Oceanography Vocab
advertisement

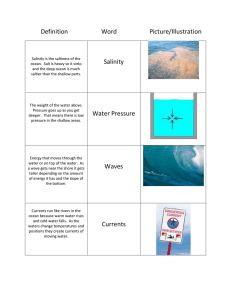
Abyssal Plain- A feature of the deep-sea floor; the flattest of all earth’s surface areas. (Pg 517) Ex. Abyssal plains the composed of sediments, most of which came from continents. Barrier Island- Sandbars that form on coasts with straight shorelines; not attached to the shore (Pg 352) Ex. Since barrier islands are not attached to the shore, they run parallel to it at some distance offshore. Continental Shelf- Part of the continent that extends from the shoreline out to the continental slope. (Pg 514) Ex. Continental shelves tend to be very flat and their widths vary. Continental Slope- Begins at the shelf edge, where water depth begins to increase rapidly. (Pg 514) Ex. Sediments tend to build up temporarily on the continental slope; eventually they become unstable and tumble downward to form the continental rise. Continental Rise- Descends gradually from the continental slope to the ocean floor at between four and eight miles per kilometer. (Pg 514) Ex. The continental rise connects the continental slope and the abyssal plain. Echo Sounding- A technique used to find the distance to the ocean floor. (Pg 510) Ex. Echo sounding works by sending a signal through the water to the sea floor, seeing how long it takes to reach the bottom and then echo back to the ship. Climate- An area’s long-term pattern of weather (Pg 466) Ex. Climate includes many characteristics including how hot the summers are, how cold the winters are, and how much precipitation falls at different times of the year. Oceanography- The scientific study of the ocean using chemistry, biology, physics, geology, and other sciences. (Pg 490) Ex. Studying the habitat in which dolphins live in would be considered oceanography. Apogee- When the moon is farthest from earth. (Pg 542) Ex. When the moon is at apogee, the tidal effect is less. Crest- A wave’s high point. (Pg 344) Ex. The opposite of a crest is a trough, which is a wave’s low point. Guyot- Flat-topped sea mounts. (Pg 520) Ex. When a seamount gets extreme wave action, the top will flatten over time. Island- A piece of land completely surrounded by water, formed by volcanic action and a midocean ridge. (Pg 177, 518) Ex. Volcanic island chains are called island arcs. Lagoon- Sandbars usually protect the water behind them from strong winds and waves; the protected areas are lagoons. (Pg 351) Ex. If the Lagoon fills with sediment, it becomes a salt marsh. Longshore Current- An ocean current that slows parallel to the shoreline. Ex. Along irregular shorelines, longshore currents carry away most of the sand and pebbles eroded from the headlands. Mid-ocean Ridge- A long chain of mountains with a central rift valley that is located along a divergent boundary on the ocean floor. (Pg 174) Ex. Mid-ocean ridges form at divergent plate boundaries where two lithospheric plates are moving apart. Upwelling- A vertical current; occurs when cold deep water comes to the surface. (Pg 538) Ex. Although upwelling can occur anywhere, it is most common on the western sides of continents. Estuary- the tidal mouth of a large river, where the tide meets the stream. Ex. Estuaries are often referred to as “Delta”, such as the Nile Delta. Tides- The periodic rise and fall of the ocean surface due to the gravitational pulls of the moon and sun. (Pg 541) Ex. The phases of the moon have a great effect on the tides that occur in the ocean. Salinity- A measure of the dissolved salts in water. (Pg 495) Ex. You can measure the salinity of a sample of seawater in a beaker by evaporating the water and weighing the salt that remains at the bottom of the beaker. Salt Marsh- As time passes, lagoons may fill with sediment and become salt marshes. (Pg 351) Ex. Gulf Coast Salt Marshes are the most commonly known/visited salt marshes. Seamount- Cone shaped mountain peaks that rise high above the deep ocean floor. (Pg 520) Ex. Seamounts are typically found in clusters and rows. Spit- A narrow point of land that extends to a body of water formed by ocean waves. (Pg 351) Ex. Waves and crosscurrents may curve the end of a spit and then it is referred to as a “hook” instead of a spit. Trough- A wave’s low point. (Pg 344) Ex. The opposite of a trough is a crest, which is a wave’s high point. El Niño- A warm surface current in the Pacific Ocean. (Pg 485) Ex. Scientists still do not exactly understand what causes El Niño in some years and not in others, or just how it causes major changes in the world’s weather. Current- Any continuous flow of water along a broad path in the ocean. (Pg 532) Ex. Currents can flow at the surface or far below it. Climate Controls- The set of conditions in which the climate of a location depends on. (Pg 467) Ex. Some of the climate controls are latitude, elevation, nearby water, ocean currents, topography, prevailing winds and vegetation. Perigee- When the moon is closest to earth. (Pg 542) Ex. When the moon is at perigee, the tidal effect is greater, especially if it occurs during the new or full moon phases. Questions Answers Page #’s 1) What percentage of earth’s surface is covered by