cell organelle test
advertisement

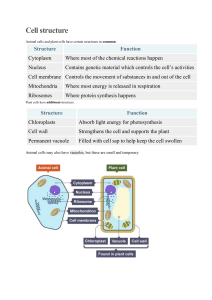
Name: _____________________________ Section: ______ Date: ____________________ Cells End of Unit Exam Covered in End of Unit Assessment: o Recognize that all organisms are composed of cells, and that many organisms are singlecelled (unicellular). o Cells are the smallest unit of life, or the smallest living thing. o All cells come from pre-existing cells. o Differentiate between pro- and eukaryotic cells. o Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles). o Explain the structure and function of cells and their organelles. o Explain the levels of organization within a body from cell to organism. o Communicate the cell theory. Your performance… Question Number: Standard 1, 2 Cell Theory 2 3, 4, 12, 16, 23 Types of Cells 5 10, 15 Structure of Organelles 2 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 Function of Organelles 13 6 Organization of Life 1 1-12 or 1-13 Drawing Structure 12 1-12 or 1-13 Written Function 12 Points Earned, Points Possible, and Your Grade: Charbonneau 2019 Points Earned Points Possible Percentage Mastery % Cells Unit Exam (Please read all of the answers before putting your mark on the Scantron sheet. Good luck!) 1. What is the basic structural unit of living organisms, or the smallest piece of life? a. Cell b. Nucleus c. Atom d. Tissue 2. Which statement is NOT a part of cell theory? a. Cells are the basic unit of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Cells come from other cells. d. Cells parts such as chloroplasts are self-replicating (copy themselves). 3. The old and the new models of a cell are ….. a. eukaryotes and prokaryotes. b. animal and plant c. bacteria and human d. archea bacteria and bacteria Loose DNA 4. A single prokaryotic cell can divide several times per hour. Eukaryotic cells cannot divide as quickly. Which of the following best explains the difference? a. Eukaryotes are smaller than prokaryotes. b. Eukaryotes have cell walls. c. Eukaryotes have more complex structures than prokaryotes. d. Prokaryotes have more DNA than eukaryotes. 5. You can see most cells without a microscope: a. True b. False 6. Choose the correct order if going from smallest to largest…. a. Organ, cell, organ system, tissue b. Organ, cell, tissue, organ system c. Cell, organ, organ system, tissue d. Cell, tissue, organ, organ system Charbonneau 2019 7. Which organelle would your muscles be using the most if you were running a sprint? a. mitochondria b. nucleus c. ribosome d. vacuole 8. The water molecules in a plant are stored in what organelle? a. soil b. nucleus c. ribosome d. vacuole 9. Many animals have skeletons that provide support. Which part of plant cells plays a similar role? a. cell membrane b. cell wall c. chloroplast d. cytoplasm 10. If you saw this under a microscope you would be looking at a. an animal cell b. a plant cell c. a mitochondria d. a cheek cell 11. Which organelle is correctly paired with its function? a. nucleus – makes proteins b. chloroplast – site of cellular respiration c. lysosome – break things down and recycles them d. nucleolus – site of photosynthesis 12. Bacteria, plant, and animal cells all have which parts? a. cell wall and mitochondria b. nucleus and cell membrane c. chloroplasts and ribosomes d. cell membrane and ribosomes Charbonneau 2019 13. A cell has a defect (mutation) that results in the loss of its ability regulate the passage of water, food, and wastes into and out of the cell. In which of the following cell structures is this defect most likely to be located? a. Ribosomes b. Chloroplasts c. Cell membrane d. Endoplasmic reticulum 14. Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells contain more mitochondria than some other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others? a. They use more energy. b. The cells break up more proteins c. The cells divide more frequently. d. The cells store more nutrients. 15. This diagram best represents a a. nucleus b. cell membrane c. cytoplasm d. golgi body 16. A student sees a small cell that has a strand of DNA but it does not have a nucleus. What type of cell is it? a. prokaryote b. eukaryote c. animal d. plant 17. If we could add these organelles to our cells we would not have to breathe or eat. a. Chloroplast b. Ribosomes c. Cytoplasm d. Chromosomes Charbonneau 2019 18. Chloroplasts use sunlight to make a. Protein b. Carbon dioxide c. Cytoplasm. d. Glucose (sugar) 19. This organelle is like jelly that holds all of the other organelles a. chromosome b. cytoplasm c. endoplasmic reticulum d. chloroplasts 20. Which organelle makes the protein used to build our body? a. DNA b. ribosomes c. mitochondria d. golgi body 21. Which organelle transports molecules within the cell? a. cytoplasm b. golgi body c. endoplasmic reticulum d. cell membrane 22. Which organelle “tags” molecules and prepares them to be moved out the cell? a. cytoplasm b. golgi body c. endoplasmic reticulum d. cell membrane 23. What cell structures do plant and animal cells have in common? a. Cell nucleus b. Cell membrane c. Vacuoles d. All of the above e. Charbonneau 2019 Name __________________________ Per ________________ PLANT CELL 2. 8. 1 . 9. 3. . 10. 4. 11. 5. 6. 12. 7. . Name of Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplasts Chromosomes Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Body Lysosome Mitochondria Nucleus Ribosomes Vacuole Charbonneau 2019 Number on Drawing Function of Organelle Name __________________________ Per ________________ Name of Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplasts Chromosomes Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Body Lysosome Mitochondria Nucleus Ribosomes Vacuole Charbonneau 2019 Number on Drawing Function of Organelle