Electron Configurations & Atomic Structure Practice
advertisement
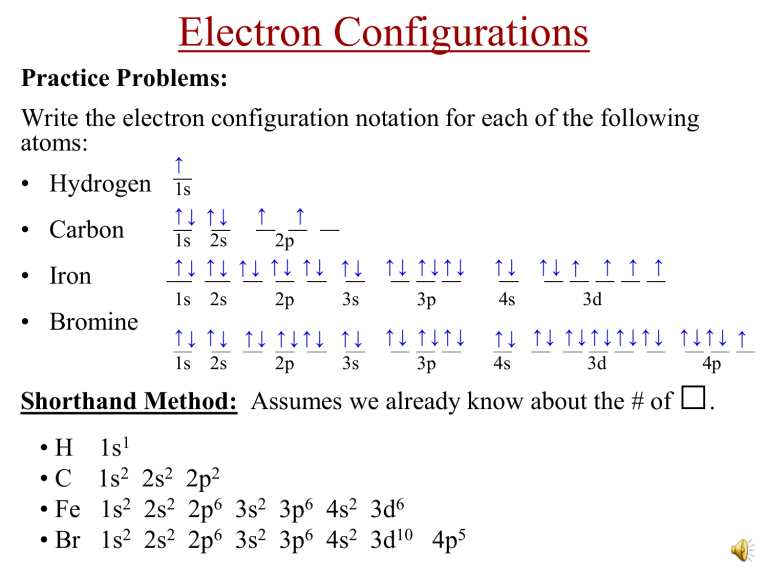
Electron Configurations Practice Problems: Write the electron configuration notation for each of the following atoms: • Hydrogen • Carbon • Iron • Bromine ↑ 1s ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 1s 2s 2p ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s 2p 3s ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓↑↓ ↑↓ 1s 2s 2p 3s ↑↓ ↑↓↑↓ ↑↓ 3p 4s ↑↓ ↑↓↑↓ 3p ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ 3d ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓↑↓↑↓↑↓ ↑↓↑↓ ↑ 4s 3d 4p Shorthand Method: Assumes we already know about the # of •H •C • Fe • Br 1s1 1s2 2s2 2p2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5 □. How Electron Configurations Relate to the Organization of the Periodic Table s p d f Orbitals being filled for elements in various parts of the periodic table: • • • Electron Configurations & Properties How do electron configurations relate to the chemical and physical properties of an element? All elements with the _________ same outer shell e- configurations have the ________ similar properties. This means that elements in the same ____________ vertical group have similar properties. Examples: (1) Li, Na, K, Rb, and Cs all have __ 1 lone “__” s e- for their last orbital... (_____, 2s1 _____, 3s1 _____, 4s1 etc.) This makes all of them ___________ very reactive. They all react with __________ to produce hydrogen gas. water (2) Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn all have the outer energy level completely filled with electrons...(________, 3s2 3p6 ________, __________ 2s2 2p6 ________, 4s2 4p6 etc.) This makes all inert of them ______________. They do not produce ________________ . compounds (3) Since SiO2 can be a ceramic, SnO2 may be as well. More Practice Problems (1) Which element has its last electron as a 4p5? ___________ Bromine F, Cl, I, At (2) Which elements are similar in properties as Bromine? __________ (3) What would the last outer shell electron configuration look like for the element underneath Radon, (Rn)? …7p6 3d1 (4) Which electron is added after 4s2? ________ sphere (5) What is the shape of the last orbital filled in Calcium, (Ca)? _____ 4 (6) How many electrons are in the last “p-orbital” of Sulfur, (S)? ____ (7) Would you expect the element underneath Francium to react violently with water? Yes…the _____ other Group 1 metals do too. Electron Dot Notation • When atoms form bonds, only the outermost electrons are involved. These are called the “valence” electrons. • The inner electrons are called “core” electrons. • The electron dot notation (sometimes called the Lewis Structure) is a way to represent the valence electrons. • The “Group A” number on the periodic table equals the # of valence electrons and therefore the # of dots. How Light is Produced • • When atoms get hit with energy (by _____________ zapping them with heating electricity or by ____________ them up), the valence e− absorb jump this energy and __________ to a higher energy level called an “excited state”. Figure (a) As they immediately fall back ground down to the “____________ state”, they give off this energy in the form of a particle of light ___________ (or other types of electromagnetic radiation) called a _________. photon Figure (b) How Light is Produced • • Each photon emitted has a color specific ___________ (or frequency). The color of the light that is given off depends on how far the electron _______ fell _____ (which depends on how big of a jump it originally made.) The farther the fall, the greater ___________ energy the photon has. Photons of red and blue light. How Light is Produced • • Since electrons are located only in certain __________ energy levels (or orbitals) around the nucleus, only certain specific _________ color of light are emitted. spectroscope Scientists use a _________________ to separate these colors into bar code of color bands of light. These bands of color look like a ______ which is characteristic of that element. No two elements produce the spectrum same ______________ of colors. This can be used to distinguish one element from another contained in a sample. Emission Spectrum Hydrogen Spectrum Neon Spectrum Measuring the Energy of Photons • The photons of light given off or absorbed by atoms have specific energies that can be calculated according to the following formula: E=hν (E = h f…some textbooks write it this way.) E = energy (in joules) h = Planck’s constant = 6.63×10−34 J·s ν (nu) = frequency of the light in units of Hertz (waves per second)…s-1 • The frequency of light can be determined if given the wavelength (in meters) according to the following formula: c=λν (c = f λ…some textbooks write it this way.) c = the speed of light = 3.0 x 108 m/s λ (lambda) = wavelength (in meters) Both of these equations are given to you on the AP Equation Sheet. The Energy of Hydrogen’s Four Visible Photons All the Photons Produced by Hydrogen Counting p+, no and e− in an Atom • Protons = Atomic Number • Electrons = protons (in a neutral atom) • Neutrons = Mass # − protons • Mass Number = protons + neutrons Ions Gaining electrons gives an atom a (−) charge. Losing electrons gives an atom a (+) charge. Isotopes • An isotope refers to atoms that have the same # of ___________, protons neutrons but they have a different # of ___________. mass #’s (or simply, • Because of this, they have different _________ masses different ___________.) • Isotopes are the same element, but the atoms weigh a different neutrons amount because of the # of ______________. Examples---> (1) Carbon-12 & Carbon-13 (2) Chlorine-35 & Chlorine-37 (The # shown after the name is the mass #.) • For each example, the elements have identical ___________ #’s, atomic (# of p+) but different _________ mass #’s, (# of n0). • Another way to write the isotopes in shorthand is as follows: 12 6 C 35 17 Cl mass #, and the bottom # is the __________ atomic The top number is the ________ subtracting number. Calculating the # n0 can be found by _____________ the #’s! Isotoprah One of two or more Oprahs having the same social security number but different mass numbers Two Isotopes of Sodium Mass Spectroscopy • The discovery of concept of isotopes altered Dalton’s Atomic Theory…atoms of the same element can have differences! • A mass spectrometer can separate atoms by mass, and it can determine the % abundance of each isotope. Mass Spectroscopy • Mass spectroscopy explainedhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tOGM2gOHKPc • Mass spectroscopy data used in calculating the average atomic masshttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KF9_f7uRMoY Sections of the Periodic Table More Sections of the Periodic Table