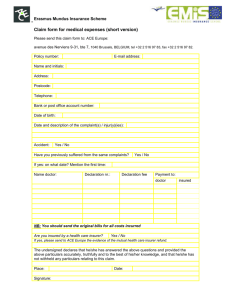
Multi Choise Questions
advertisement

Multi Choise Questions Circle the letter that corresponds to the BEST answer. Chapter 1 - Risk in Our Society 1) Traditionally, risk has been defined as A) any situation in which the probability of loss is one. B) any situation in which the probability of loss is zero. C) uncertainty concerning the occurrence of loss. D) the probability of a loss occurring. Answer: C 2) Objective risk is defined as A) the probability of loss. B) the relative variation of actual loss from expected loss. C) uncertainty based on a personʹs mental condition or state of mind. D) the cause of loss. Answer: B 3) An insurance company estimates its objective risk for 10,000 exposures at 10 percent. Assuming the probability of loss remains the same, what would happen to the objective risk if the number of exposures were to increase to 1 million? A) It would decrease to 1 percent B) It would decrease to 5 percent. C) It would remain the same D) It would increase to 20 percent. Answer: A 4) Uncertainty based on a personʹs mental condition or state of mind is known as A) objective risk B) subjective risk. C) objective probability D) subjective probability. Answer: B 5) The long-run relative frequency of an event based on the assumption of an infinite number of observations with no change in the underlying conditions is called A) objective probability B) objective risk. C) subjective probability D) subjective risk. Answer: A 6) Which of the following statements about a priori probabilities is correct? A) They are subjective probabilities based on ambiguity in the way probability is perceived. B) They are subjective probabilities that may vary among individuals because of factors such as age, gender, education, and the use of alcohol. C) They are objective probabilities that can be determined by deductive reasoning. D) They are objective probabilities that can be determined by subjective reasoning. Answer: C 7) An individualʹs personal estimate of the chance of loss is A) an objective probability B) an objective risk. C) a subjective probability D) an a priori probability. Answer: C 8) A peril is A) a moral hazard C) a condition which increases the chance of a loss Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc B) the cause of a loss D) the probability that a loss will occur 1 9) An earthquake is an example of a A) moral hazard C) physical hazard Answer: B B) peril D) objective risk 10) Dense fog that increases the chance of an automobile accident is an example of a A) speculative risk B) peril. C) physical hazard D) moral hazard. Answer: C 11) Faking an accident to collect insurance proceeds is an example of a A) physical hazard B) objective risk C) moral hazard D) morale hazard Answer: C 12) Indifference to loss because of the existence of insurance is an example of a A) physical hazard B) objective probability C) moral hazard D) morale hazard Answer: D 13) Some characteristics of the judicial system and regulatory environment increase the frequency and severity of loss. This hazard is called A) moral hazard B) physical hazard C) morale hazard D) legal hazard Answer: D 14) Taylor Tobacco Company is concerned that the company may be held liable in a court of law and ordered to pay a large damage award. The characteristics of the judicial system that increase the frequency and severity of losses are known as A) moral hazard B) particular risk. C) speculative risk D) legal hazard. Answer: D 15) A phrase that encompasses all of the major risks faced by a business firm is A) financial risk B) speculative risk C) enterprise risk D) pure risk Answer: C 16) Which of the following statements about financial risk is (are) true? I. Enterprise risk does not include financial risk. II. Financial risk is easily addressed through the purchase of insurance. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 17) All of the following are considered financial risks EXCEPT A) the decline in the value of a bond portfolio because of rising interest rates. B) increased cost of production because of rising commodity prices. C) loss of money because of adverse movements in currency exchange rates. D) loss of profits after a physical damage loss occurs. Answer: D 18) Katelyn was just named Risk Manager of ABC Company. She has decided to create a risk management program which considers all of the risks faced by ABC-pure, speculative, operational, and strategic-in a single risk management program. Such a program is called a(n) EG Test Insurance.doc 2 A) financial risk management program C) fundamental risk management program Answer: B B) enterprise risk management program D) consequential risk management program 19) A pure risk is defined as a situation in which there is A) only the possibility of loss or no loss B) only the possibility of profit C) a possibility of neither profit nor loss D) a possibility of either profit or loss Answer: A 20) The premature death of an individual is an example of a A) pure risk B) speculative risk. C) fundamental risk D) physical hazard. Answer: A 21) Which of the following statements about speculative risks is true? A) They are almost always insurable by private insurers B) They are more easily predictable than pure risks C) Their occurrence may benefit society