with the given number of valence electrons. 1. 2nd period, 5 valence electrons 2. Beryllium 2. 5th period, 1 valence electron 3. Carbon 3. 3rd period, 7 valence electrons 4. Neon 4. 6th period, 8 valence electrons 5. Chlorine 5. 4th period, 3 valence electrons 6. Sodium 6. 3rd period, 6 valence electrons 7. Aluminum 7. 1st period, 2 valence electrons 8. Arsenic 8. 5th period, 8 valence electron 9. Sulfur 9. 3rd period, 4 valence electrons 10. Bromine 10. 2nd period, 6 valence electrons Fill in the isotope names and any missing information on the chart. Use your periodic table and the information provided. Assume all atoms are neutral. # of protons # of protons 25 32 # of neutrons # of neutrons 17 # of electrons 15 30 # of electrons 32 Metals Metalloids Non-metals Place the properties below in the chart above in either metals, non-metals, or metalloids. usually solid at dull or shiny usually brittle malleable (can be room temperature bent and pounded some conduct poor conductors into thin sheets) heat and of heat and good conductors of heat and electricity, some electricity often make good electricity do not semiconductors usually less dense ductile (can be often ductile tend to gain usually low drawn into wire) electrons in melting point of often malleable chemical solids usually dense may gain or lose reactions dull appearance electrons in high luster (shiny) Most have a low reactions Most have a high most have a very boiling point boiling point high melting readily lose electrons point