Due Process 2017
advertisement

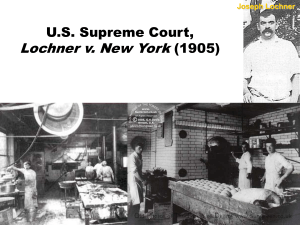
Due Process • 5th Amendment – “No person shall be….deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law……” • 14th Amendment – No State shall deprive any person of life, liberty or property, without due process of law…….” • What does due process mean? – done fairly – not arbitrarily – with reason – according to an established set of rules • What does due process look like in actual practice? It has been and continues to be defined and refined on a case by case basis by the courts. • There are 2 types of due process: • Procedural – Rochin v. California 1952 • The government must act fairly • Substantive - Pierce v. Society of Sisters 1922 • The laws themselves must be fair. Process of Incorporation • The due process clause has been used by the Supreme Court to hold most of the protections found in the Bill of Rights (speech, search & seizure, cruel /unusual punishment) to apply against the States as well. POLICE POWER (not the power of the police) a product of federalism (state powers) The power of the STATE to act to protect public HEALTH drinking age; smoking regulations; pollution standards SAFETY seat belt laws; safety glass; traffic regulations MORALS gambling; public nudity; prostitution GENERAL WELFARE mandatory school attendance; professional licensing