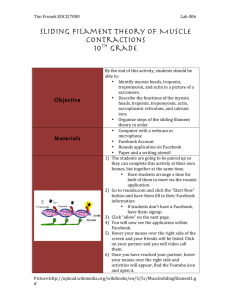
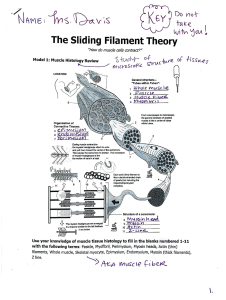
Muscle Contraction Steps: A Detailed Guide

Muscle
Contraction
Steps
Step 1:
The tropomyosin (not shown) & troponin (purple) are blocking the interaction between the twisted actin strand and the myosin heads.
Step 2:
Calcium ions are released when a nerve stimulates the muscle. These Calcium ions bind with the troponin & move the troponin & tropomyosin out of the way.
Step 3:
The myosin heads must receive energy from a molecule of ATP in order to move.
Step 4:
The ATP is converted into less energetic ADP + Pi
(independent phosphate) and the energy they had allows the myosin head to cock back.
Step 5:
The myosin head forms a cross-bridge with the actin filament and moves it. This causes the sarcomere to shorten, contracting the muscle fiber. This is called the
“power stroke”.
Step 6:
The myosin head accepts energy from another ATP molecule.
Step 7:
The energy from the ATP molecule is used by the myosin head to release from the actin filament and return to its original position. This is called the “return stroke”. The ATP has been converted into ADP +
Pi.
Step 8:
The Calcium ions are pumped back out of the muscle cell and the ADP + Pi is released from the myosin.
Step 9:
After the release of Calcium, the troponin and tropomyosin return to their original positions and the muscle fiber relaxes.