Chapter 1
Principles of
Corporate Finance
Tenth Edition
Goals and
Governance of the
Firm
Slides by
Matthew Will
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Key Terms
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
➢
Investment decision: Quyết định đầu tư
Financing decision: QĐ tài trợ
Agency Problem: vấn đề đại diện
Agency Cost: CP đại diện
Real assets: Tài sản thực
Capital budget: Ngân sách vốn
Capital Expenditure (CAPX) Chi tiêu vốn
Treasurer: Ngân quỹ
Shareholder: Cổ đông
Dividend: Cổ tức
Compensation: Bồi thường
Stakeholder: các bên liên quan
1-2
Chapter Outline
1-3
1
• Corporate Investment and
Financing Decisions
2
• The Role of the Financial Manager
and the Opportunity Cost of Capital
3
• Goals of the Corporation
4
• Agency Problems and Corporate
Governance
1-4
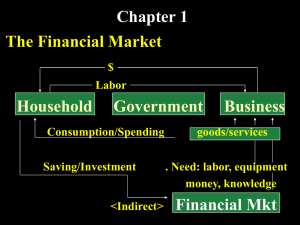
Investment and Financing Decisions
➢ Common Finance
Terminology
– Real assets
– Financial assets /
Securities
– Capital markets and
financial markets
– Investment / capital
budgeting
– Financing
1-5
Investment and Financing Decisions
Assets used to produce
goods and services
Financial claims to the
income generated by
the firm’s real assets
1-6
Investment and Financing Decisions
Purchase of
real assets
Sale of
financial assets
1-7
Investment and Financing Decisions
➢Capital Budgeting
Decision
– Decision to invest in
tangible or intangible
assets.
➢…also called the
Investment Decision
➢…also called Capital
Expenditures or
(CAPEX)
1-8
Investment and Financing Decisions
1-9
Investment and Financing Decisions
Company (revenue in billions
for 2007 or 2008)
Boeing ($61 billion)
Recent Investment Decision
1-10
Recent Financing Decision
Began production of its 787 Dreamliner The cash flow from Boeing’s
aircraft, at a forecast cost of more than
operations allowed it to repay some
$10 billion.
of its debt and repurchase $2.8
billion of stock.
Royal Dutch Shell ($458 billion)
Invests in a $1.5 billion deep-water oil
In 2008 returned $13.1 billion of
and gas field in the .
cash to its stockholders by buying
back their shares.
GlaxoSmithKline (£24 billion)
Spent £3.7 billion in 2008 on research
Financed R&D expenditures largely
and development of new drugs.
with reinvested cash flow generated
by sales of pharmaceutical products.
Wal-Mart ($379billion)
LVMH (€17 billion )
Lenovo ($16 billion)
In 2008 announced plans to invest over
In 2008 raised $2.5 billion by an
a billion dollars in 90 new stores.
issue of 5-year and 30-year bonds.
Acquired the Spanish winery, Bodega
Issued a 6-year bond in 2007, raising
Numanthia Termes.
300 million Swiss francs.
Expanded its chain of retail stores to
Borrowed $400 million for 5 years
cover over 2,000 cities.
from a group of banks
Role of The Financial Manager
(2)
(1)
Financial
manager
Firm's
operations
(3)
1-11
(4a)
(4b)
(1) Cash raised from investors
(2) Cash invested in firm
(3) Cash generated by operations
(4a) Cash reinvested
(4b) Cash returned to investors
Financial
markets
Who is The Financial Manager?
1-12
The Investment Trade-off
1-13
The Investment Trade-off
➢Hurdle rate
➢Cost of capital
➢Opportunity cost of capital
1-14
Goals of The Corporation
Each stockholder wants three things:
1. To be as rich as possible, that is, to maximize his or her current
wealth.
2. To transform that wealth into the most desirable time pattern of
consumption either by borrowing to spend now or investing to
spend later.
3. To manage the risk characteristics of that consumption plan.
1-15
Goals of The Corporation
1-16
➢ Profit maximization is not a well-defined financial objective, for at least
two reasons:
1. Maximize profits? Which year’s profits? A corporation may be able to
increase current profits by cutting back on outlays for maintenance or staff
training, but that may add value. Shareholders will not welcome higher
short-term profits if long-term profits are damaged.
2. A company may be able to increase future profits by cutting this year’s
dividend and investing the freed-up cash in the firm. That is not in the
shareholders’ best interest if the company earns less than the opportunity
cost of capital.
1-17
Whose Company Is It?
** Survey of 378 managers from 5 countries
3
Japan
97
17
Germany
22
France
United States
71
76
24
0
All Stakeholders
78
29
United Kingdom
The Shareholders
83
20
40
60
80
% of responses
100
120
1-18
Dividends vs. Jobs
** Survey of 399 managers from 5 countries. Which is more important...jobs
or paying dividends?