D) They involve only a chance of loss Answer: C 22) An automobile that is a total loss as a result of a collision is an example of which of the following types of risk? I. Speculative risk II. Fundamental risk A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 23) All of the following are programs to insure fundamental risks EXCEPT A) federally subsidized flood insurance B) auto physical damage insurance. C) Social Security D) unemployment insurance Answer: B 24) All of the following are examples of personal risks EXCEPT A) poor health B) unemployment. C) premature death D) flood. Answer: D 25) Which of the following is a reason why premature death may result in economic insecurity? I. Additional expenses associated with death may be incurred. II. The income of the deceased personʹs family may be inadequate to meet its basic needs. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 26) Which of the following are often consequences of long-term disability? I. Continuing medical expenses II. Loss or reduction of employee benefits A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 27) All of the following are examples of direct property losses EXCEPT A) the theft of a personʹs jewelry. B) the destruction of a firmʹs manufacturing plant by an earthquake. C) the cost of renting a substitute vehicle while a collision-damaged car is being repaired. D) the vandalism of a personʹs automobile. Answer: C EG Test Insurance.doc 3 28) The extra expense incurred by a business to stay in operation following a fire is an example of a(n) A) fundamental risk B) speculative risk. C) direct loss D) indirect loss. Answer: D 29) Which of the following statements about liability risks is (are) true? I. Future income and assets can be attached to pay judgments if inadequate insurance is carried. II. There is an upper limit on the amount of loss. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 30) All of the following are burdens to society because of the presence of risk EXCEPT A) The size of an emergency fund must be increased. B) Individuals may profit from accepting a speculative risk. C) Society is deprived of certain goods and services. D) Mental fear and worry are present. Answer: B 31) Loss control includes which of the following? I. Loss reduction; II. Loss prevention A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 32) Following good health habits can be categorized as A) loss prevention B) loss retention. C) noninsurance transfer D) personal insurance. Answer: A 33) From the insuredʹs perspective, the use of deductibles in insurance contracts is an example of A) risk transfer B) loss control. C) risk avoidance D) risk retention. Answer: D 34) The use of fire-resistive materials when constructing a building is an example of A) risk transfer B) loss control. C) risk avoidance D) risk retention. Answer: B 35) All of the following statements about risk retention are true EXCEPT A) It may be used intentionally if commercial insurance is unavailable. B) It may be used passively because of ignorance. C) Its use is most appropriate for low-frequency, high-severity types of risks. D) Its use results in cost savings if losses are less than the cost of insurance. Answer: C 36) All of the following are methods of noninsurance transfer EXCEPT A) entering into a hold-harmless agreement B) avoiding dangerous activities C) hedging risk using futures contracts D) incorporating a business Answer: B 37) Curt borrowed money from a bank to purchase a fishing boat. He purchased property insurance on the boat. Curt had difficulty making loan payments because he did not catch many fish, and fish prices were EG Test Insurance.doc 4 low. Curt intentionally sunk the boat, collected from his insurer, and paid off the loan balance. This scenario illustrates the problem of A) adverse selection B) moral hazard. C) fundamental risk D) morale hazard. Answer: B 38) Jenna opened a successful restaurant. One night, after the restaurant had closed, a fire started when the electrical system malfunctioned. In addition to the physical damage to the restaurant, Jenna also lost profits that could have been earned while the restaurant was closed for repairs. The lost profits are an example of A) direct loss B) fundamental risk. C) speculative risk D) indirect loss. Answer: D 39) Brad started a pest control business. To protect his personal assets against liability arising out of the business, Brad incorporated the business. Bradʹs use of the corporate form of organization to shield against personal liability claims illustrates A) fundamental risk B) noninsurance transfer. C) risk retention D) objective risk. Answer: B 40) ABC Insurance Company plans to sell homeowners insurance in five Western states. ABC expects that 8 homeowners out of every 100, on average, will report claims each year. The variation between the rate of loss that ABC expects to occur and the rate of loss that actually does occur is called A) objective probability B) subjective probability C) objective risk D) subjective risk Answer: C 41) Williams Company installed smoke detectors, a sprinkler system, and fire extinguishers in its new manufacturing facility. These devices are all examples of A) loss control B) noninsurance transfer C) risk avoidance D) risk retention Answer: A 42) Tyndal