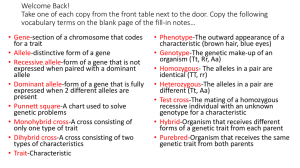
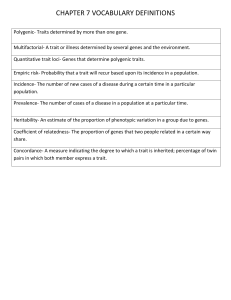
Unit 3 Test Study Guide (Genetics) NEED TO KNOW vocabulary: Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Heredity Genes Chromosomes Alleles Genotype Phenotype Dominant trait Recessive trait Homozygous / Purebred Heterozygous / Hybrid Genetic Engineering Selective breeding Inbreeding Punnett Square Gamete Reproduction using ONE parent Examples of organisms that reproduce this way: bacteria, yeast (mostly unicellular, some multicellular organisms) 3 types: Binary fission, regeneration, budding Reproduction using TWO parents Examples of organisms that reproduce this way: most multicellular organisms (humans, pigs, fish, etc.) Passing of genes from parents to offspring A unit of heredity that is located at a certain point on a chromosome. Each gene codes for a particular trait. Structures inside the nucleus of a cell that stores genetic information. Genes are located here. Various forms of the same gene. We represent these with singular letters. Examples: B, b The name for the genes an organism has. We represent the genotype with a pair of alleles (two letters). Examples: BB, Bb, bb Characteristics of a trait that can be observed. This is what we actually see! Examples: brown hair, blue eyes, dimples A trait that will be expressed even if only one of the parents carries the trait. We usually represent this with a capital letter! Example: B This trait will only be expressed if both of the parents carry and pass on the trait. We represent this by a lowercase letter! Example: b A pair of alleles that are the SAME. Examples: BB, bb A pair of alleles that are DIFFERENT. Example: Bb The ability to alter the DNA of an organism in order to get the traits that are desired. Selecting two organisms with desired traits to serve as the parents of the next generation. Example: Horse breeders breed their two “fastest” horses in order to get more horses that produce the same or faster results when racing. When two organisms that have very similar or the same characteristics are mated. Inbreeding increases the risk of recessive genetic disorders. Offspring lack diversity. A tool used to predict the traits of offspring in a genetic cross. A sex cell (female = egg / male = sperm) These cells have HALF the chromosomes of body cells. A human has 46 chromosomes in each body cell, and 23 in each of their sex cells.