AP World History: Trade Networks (600-1450 CE)
advertisement

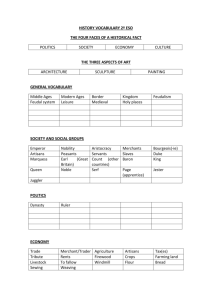
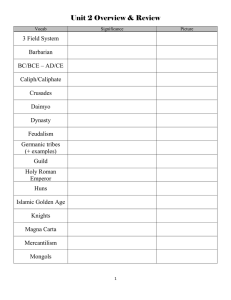
Period 3 (600 CE – 1450 CE) Name: ___Maika Belizor_______________________________________________________ Period: ____3__________ Key Concept 3.1 Expanded Trade Networks and Diffusion SILK ROAD Explain the significance of NEW trading cities Baghdad was an ideal spot for transSaharan trade, Baghdad soon rival Constantinople in both wealth and population. The expansion of education represented a “golden age” of learning. Baghdad Hangzhou Hangzhou was the center of culture in southern China. Trade from Russia and India brought diversity to Hangzhou. It was a departure point for Chinese goods to Korea, Japan, southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean trade network. Define Caravanserai Explain the role of each money economy on this trade route A system of credit known as flying cash was developed. This allowed a merchant to deposit paper money under his name in one Paper Money location and withdraw the same amounts from another location. Bills of Exchange A written order without interest which binds one party to pay a fixed sum to another party at a predetermined date in a future. A caravanserai were inns along trade routed where travelers could trade, rest, and replenish. Explain the significance of the Grand Canal in promoting trade Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes covering Asia, North Africa and Southeast Europe, especially along the Silk Road. Good Silk Porcelain Identify key luxury goods traded along the Silk Road Originating Location Destination Location China Byzantine Empire, Kievan rus, Islamic caliphates, and India China Western Europe, Byzantine Empire, Islamic caliphates Cause of Demand/Uses It use for clothes. It show signs of high nobility. For everyday use TRANS-SAHARAN TRADE ROUTES Explain the significance of NEW trading cities Timbuktu It became an exchange point for west African gold and north African salt. Because of the trade in books, the city also became an important city for Islamic scholarship and education. Developed into centers of Islamic life into the region. It became a world-renowned center of Islamic learning. By the 1500s, books created and sold in Timbuktu brought prices higher than any other goods. Good Slaves gold Identify key luxury goods traded along the Trans-Saharan Trade Routes Originating Location Destination Location Cause of Demand/Uses Western and Eastern Africa Swahili city-states, Africa east Laborer work, military, and coast, west Africa household responsibility Ghana Middles east , Swahili citywealth states, Swahili city-states Africa east coast MEDITERRANEAN SEA ROUTES Explain the significance of NEW trading cities Explain the role of each money economy on this trade route A wealthy city-state in northern Italy had a contract to transport Crusaders to the Middle East. Venice Good Olive oil A merchant would place his wealth in the safe keeping of a banking house which would in turn issue a bill of credit that could be used to purchase goods Identify key luxury goods traded along the Mediterranean Sea Originating Location Destination Location Cause of Demand/Uses India Everyday use Byzantine Empire, Keivan Rus, Islamic caliphates Banking Houses Arabia pensula Cotton textile Clothes Byzantine Empire, Keivan Rus, Islamic caliphates INDIAN OCEAN MARITIME ROUTES Explain the significance of NEW trading cities Bustling port city for merchant in search of spices from southern India. Foreign merchants from Arabia and China met in Calicut to exchange from the West to the East. Calicut Had bustling commercial centers Kilwa This city imposes taxes on ships that passed through the Strait of Melaka. Melaka’s prosperity was based on trade rather than agriculture or mining. Melaka/ Malacca Good Spices Explain the role of each money economy on this trade route Cheque/Sakk Mufawada Bills of Exchange (cha/chap) Merchants used bills of exchange to purchase imported goods without the hazards of carrying an expensive medium of exchange. The bills, which worked like modern checks, required the existence of two established networks, one of bankers and another of merchants. Identify key luxury goods traded along the Indian Ocean Maritime Routes Originating Location Destination Location Cause of Demand/Uses Indonesia & Malaysia Food Cotton India Identify the new navigational technology below Clothes Identify the new navigational technology below Stern rudder Magnetic Compass Explain the significance of new communication and trade networks in the Americas Mississippi River Valley Mesoamerica Andes Identify how each group used environmental knowledge and technological innovations to trade over long distances Vikings They traveled in lights long ships that enable sailors to travel far inland Berbers/Arabs Central Asian Nomads They used camels to travel far in deserts. They use horses and yurt. Explain the significance of diasporic communities along important trade routes Muslim merchants in the Indian Ocean Calicut was city Chinese merchants in Southeast Asia Jewish communities in