Products Company produces cereal. The company has entered into contracts to deliver 500,000 boxes of cereal during the next 18 months. The company is concerned that the prices of two ingredients, corn and wheat, may increase over the next 18 months. The company used grain futures contracts to hedge the price risk associated with these commodities. Tyndalʹs use of hedging illustrates which risk management technique? A) noninsurance transfer B) risk avoidance C) risk retention D) risk assumption Answer: A 43) Cathyʹs car hit a patch of ice on the road. The car skidded off the road and hit a tree. The presence of ice on the road is best described as a(n) A) peril B) subjective risk C) physical hazard D) indirect loss Answer: C 44) Jim and Paula Franklin started a dry cleaning business. The business may be successful or it may fail. The type of risk that is present when either a profit or loss could occur is called A) pure risk B) subjective risk. C) fundamental risk D) speculative risk. Answer: D 45) Ben is concerned that if he injures someone or damages someoneʹs property he could be held legally responsible and required to pay damages. This type of risk is called a EG Test Insurance.doc 5 A) speculative risk C) fundamental risk Answer: B B) liability risk D) property risk 46) MLX Drug Company would like to market a new hypertension drug. While the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was testing the drug, it discovered that the drug produced a harmful side effect. When MLX learned of the FDAʹs test result, MLX abandoned its plan to produce and distribute the drug. MLXʹs reaction illustrates A) risk avoidance B) hedging C) risk transfer D) risk retention Answer: A 47) ABC Health Insurance Company sells health insurance in one state. Recently, that stateʹs legislature passed a law forbidding health insurers from considering an individualʹs health history when selecting applicants to insure. This change in law will increase the possibility of unprofitable results for ABC. This type of hazard is an example of A) physical hazard B) legal hazard C) moral hazard D) morale hazard Answer: B 48) All of the following are characteristics of the liability risk that most people face EXCEPT A) a lien may be placed on your income and assets to satisfy a legal judgment. B) substantial legal expenses may be incurred defending the claim. C) there is no upper limit on the amount of the loss. D) owning liability insurance eliminates the possibility of being held legally liable. Answer: D 49) Which of the following statements about chance of loss and risk is (are) true? I. If the chance of loss is identical for two groups, the objective risk must be the same. II. Two individuals may perceive differently the risk inherent in a given activity. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B Chapter 2 - Insurance and Risk 1) All of the following are characteristics of insurance EXCEPT A) risk avoidance B) pooling of losses C) payment of fortuitous losses D) indemnification Answer: A 2) Which of the following is implied by the pooling of losses? A) sharing of losses by an entire group B) inability to predict losses with any degree of accuracy C) substitution of actual loss for average loss D) increase of objective risk Answer: A 3) According to the law of large numbers, what happens as the number of exposure units increases? A) Actual results will increasingly differ from probable results B) Actual results will more closely approach probable results C) Fundamental risk will decrease D) Objective risk will increase Answer: B 4) According to the law of large numbers, what should happen as an insurer increases the number of units insured? A) The amount the insurer expects to pay in claims should decrease EG Test Insurance.doc 6 B) Underwriting expenses should decrease C) Actual results will more closely approach expected results D) The insurerʹs profitability should become more variable Answer: C 5) Characteristics of a fortuitous loss include which of the following? I. The loss is certain to occur. II. The loss occurs as a result of chance. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 6) From the viewpoint of the insurer, all of the following are characteristics of an insurable risk EXCEPT A) The loss must be accidental B) The loss should be catastrophic C) The premium must be economically feasible D) There must be a large number of exposure units Answer: B 7) From the standpoint of the insurer, all of the following are characteristics of an insurable risk EXCEPT A) The loss must be unintentional B) The chance of loss must be calculable. C) The loss must be indeterminable D) The loss must be measurable. Answer: C 8) Why is a large number of exposure units generally required before a pure risk is insurable? A) It prevents the insurer from losing money B) It eliminates intentional losses. C) It minimizes moral hazard D) It enables the insurer to predict losses more accurately. Answer: D 9) The requirement that losses should be accidental and unintentional in order to be insurable results in which of the following? I. Decrease in moral hazard II. More accurate prediction of future losses A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 10) Which of the following is implied by the requirement that a loss should be determinable and measurable to be insurable? I. The loss must be definite as to place. II. The loss must be definite as to amount. