Components of map new
advertisement

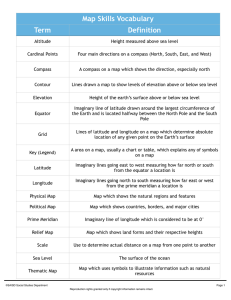
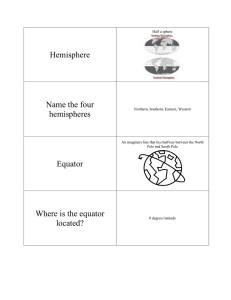
Components (Elements) of a Map ● A map is a representation of a larger portion of the earth, and is a basic tool in Geography. A map allows us to depict space on a paper. ● All maps must have 4 of the following: Scale, Legend, Compass Rose, and a Title. Sometimes an In-set map is included as well. Title ● What the map is about. Streets, Cities, Country, Schools etc. LEGEND OR KEY: ● ● ● ● ● This is an area of the map that tells the reader what symbols mean. A cross would represent a church or a place of worship. A blue sign with a large white H represents a hospital. While roads or highways can be a combination of lines. The legend can be found in the corner of the map, or on the flip side of the map. Compass Rose ● cardinal directions directions ● ● ● of north (N), south (S), east (E), and west (W) compass rose a directional arrow that shows cardinal and sometimes intermediate directions on a map intermediate directions directions of northeast (NE), northwest (NW), southeast (SE), and southwest (SW) direction arrow determines direction, with a true North Pole at the top of the page (Bar) Scale ● A scale is representation of a portion of the earth’s surface. ● It tells us a certain distance on the ground objects are away from each other. ● Scales can be in a ratio or fraction. 1:100,000. (1cm on the map equals 100,000cm on the earth. ● A word statement, ● 1 cm represents 1,000,000km. Contiguous, Continental, vs. Complete Maps contiguous sharing an edge or boundary; touching Continental all belonging on the same continent Complete including all, excluding none. Political vs. Physical Map Elements: ● inset map a smaller map set within the border of a larger one ● international border a border between countries physical map a map that shows natural features, indicate the forms of landscape, bodies of water, elevation, and climate. political map a map that shows human-made features and boundaries such as cities, highways, and countries Parallels & Meridians: the Globes ● ● ● ● ● ● ● degrees units of latitude or longitude (° is the symbol for degrees) equator an imaginary line that runs around the center of Earth, halfway between the North and South Poles at 0° latitude meridians (lines of longitude) imaginary lines on Earth that run between the North and South Poles North Pole the point on Earth located at 90 degrees (90°) north latitude, where the lines of longitude meet parallels (lines of latitude) imaginary lines on Earth that run parallel to the equator prime meridian an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole of Earth at 0° longitude South Pole the point on Earth located at 90 degrees (90°) south latitude where the lines of longitude meet ● cartographer mapmaker ● equator an imaginary line that runs around the center of Earth, halfway between the North and South Poles at 0° latitude ● hemisphere half of the Earth ● North Pole the point on Earth located at 90 degrees (90°) north latitude, where the lines of longitude meet ● prime meridian an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole of Earth at 0° longitude ● South Pole the point on Earth located at 90 degrees (90°) south latitude where the lines of longitude meet The 4 Hemispheres Map Grid & Index ● grid a pattern of lines that form squares ● index an alphabetical listing of place names on a map and the grid squares in which they are found Index: Barcelona Gerona Madrid Malaga Sevilla ___ ___ E6 ___ ___ ● ● ● ● ● geographic grid the intersecting pattern formed by the lines of latitude and longitude hemisphere half of the Earth meridians (lines of longitude) imaginary lines on Earth that run between the North and South Poles lines of latitude (parallels) imaginary lines on Earth that run parallel to the equator projection a system for mapping the round Earth on a flat surface Maps are the basic tool in Geography, and can be interpreted and analyzed in many different ways. Learning to use maps helps with communication in any language. ● Create a map of any room in your home, using the major components that all maps must have. ● Title: What room is it? I.e. bedroom, kitchen, den. Etc. ● Direction? Don’t forget the sun rises in the east and sets in the west. Most maps have north at the top of the page. ● Scale: You will have to do some measuring of the room, and then calculate the difference. Your scale can be a direct statement, or a ratio (compare cm’s to cm’s) ● The key or legend will be used to tell the reader what objects are in the room. Use appropriate colour or shade for the objects. ● Map Grid & Index: You will need to put a grid on your map and include an index of at least 5 important items that are in the room. ● Bonus: In-set Map: include a small simple outline of the whole house/street and where the room you mapped is located within it.