the Mediterranean Explain the significance of each of the following travelers within Afro-Eurasia Marco Polo Ibn Battuta Xuanzang BANTU MIGRATION Approximate Date of Migration Originating Location Evidence of Migration Destination Location Impact of Migration POLYNESIAN MIGRATION Approximate Date of Migration Evidence of Migration Originating Location Destination Location Impact of Migration Explain how new and expanding trade routes promoted the diffusion of crops and pathogens Bubonic Plague Bananas in Africa Champa rice in Asia Islam Define Muhammad Describe the key religious text Describe each of the key concepts/moral philosophies Quran Hadith Five Pillars of Islam Describe key Islamic sects Sunni Shia/Shiite Sharia Sufi Identify the religious building below Explain how different faiths influenced the development of Islam Judaism Christianity Zoroastrianism Explain the influence of military expansion on the spread of Islam Explain the role of merchants in the spread of Islam A) Identify the originating location of each cultural system B) Color the areas that each cultural system expanded to during this period Christianity Neoconfucianism Hinduism Buddhism Islam Toltec/Mexica Key Concept 3.2 Continuity and Innovation of State Forms and Their Interactions BYZANTINE EMPIRE Justinian Corpus Juris Civilis (Justinian’s Code) Explain key aspects of Byzantine governance Emperor Bureaucracy Describe how the Byzantine Empire was a theocracy Explain the significance of the Great Schism of 1054 Explain the geographic significance of the city of Constantinople Explain how each of the following affected Byzantine economic power Plague of Justinian Silk Fourth Crusade (1204) Identify the image below Explain why the Fall of Constantinople (1453) marks a turning point in world history (periodization) SUI CHINA Explain the political impact of the Grand Canal on China TANG CHINA Wu Zetian Xuanzong Explain key aspects of Tang governance Imperial Examinations Equal Field System Census Religion Explain the role of women in Tang China Explain the role of each religion in Tang China Buddhism Daoism Islam Identify key technological and scientific innovations during the Tang Dynasty Engineering Medicine Metallurgy Woodblock Printing Explain the significance of the An Lushan Rebellion SONG CHINA Neo-Confucianism Explain the role of gentry class in Song China Explain the role of joint-stock companies in Song China Explain the significance of paper money in Song China Explain key technological and scientific innovations during the Song Dynasty Magnetic Compass Gunpowder Movable Type Printing Iron Metallurgy ISLAMIC CALIPHATES Umayyad Caliphate Abbasid Caliphate Al-Andalus Explain key aspects of Islamic Caliphate governance Caliph Umma Dhimmi Dar al-Islam Explain the role of women during the Abbasid Caliphate Explain why the Abbasid Caliphate is considered the Golden Age of Islam Identify the cultural, scientific, and/or technological achievements of Islamic scholars al-Khwarizmi al-Kindi Avicenna Explain how the Crusades affected technological and cultural transfers Identify the image below Explain why the Siege of Baghdad (1253) marks a turning point in world history (periodization) MONGOL EMPIRE Genghis Khan Kublai Khan Yuan China Explain key aspects of Mongol society Yassa Yam (route) Religious Tolerance Role of Women Explain the impact of the Mongol Empire on Eurasia Islamic World China Kievan Rus (Russia Define feudalism Define serfdom In the diagram below, compare and contrast feudalism AND serfdom in European and Japanese societies EUROPE JAPAN MAYA CIVILIZATION Explain key aspects of Mayan society Long Distance Trade Human Sacrifice Role of Women Explain the significance of the Mayan calendar system Explain the significance of the Popol Vuh Identify the image below AZTEC EMPIRE Triple Alliance Huitzilopochtli Flower Wars Explain the role of tributes in the Aztec imperial system Explain the importance of human sacrifice in the Aztec Empire INCA EMPIRE Pachacuti Explain key aspects of Incan society Mit’a Labor Role of Women Quechua Reincarnation Explain the significance of the Incan Road System Identify the image below Identify the image below Key Concept 3.3 Economic Productivity and Consequences Innovation Identify key facets of agricultural innovations during the time period Location Description of Method Chinampas Waru Waru Horse Collar Three Field System Explain an example of how each factor led to urban decline Invasion Disease Little Ice Age Explain an example of how each factor led to urban renewal End of Invasions Safe and Reliable Transportation Global Warming Trends (800 CE-1300CE) Population Increases Explain each type of diversified labor organization Free Peasant Labor Military Obligations Nomadic Pastoralism Guild Organization Craft Production Coerced Labor Identify non-patriarchal roles of women in the societies listed West Africa Japan Southeast Asia Explain key examples of free peasant revolts in the regions listed Byzantine Empire China Explain the impact of post-classical diffusion of religion on gender relations and family structure Buddhism Christianity Islam Neoconfucianism