Optics unit test
advertisement

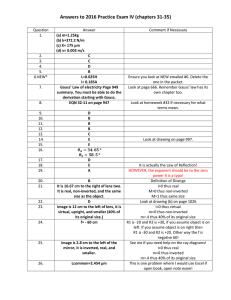
Name: _________ Optics Unit Test /53 Part One: Multiple Choice: Identify the BEST answer and place your choice in the chart provided. [20] 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 1. The proper name for far sightedness is: a. hyperopia b. myopia c. presbyopia d. astigmatism 2. A light angle has an angle of incidence of 27o. The reflected ray will make what angle of reflection? a. 43o b. 66o c. 34o d. 27o 3. Below is a list of materials and their indexes of refraction. The substance that is most optically dense is: a. water, n= 1.33 b. glycerine, n=1.47 c. zircon, n= 1.92 d. glass, n=1.65 4. An incident ray hitting a concave mirror through V will always reflect: a. parallel b. through C c. through V d. through F 5. The light rays directed at a convex mirror will always produce images that appear a. upright and smaller b. upside down and smaller c. upside down and larger 6. In which material will light travel the fastest? a. water, n= 1.33 b. glycerine, n=1.47 c. zircon, n= 1.92 d. glass, n=1.65 7. The ______ is responsible for detecting light in the eye a. pupil b. lens c. optic nerve d. cornea e. retina 8. The part of the eye that refracts light into the pupil is the a. pupil b. iris c. optic nerve d. cornea e. retina 9. The part of the eye that sends the signal to the brain is the: a. pupil b. iris c. optic nerve d. cornea e. retina 10. When light hits a converging lens it refracts and: a. diverges through F b. converges through F c. diverges through 2F d. upright and larger d. converges through 2F 11. Where would you place an object to get an image that is inverted and the same size as the object? a. at C b. between F and V c. between F and C d. at F 12. An object is placed in front of F, what kind of image will be produced? a. a virtual upright image b. a real inverted image c. no image d. a virtual inverted image 13. An object is placed at F, what kind of image will be produced? a. a virtual upright image b. a real inverted image c. no image d. a virtual inverted image 14. A plane mirror is only makes _______ images: a. virtual and upright b. real and inverted c. real and upright d. virtual and inverted 15. When light travels from air to water it: a. speeds up and bends towards the normal b. speeds up and bends away from the normal c. it slows down and bends towards the normal d. it slows down and bends away from the normal 16. Which of the following types of electromagnetic waves travels fastest in a vacuum? A. microwaves B. visible light C. x-rays D. They all travel at the same speed. 17. A light ray travels from vegetable oil to air. It will: a. speed up and bend away from the normal b. slow down and bend toward the normal c. slow down and bend away from the normal d. speed up and bend toward the normal 18. Which of the following is non-luminous? a. a laser beam b. the moon c. star d. a flame 19. What type of image does a diverging lens ALWAYS produce? a. virtual b. real c. no image d. real or virtual 20. In order for a converging lens to produce a virtual image, the object must be placed where? a. at 2F b. at C c. at F d. in front of F e. A or B Part B. Short Answer: Answer the following questions in the space provided. [20] 1) Glass’s index of refraction is 1.52, what is the speed of light in glass? [3] SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.0 x 108 m/s and V = C/N Name: _________ Optics Unit Test /53 2. Complete the following ray diagrams. Use SALT to describe the images [8] a) C F b) A 1 cm object is 5 cm from a convex mirror with a focal length of 4 cm. 3. Draw and label a diagram showing what happens to light when it travels from a fast medium like air to a slow medium, like water, [5] 4. Show where the image will appear. Describe the image using SALT. [4] 5. What is presbyopia and how is it different from hyperopia? [2] Part Three: Matching, match the term to its correct definition [11] 1. photon A light produced from friction 2. Light emitting diode B Light emitted when a material has been heated. 3. X-ray C Light that reflects in an unpredictable pattern 4. Chemiluminescence D Smallest quantity of energy that can be transported 5. triboluminescence E Light emitted as the result of a chemical reaction 6. Electric discharge F 7. incandescence G light produced from an electric current flowing through a semiconductor Low energy light 8. bioluminescence H Light created by a living organism 9. Diffuse reflection I Light that reflects in a predictable pattern 10. Specular reflection J Light that is produced as a result of an electric current 11. microwave K. High energy light