V Enzyme Lab Report
advertisement

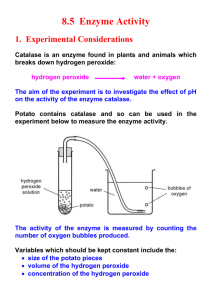
Enzyme Lab Report Billy Wu P4 CP Bio I Purpose: This lab was conducted to find out the activity of enzyme catalase in different conditions, for example, different pH. II Material: i. Five potato cubes of 1 cm^3 (four raw: #1 #2 #3 #4, one boiled: #5) ii. Vinegar (acid) iii. Hydrogen peroxide iv. Ammonia (base) v. Six beakers A, B, C, D ,E ,F vi. Mortar and pestles III Procedure: i. Temperature change: 1) Put the raw potato#1 cube in 50ml of hydrogen peroxide in beaker A. 2) Leave the cube for five minutes, observe and record the result. 3) Put the boiled potato cube#5 in 50ml of hydrogen peroxide in beaker B. 4) ii. Leave the cube for five minutes, observe and record the result. pH change: 1) Put the raw potato cube#2 in 20ml of vinegar (acid) in beaker C and leave it for five minutes. 2) Put the potato cube#2 into hydrogen peroxide in beaker D and leave it for five minutes, observe and record the result. 3) Put the raw potato cube#3 in 20ml of ammonia (base) in beaker D and leave it for five minutes. 4) Put the potato cube#3 into hydrogen peroxide in beaker E and leave it for five minutes, observe and record the result. iii. Shape change: 1) Mash the raw potato cube#4 2) Put the mashed potato cube#4 into 50ml of hydrogen peroxide in beaker F. 3) Leave it in the beaker for five minutes, observe and record the result. IV Data: Result Table for Enzyme Lab Treatment of potato Observation Raw#1 (in hydrogen peroxide) A lot of bubbles came out fast. Boiled#5 (in hydrogen peroxide) No bubble came out. Raw#2 (in acid) No bubble came out. Raw#3 (in base) Very few bubbles came out. A lot of bubbles came out Raw#4 (mashed in hydrogen peroxide) violently. V Discussion Questions: i. Pre-Lab Questions: 1) Gather Background Information: a) Q: Why do we need Enzymes? A: Enzymes help us speed up the biochemical reactions in body, so it takes less time to finish the process, such as breaking down food. b) Q: Why is the relationship between an enzyme and its substrate compared to a lock-and-key? A: Because it’s just like a lock and its key, a specific kind of enzyme will only work on specific types of substrates. c) Q: Why is it important for our enzymes that we keep our body’s temperature and pH stable? A: The unstable temperature and pH can make enzymes lose their shapes and unable to work with their substrates. d) Q: What does the enzyme catalase do? A: The catalase breaks down H2O2, a harmful product of certain metabolic reactions, into water and hydrogen gas. e) Q: How can we tell if catalase is active (working)? A: If there are lots of bubbles produced, the reaction speed is fast and the catalase enzyme is active. Vice versa. 2) State a problem: Direction: We will test them one at a time, because in a controlled experiment you never want to change more than one thing at a time. f) How does changing the temperature of a potato affect the activity of catalase? g) How does changing the pH of a potato affect the activity of catalase? h) 3) How does mashing the potato affect the activity of catalase? Hypothesize: i) If I boil my potato then the activity of catalase will decrease because the heat will break up the bonds of protein. j) If I put my potato in vinegar (an acid) then the activity of catalase will decrease because enzymes will be denatured when there is any change in pH. k) If I put my potato in ammonia (a base) then the activity of catalase will decrease because enzymes will be denatured when there is any change in pH. l) If I mash up my potato then the activity of catalase will stay the same because the enzyme is actually not affected, it’s just the physical change of the shape of the potato. ii. Analyze Results: 4) The important part In this experiment Independent variable Different potato treatments Dependent variable Bubbles different potato cubes produced Experimental group(s) Raw#2, Raw#3, Raw#4, Boiled#5 Control group Raw#1 1. The origin of potato cubes 2. The size of potato cubes Constants 3. The origin of hydrogen peroxide 4. The amount of hydrogen peroxide 5) Q: How did increasing the temperature of the potato affect the activity of catalase? A: The increasing temperature lowered the activity of the catalase, as the high temperature broke down bonds in proteins of enzyme catalase. 6) Q: How did changing the pH of the potato affect the activity of catalase? A: The change in pH lowered the activity of catalase, as every enzyme catalase had an interval of pH of the best activity, and once the pH was out of that interval, the activity would be affected negatively. 7) Q: In which potato was catalase the most actively? Why do you think this was? A: The mashed potato cube#4 released the most bubbles in hydrogen peroxide and the speed was the fastest, because the mashed potato cube had a larger surface area to hydrogen peroxide, so more enzyme catalase was active. iii. Post-Lab Questions: 8) Q: Why is the relationship between an enzyme and its substrate compared to a lock and key? A: Because an enzyme only works perfectly on its substrate, just like a key only opens a specific lock. 9) Q: Changing in temperature or pH can change an enzyme’s shape. Why will an enzyme no longer work if it loses its shape? A: Once an enzyme loses its shape, known as being denatured, the enzyme doesn’t fit its specific substrate anymore, so it will no longer work. 10) Q: What is the optimum pH of enzyme X? A: pH of 8 is the optimum pH of enzyme X. 11) Q: What is the optimum temperature of enzyme X? A: 20°C is the optimum temperature of enzyme X. 12) Q: Why do you think enzyme X has low activity at a pH of 10? A: Because it comes to a base when the pH is 10, and base will break bonds of proteins in enzymes, which lowers the activity of enzyme X. 13) Q: Enzyme X performs critical life functions. Use the data above to explain why a fever of 40 degrees may be dangerous. A: The optimum temperature for enzyme X is 20°C, and when it comes to 40°C it totally stops working. Since enzyme X is a critical life functions, when one has a fever of 40°C the enzyme loses its functions, so this person probably will die because of lacking that critical life function enzyme X brings. VI Conclusion: This lab was conducted to find out the activity of enzyme catalase in different conditions: different pH, different temperature and different surface area. In the experiment, control groups were set for comparing how changing environments could affect the activity of enzyme catalase. As a result, it showed that the change in pH and temperature affected the activity of enzyme catalase negatively, and the increasing surface area affected the activity positively. The explanation for the result is that, high temperature would break the bonds in proteins of the enzyme, and the changing pH would denature the enzyme, which both lowered the activity; however, the increasing surface area increased the activity of enzyme catalase because more enzyme is in reaction with hydrogen peroxide. VII Source of Errors: 1. Potato 2. Quality of ammonia, vinegar, and hydrogen peroxide 3. Quantity of ammonia, vinegar, and hydrogen peroxide