3
Japan
97
40
Germany
41
France
United States
89
89
11
0
Job Security
59
11
United Kingdom
Dividends
60
20
40
60
80
% of responses
100
120
Goals of The Corporation
➢ Shareholders desire wealth maximization
➢ Do managers maximize shareholder
wealth?
➢ Mangers have many constituencies
“stakeholders”
➢ “Agency Problems” represent the conflict
of interest between management and
owners
1-19
Agency Problem
Ownership vs. Management
1-20
Agency Problem
➢Agency costs are incurred when:
1. managers do not attempt to maximize firm value and
2. shareholders incur costs to monitor the managers and
constrain their actions.
1-21
The conflict of goals between managers and
shareholders
22
1-22
Group Activities: Agency Problems
1
2
3
23
• What is the main reasons of
agency cost?
• Example of agency cost?
• Could we completely solve agency
costs by firing the manager?
1-23
1-24
Control of Agency Problems
Legal and
Regulatory
Requirements
Takeovers
Compensation
plans
Board of
Directors
24
Monitoring
Control
Agency
Costs
Shareholder
pressure
Web Resources
Click to access web sites
Internet connection required
www.corpgov.net
www.thecorporatelibrary.com
www.riskmetrics.com
1-25
Question 3
1. Generally, a corporation is owned by the:
I) Managers; II) Board of Directors; III)
Shareholders
A. I only
B. II and III
C. III only
D. I, II and III
1-26
Question 1
2. Finance, generally, deals with:
I) Money; II) Markets; III) People
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
1-27
Question 2
3. Shareholders of a corporation may be,
among others:
I) Individuals; II) Pension Funds; III)
Insurance Companies
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II only
D. I, II and III
1-28
Question 4
4. Corporations, potentially, have infinite
life because:
A. it is a legal entity
B. of separation of ownership and
management
C. it has limited liability
D. none of the above
1-29
Question 5
5. Limited liability is an important feature of:
A. Sole proprietorships
B. Partnerships
C. Corporations
D. All of the above
1-30
Question 6
6. The following are examples of intangible
assets except:
A. Building
B. Trademarks
C. Patents
D. Technical expertise
1-31
Question 7
7. The following are examples of tangible
assets except:
A. Machinery
B. Factories
C. Trademarks
D. Offices
1-32
Question 8
8. A firm's investment decision is also
called the:
A. Financing decision
B. Liquidity decision
C. Capital budgeting decision
D. None of the above
1-33
Question 9
9. The following are examples of financial
assets except:
A. Common stock
B. Bank loan
C. Preferred stock
D. Buildings
1-34
Question 11
10. The controller usually oversees the
following functions of a corporation:
I) Preparation of financial statements; II)
Internal accounting; III) Cash management
and IV) Taxes
A. I, II and IV only
B. III only
C. I and II only
D. II and III
1-35
Question 10
1-36
10. The treasurer usually oversees the following
functions of a corporation except:
I) Preparation of financial statements; II) Investor
relationships; III) Cash management; IV) raising
new capital
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II, III and IV only
D. III only
Question 12
12. The following are important functions of
financial markets:
I) Source of financing; II) Provide liquidity;
III) Reduce risk; IV) Source of information
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I, II, III, and IV
D. IV only
1-37
Question 13
13. Conflicts of interest between shareholders
and managers of a firm result in:
A. Principal-agent problem
B. Increased agency costs
C. Both A and B
D. Managers owning the firm
1-38
Question 14
14 In the principal-agent framework:
A. Shareholders are the principals
B. Managers are the principals
C. Managers are the agents
D. A and D
1-39
Question 15
15. Costs associated with the conflicts of
interest between the bondholders and the
shareholders of a corporation are called:
A. Legal costs
B. Bankruptcy costs
C. Administrative costs
D. Agency costs
1-40
Question 16
16. Agency costs are incurred by a
corporation because:
A. managers may not attempt to maximize the
value of the firm to shareholders
B. shareholders incur monitoring cost
C. separation of ownership and management
D. all of the above
1-41
Question 17
17. The financial goal of a corporation is to:
A. Maximize profits
B. Maximize sales
C. Maximize the value of the firm for the
shareholders
D. Maximize managers' benefits
1-42
Question 18
18. The purchase of real assets is also referred
to as the:
A. Capital decision
B. CFO decision
C. Financing decision
D. Investment decision
1-43
Question 19
19. The sale of financial assets is also referred
to as the:
A. Capital decision
B. CFO decision
C. Financing decision
D. Investment decision
1-44
Question 20
20.The mixture of debt and equity, used to
finance a corporation is also known as:
A. Capital budgeting
B. Capital structure
C. Investing
D. Treasury
1-45