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 11) Methods by which insurers may minimize or avoid catastrophic losses include which of the following? I. The use of reinsurance. II. Concentrating coverage written in one geographic region A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 12) Which of the following types of risks best meets the requirements for being insurable by private insurers? A) market risks B) property risks C) financial risks D) political risks Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 7 13) Reasons why market, financial, and production risks are often uninsurable include which of the following? I. The potential to produce a catastrophic loss is great. II. The chance of loss cannot be accurately estimated. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 14) Which of the following types of risks is normally uninsurable by private insurers? A) personal risks B) property risks C) liability risks D) market risks Answer: D 15) Which of the following is a result of adverse selection? A) The insurerʹs financial results will be substantially improved. B) Persons most likely to have losses are also most likely to seek insurance at standard rates. C) It is unnecessary for the insurance company to use underwriting. D) Insurance can be written only by the federal government. Answer: B 16) The tendency for unhealthy people to seek life or health insurance at standard rates is an example of A) moral hazard B) fundamental risk. C) morale hazard D) adverse selection. Answer: D 17) Which of the following statements regarding insurance and gambling is (are) true? I. Insurance is used to handle existing pure risks, while gambling creates a new speculative risk. II. Insurance usually involves risk avoidance, while gambling typically involves only risk reduction. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 18) In addition to marketing life insurance, life insurers typically sell which of the following products? I. Retirement annuities II. Disability income insurance A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 19) Inland marine insurance provides coverage for A) goods being shipped on land B) premature death of members of the armed forces C) goods being shipped on ocean-going vessels. D) liability exposures of nonprofit organizations. Answer: A 20) All of the following are classified as casualty insurance EXCEPT A) life insurance B) general liability insurance. C) workers compensation insurance D) burglary and theft insurance. Answer: A 21) Which of the following is a form of casualty insurance? A) fire insurance B) general liability insurance C) inland marine insurance D) ocean marine insurance Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 8 22) The term ʺmultiple-line insuranceʺ is used to describe a type of insurance that combines which of the following coverages into a single contract? A) workers compensation and health insurance B) life and disability insurance C) property and casualty insurance D) pensions and annuities Answer: C 23) All of the following are benefits to society that result from insurance EXCEPT A) less worry and fear B) elimination of moral hazard C) indemnification for loss D) loss prevention Answer: B 24) Which of the following statements about the insurance industry as a source of investment funds is (are) true? I. These funds result in a lower cost of capital than would exist in the absence of insurance. II. These funds tend to promote economic growth and full employment. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 25) All of the following are social costs associated with insurance EXCEPT A) insurance company operating expenses B) fraudulent claims. C) inflated claims D) increased cost of capital. Answer: D 26) A group of farmers agreed that if any farmer suffered a property loss, the loss would be spread over the entire group. In this way, each farmer is responsible for the average loss of the group rather than the actual loss that the farmer sustained. Which characteristic of insurance is embodied in this agreement? A) pooling of losses B) fortuitous losses C) risk avoidance D) indemnification Answer: A 27) XYZ Insurance Company writes coverage for most perils which can damage property. XYZ, however, does not write flood insurance on property located in flood plains. Which requirement of an insurable risk might be violated if XYZ wrote flood insurance on property located in flood plains? A) There must be a large number of similar exposure units. B) The loss should not be catastrophic. C) The chance of loss must be calculable. D) The losses must be determinable and measurable. Answer: B 28) ABC Appliance offers a warranty requiring an annual fee. The warranty may be purchased at the time of sale or at any time within the first year after the appliance was purchased. The warranty fee after the date of purchase is twice the time-of-purchase fee. When asked why the fee was higher after the date of purchase, ABCʹs president said, ʺBuying a warranty is voluntary. Weʹve noted that those who buy the warranty after the purchase date have a greater need for service.