ppt Graphing Motion updated

Interpreting Motion
Graphs
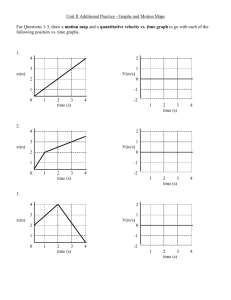
Two Types of Graphs
Position time graphs
Velocity time graphs
Position vs. time graphs
The slope of the graph is equal to the velocity
If the x/t graph is a straight line
(no curve) then the velocity is constant.
Reference Point….
Position vs. time graphs
A line with a positive slope indicates positive velocity and the object is moving away from the reference point
A line with a negative slope indicates negative velocity and the object is moving towards the reference point.
Position vs. time graphs
If the line is horizontal (no slope) then the object is stationary (no velocity)
Position vs. time graphs
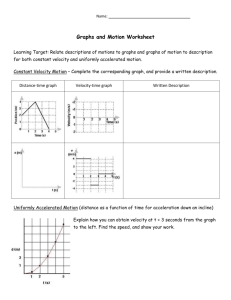
Accelerated Motion
If the object is accelerating, the velocity is changing
x/t graph will no longer be a straight line, but will have a changing slope, resulting in a curve.
Position vs. time graphs
Concave “ Up like a cup ” …the acceleration is positive
Speeding up away Slowing down towards
Position vs. time graphs
Concave “ Down like a frown ” …the acceleration is negative
Speeding up towards Slowing down away
Velocity vs. time graphs
•
The slope is equal to the acceleration.
Positive slope implies an increase in velocity in the positive direction .
• Negative slope implies an increase in velocity in the negative direction .
• Zero slope implies motion with constant velocity .
Velocity vs. time graphs
Positive velocity indicates the object is moving away from the reference point
The x axis means v=0
Green is slower, getting closer to zero.
Purple is speeding up, moving farther from the x axis.
Velocity vs. time graphs
Negative velocity indicates the object is moving toward the reference point.
Velocity vs. time graphs
(Acceleration)
When the slope is zero:
–horizontal line
– velocity is constant
–acceleration is zero
Velocity vs. time graphs
When the slope of the graph is positive:
– the acceleration is positive
Velocity vs. time graphs
When the slope of the graph is negative:
– the acceleration is negative
Velocity vs. time graphs
We cannot determine where an object ’ s position from a v/t graph, only its
change
in position.