25963271-Rockwell-Hardness-Test
advertisement

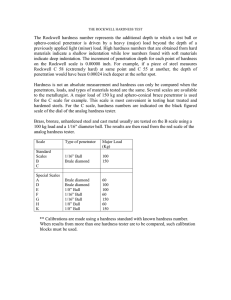
facebook.com/adilch twitter.com/adilch scribd.com/adilch 3. To perform hardness test on given steel specimens using Rockwell Hardness Testing Machine. (17-09-08) Apparatus Shimadzu Rockwell hardness Testing Machine Diamond Cone and Steel Ball Indenters Steel Specimen Purpose To check the hardness of material Indirect strength test of material Quality control in industries Related Theory Hardness Hardness is the property of material that enables it to resist plastic deformation usually by penetration. However, the tern hardness may also refer to resistance to bending, scratching, abrasion or cutting. Hardness testing Methods Brinall Hardness Test Vivkers Hardness Test Rockwell Hardness Test 1 To perform hardness test using Rockwell Hardness Testing Machine 07 CIVIL 73 facebook.com/adilch twitter.com/adilch scribd.com/adilch Rockwell hardness Test (BS-891) The Rockwell hardness test method consists of indenting the test material with a diamond cone or hardened steel ball indenter. The indenter is forced into the test material under a preliminary minor load F0 (Fig. 1A) usually 10 kgf. When equilibrium has been reached, an indicating device, which follows the movements of the indenter and so responds to changes in depth of penetration of the indenter, is set to a datum position. While the preliminary minor load is still applied an additional major load is applied with resulting increase in penetration (Fig. 1B). When equilibrium has again been reach, the additional major load is removed but the preliminary minor load is still maintained. Removal of the additional major load allows a partial recovery, so reducing the depth of penetration (Fig. 1C). The permanent increase in depth of penetration, resulting from the application and removal of the additional major load is used to calculate the Rockwell hardness number. HR = E - e F0 = preliminary minor load in kgf F1 = additional major load in kgf F = total load in kgf e = permanent increase in depth of penetration due to major load F1 measured in units of 0.002 mm E = a constant depending on form of indenter: 100 units for diamond indenter, 130 units for steel ball indenter HR = Rockwell hardness number D = diameter of steel ball Fig. 1.Rockwell Principle 2 To perform hardness test using Rockwell Hardness Testing Machine 07 CIVIL 73 facebook.com/adilch twitter.com/adilch scribd.com/adilch Rockwell Hardness Scales Scale A B C D E F G H K L M P R S V Indenter Minor Load Major Load Total Load Value of F0 F1 F E kgf kgf kgf Diamond cone 10 50 60 100 1/16" steel ball 10 90 100 130 Diamond cone 10 140 150 100 Diamond cone 10 90 100 100 1/8" steel ball 10 90 100 130 1/16" steel ball 10 50 60 130 1/16" steel ball 10 140 150 130 1/8" steel ball 10 50 60 130 1/8" steel ball 10 140 150 130 1/4" steel ball 10 50 60 130 1/4" steel ball 10 90 100 130 1/4" steel ball 10 140 150 130 1/2" steel ball 10 50 60 130 1/2" steel ball 10 90 100 130 1/2" steel ball 10 140 150 130 Advantages of the Rockwell hardness method include the direct Rockwell hardness number readout and rapid testing time. Disadvantages include many arbitrary non-related scales and possible effects from the specimen support anvil (try putting a cigarette paper under a test block and take note of the effect on the hardness reading! Vickers and Brinell methods don't suffer from this effect). Rockwell Hardness Test Procedure 1. Bring the specimen in contact with indenter and continuously raise the sample until a small inset pointer on the dial das reached the reference point. 2. Set the main dial to correct reference point (At ‘0’ for diamond cone and at ‘30’ for steel ball indenter) 3. After application of seating load (Minor Load i.e. 10 kgf) apply major load (depends on the scale) and maintain it for approximately 4-7 seconds. 4. Remove the major load to permit elastic recovery while keeping on the minor load. Read the hardness number from the dial directly and write it in the standard format i.e. HR 70B (HR means Rockwell Hardness, ‘70’ is the hardness number and “B” represents the scale.) 3 To perform hardness test using Rockwell Hardness Testing Machine 07 CIVIL 73 facebook.com/adilch twitter.com/adilch scribd.com/adilch Rockwell Hardness Test Specifications Depth of indentation should not be more that 1/8th of the thickness of the specimen. Two consecutive indentations should not be made very close to each other. Indentations should not be made near the edge of specimen. Minimum three observations should be taken. Simple Hardness Test In this we use 2 types of Balls, Type of Specimen indenter Sr. No Mild 1/16" Carbon dimater 2 Steel Steel ball 3 Specimen Indenter Scale 1 High Diamond Carbon Cone 2 Steel Indenter 3 Specimen B 1 C 130 for Steel ball (B Scale) Load (kg) Major Minor Load Load Hardness Mean Number hardness 10 90 HR 92.5 B 10 90 HR 96 B 10 90 HR 92.5 B 10 140 HR 43.5 C 10 140 HR 43 C 10 140 HR 43.5 C HR 93.66 B 100 for diamond ball (C Scale) HR 43.3 C Comments By performing this experiment and knowing the hardness of any material we can control the quality of products in industries. We come to know that medium carbon steel has HR 93.66B and that of High Carbon Steel is HR 43.3C. Hence by increasing percentage of carbon its strength decreases. 4 To perform hardness test using Rockwell Hardness Testing Machine 07 CIVIL 73