ʺ Charging the same rate or a lower rate after the date of purchase would expose ABC to what problem that also impacts private insurers? A) excessive premiums B) reduced claims C) bad investments D) adverse selection Answer: D 29) Alpha Insurance Company insures a broad range of risks, including whatever is not covered by fire, marine, and life insurers. Which term best describes the wide range of risks written by Alpha Insurance? A) fidelity insurance B) casualty insurance C) social insurance D) property insurance Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 9 30) LMN Insurance markets homeowners insurance. The LMN homeowners policy combines property and casualty insurance in the same contract. Insurance policies combining property and casualty coverage in the same contract are called A) mono-line policies B) multi-year policies C) multiple-line policies D) manuscript policies Answer: C 31) One branch of government insurance programs has a number of distinguishing characteristics.These programs are compulsory, they are financed by mandatory contributions rather than general tax revenues, and benefits are weighted in favor of low-income groups. These government insurance programs are called A) welfare programs B) social insurance programs. C) casualty insurance programs D) private insurance programs. Answer: B 32) Gina would like to buy a house. She will pay 10 percent of the cost of the house as a down payment and borrow the other 90 percent from a mortgage lender. The home will serve as collateral for the loan. The lender requires Gina to purchase property insurance on the home so that the collateral supporting the loan will be protected. This scenario illustrates which of the following benefits of insurance to society? A) enhancement of credit B) reduction of fear and worry C) source of investment funds D) incentives for loss prevention Answer: A 33) ABC Insurance Company calculated the amount that it expected to pay in claims under each policy sold. Rather than selling the insurance for the amount it expected to pay in claims, ABC added an allowance to cover the cost of doing business, including commissions, taxes, and acquisition expenses. This allowance is called a(n) A) policyowner dividend B) premium C) expense loading D) rate credit Answer: C 34) JKL Insurance Company estimates that 14 out of every 100 homeowners it insures will file a claim each year. Last year, JKL insured 200 homeowners. According to the law of large numbers, what should happen if JKL insures 2,000 homeowners this year? A) The total number of claims filed by JKL policyowners should decrease. B) The total dollar value of claims will decrease. C) The average size of loss will decline in value. D) The actual results will more closely approach the expected results. Answer: D 35) Apex Insurance Company wrote a large number of property insurance policies in an area where earthquake losses could occur. When the president of Apex was asked if she feared that a severe earthquake might put the company out of business, she responded, ʺNot a chance. We transferred most of that risk to other insurance companies.ʺ An arrangement by which an insurer that initially writes insurance transfers to another insurer part or all of the potential losses associated with such insurance is called A) hedging B) speculating C) reinsurance D) loss avoidance Answer: C 36) Bronson Company manufactures tools that it sells to wholesalers. Bronson is concerned that it may be unable to collect money the company is owed by the wholesalers. To address this risk, Bronson Company could purchase A) a fidelity bond B) general liability insurance C) allied lines insurance D) credit insurance Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 10 37) Which of the following statements regarding insurance and hedging is (are) true? I. Insurance involves the transfer of insurable risk while hedging handles risk that is typically uninsurable. II. Both insurance and hedging rely on the law of large numbers to reduce risk. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 38) Ashley opened an all-you-can-eat buffet restaurant. The cost per-person was based upon what Ashley believed an average restaurant patron would consume. The restaurant began to lose money. Ashley concluded that her patrons had „above average” appetites, and were attracted to her restaurant because they could eat as much as they wanted while being charged an average price. A similar phenomenon exists in insurance markets. This problem is called A) moral hazard B) adverse selection C) morale hazard D) fundamental risk Answer: B 39) Which of the following statements is (are) true concerning private insurance? I. Social insurance programs are private insurance programs. II. Both individuals and businesses purchase private insurance. