circulatory system Chizoba edited
advertisement

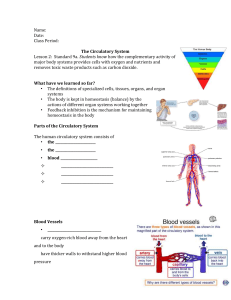
Circulatory system CHIZOBA EZENWA What is the primary function of the circulatory system? The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This system has three main functions: Transport of nutrients, oxygen, and hormones to cells throughout the body and removal of metabolic wastes. What is the primary function of blood? Blood has three main functions: transport, protectio n and regulation. Blood transports the following substances: Gases, namely oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2), between the lungs and rest of the body. Nutrients from the digestive tract and storage sites to the rest of the body. What organs makes up the circulatory system? The circulatory system consists of : the heart(cardiovascul ar), blood , and blood vessels. Describe the structure of the heart? A. In how many parts is the heart divided? The heart is divided into four chambers. B. what is the upper half called? The two upper chambers are called the atria. The right atrium and left atrium are separated by a wall of tissue called the atrial septum. C. what is the lower half called? The two lower chambers are called the ventricles, and are separated into the right and left ventricle by the ventricular septum D. what are the major blood vessels connected to heart? Five great vessels enter and leave the heart: the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery, the pulmonary vein, and the aorta. The superior vena cava and inferior vena cava are veins that return deoxygenated blood from circulation in the body and empty it into the right atrium. Heart pumps blood carrying materials to different cells. Blood travels through tube like structure called blood vessels. Circulation takes place in two pathways: 1. Pulmonary Circulation 1. 2. Carries blood to lungs and back to the heart. Systemic Circulation 1. Carries blood to body and back to the heart. In what way the heart facilitates the circulation? There Are Two Types of Circulation: Pulmonary Circulation and Systemic Circulation. Pulmonary circulation moves blood between the heart and the lungs. It transports deoxygenated (blood without oxygen) blood to the lungs to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide out of body. IN WHAT WAY THE HEART FACILITATES THE CIRCULATION OF BLOOD? Systemic circulation: is the portion of the cardiovascular system which transports oxygenated blood away from the heart through the aorta from the left ventricle where the blood has been previously deposited from pulmonary circulation, to the rest of the body, and returns oxygendepleted blood back to the heart. Your Blood Vessels: Pathway of Circulation 3 types of vessels Arteries Capillaries Veins Arteries: carries blood Away from heart to cells Large Thick-walled, Muscular Elastic Carries Oxygenated blood Carried under great pressure Steady pulsating Capillaries Smallest vessel Microscopic Walls one cell thick Nutrients and gases diffuse through these vessels in to blood. Again capillaries pass the waste/carbon dioxide to veins. Veins: Carries blood back to heart Carries blood that contains waste and CO2 Blood not under much pressure Valves to prevent much gravity pull Explain the connection between respiratory system and circulatory system? The circulatory and respi ratory systems work together to circulate blood and oxygen throughout the body. Air moves in and out of the lungs through the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. Blood moves in and out of the lungs through the pulmonary arteries and veins that connect to the heart.