water? More than 70 percent 490 2) List 3 scientific devices oceanographers use in their research JOIDES (four-story underwater laboratory) Alvin (mini submarine) Moored buoys 490 3) Describe 3 ways that polarity of water molecules affects the behavior of water -strong attraction -high boiling point -crystal lattice forms when frozen 493 4) Compare the boiling and freezing points of pure water with the boiling and freezing points of salt water The levels of salt in seawater make it 2-3 percent more dense than pure water; The boiling point increases as salt concentrations rise and the freezing point decreases 494 5) Describe 2 ways to measure salinity -Evaporating the water and weighing the salt that remains; find the ratio of the mass of salt to the mass of the water -Measuring the electrical conductivity of seawater (psu) Increase- Hot, dry area; Frozen seawater Decrease- Minerals precipitate out and settle to the ocean bottom as sediment 495 Chapter 22 6) Describe one factor that causes salinity to increase and one factor that causes salinity to decrease 496 Questions Answers Page #’s 1) What information can scientists learn from a sediment core? They can examine the different layers of the ocean floor 511 2) How do satellites determine the terrain of the ocean floor? Signals bounce off the ocean surface. The ocean surface varies depending what lies beneath it; it is slightly higher over undersea mountains and slightly lower over undersea trenches 511 3) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins Active- oceanic plate is sliding beneath, or 515 subducting under, the continental plate Passive- Not located at plate boundaries; no ocean trenches or rugged coastal mountains Both- lie in relation to a subduction zone or transform fault They are covered in sediments that have 517 been washed off the surface of continents caused by turbidity currents Chapter 23 4) Why are abyssal plains so flat? 5) What actions occur along ocean ridges? Transform vaults separate them into pieces; with the rugged terrain around them, they make up fracture zones 520 Questions Answers Page #’s 1) What is the primary cause of surface currents? The wind 532 2) Would you expect the water off the Pacific coast of the US to be warmer or colder than water off the Atlantic coast at the same latitude? Explain your reasoning 3) Why are density currents so important to marine life in the deep ocean? Colder- there are cool currents traveling near the west coast and there are warm currents near what seems to be the east coast of the US 532-533 They retain oxygen absorbed at the surface layer; such deep currents are the only source of oxygen for deep-sea life 536 4) Where does the densest water in the ocean come from? Explain why Polar regions, due to intense cooling and freezing that occurs (water takes up less space because it is cooled; molecules get packed together) 537 5) Describe 2 causes of upwelling 1- Prevailing winds blow among the coastline towards the equator 2- Two major wind belts blow on either side of the upwelling region 539 6) What are tides? The periodic rise and fall of the ocean surface due to the gravitational pulls of the moon and sun. 541 7) Explain the difference between spring and neap tides Spring- alignment of the earth, sun and moon occur at the times of a new/full moon (high/low tides are extreme) Neap- not aligned, occur during quarter phases (high/low tides are not extreme) 542 8) How does the shape of an inlet affect its tidal range? If it is a V-shape, the water piles up at the narrow end. When the shoreline is much broader than its mouth, the water spreads out over the shoreline 543 Chapter 24 Questions Answers Page #’s 1) Why doesn’t average temperature give a complete picture of climate? It only describes how hot or cold a climate is; doesn’t give variations of the weather 466 2) Choose 3 of the climate controls listed on page 467, and describe how they affect the climate where we live Prevailing winds- determine whether air masses from a hot/cold/wet/dry region Elevation- generally colder and drier the higher the altitude (mountains) Nearby water- coastal areas tend to have mild climates and precipitation (Virginia is in the east coast; VA beach) Latitude- colder towards the poles; midlatitudes have precipitation (Like in VA) Vegetation- affects insolation and how quickly air heats/cools; releases water vapor through transpiration (Lots of vegetation in VA, therefore its hot/wet) 467 3) In what way do earth’s motions change over time? -Shape of the Earth’s orbit varies with a period of about 100,000 years -The tilt of Earth’s axis varies between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees with a period of 41,000 years -Earth’s axis of rotation wobbles with a period of about 23,000 474-475 4) Explain how sunspots may affect climate The amount of energy given off by the sun increases slightly when the number of sunspots increases; if the sun emits more energy, there is more energy available to reach the earth. 475 5) Describe 3 ways scientists learn about past climate changes Sea-floor sediments, glacier samples and tree rings 476 Chapter 21