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B Chapter 5 - Types of Insurers and Marketing Systems 1) Which of the following statements about stock insurers is true? A) They issue assessable policies. B) They are not permitted to write property and liability insurance. C) Stockholders bear any losses and share in any profits. D) They are owned by their policyowners. Answer: C 2) Which of the following statements about mutual insurers is true? A) They are legally organized as partnerships. B) They have a board of directors which is selected by state insurance departments. C) They are owned by their stockholders. D) They may pay dividends to their policyowners. Answer: D 3) Why are some mutual insurers referred to as ʺassessment mutualsʺ? A) They charge low premiums because the loss exposures of their insureds are thoroughly assessed before a policy is written. B) They are noted for being very thorough in their assessment of investment opportunities. C) They are assessed for state premium taxes only if they make a profit. D) They can assess policyowners if premiums are insufficient to pay losses and expenses. Answer: D 4) The corporate structure of mutual insurers is changing rapidly. All of the following are current trends EXCEPT A) Demutualization of some insurers. B) Sharp increase in the number of mutual insurance companies. C) Increase in company mergers. D) Formation of mutual holding companies. Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 11 5) All of the following statements about fraternal insurers are true EXCEPT A) They are a form of mutual insurer. B) They specialize in writing property and liability insurance. C) They enjoy tax advantages because of their nonprofit or charitable status. D) They market their coverage to members of a social organization or religious group. Answer: B 6) Which of the following statements about a reciprocal exchange is (are) true? I. It usually specializes in health insurance. II. It is an unincorporated mutual insurance company. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 7) Which of the following statements about Lloydʹs of London is true? A) Coverage is actually written by syndicates who belong to Lloydʹs of London. B) Its underwriters specialize in writing life and health insurance. C) It operates as an admitted insurer throughout the United States. D) It allows underwriters to write coverage without meeting stringent financial requirements. Answer: A 8) Temporary evidence of insurance until a policy is actually issued is provided by a(n) A) binder B) brokerage agreement. C) pre-approval form D) endorsement. Answer: A 9) Which of the following statements about brokers is (are) true? I. They legally represent the insured rather than the insurance company. II. They are prohibited from being licensed as agents. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 10) Neil needs insurance that is unavailable in the state where he lives. To obtain insurance from a nonadmitted insurer, Neil should contact a A) surplus lines broker B) nonadmitted agent. C) general agency broker D) direct writer. Answer: A 11) All of the following statements about the general agency system used for selling life insurance are true EXCEPT A) A general agent is responsible for hiring, training, and motivating new agents. B) A general agent is a salaried employee whose responsibilities are limited to selling life insurance. C) A general agent may receive an allowance for the expenses of maintaining an agency office. D) A general agent receives a commission based on the amount of business produced. Answer: B 12) Which of the following statements about the managerial system of marketing life insurance is (are) true? I. It uses branch offices run by independent agents who represent several companies. II. The branch manager is an employee of the insurer who has the responsibility for hiring and training new agents. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 12 13) Advantages of the direct response system for marketing life insurance include which of the following? I. Advertising can be specifically directed to selected markets. II. Complex products can be easily sold. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 14) Which of the following statements about the exclusive agency system for marketing property and liability insurance is true? A) Exclusive agents typically have complete ownership of policy expirations. B) A higher commission rate is usually paid on exclusive agentsʹ renewal business than on new business. C) Exclusive agents represent several different insurance companies. D) New exclusive agents usually start as employees and after a training period become independent contractors. Answer: D 15) All of the following statements about the independent agency system are true EXCEPT A) Agents are often authorized to adjust small claims. B) Agents are compensated on the basis of commissions. C) The insurer rather than the agent owns the renewal rights to the business. D) The agent is an independent business person who represents several insurers. Answer: C 16) The salespersons of a direct writer are considered to be A) independent agents B) independent contractors C) employees D) brokers Answer: C 17) Which of the following statements about the sale of property and liability insurance through the direct response system is (are) true? I. Selling expenses are higher because market segmentation tends to be less precise than with other marketing methods. II. It is the most appropriate system for selling complex products. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 18) Under one life insurance marketing system, an insurer sells its products through established agents who are already engaged in life insurance sales. Under this system, an insurer enters into contracts with successful agents who agree to sell the insurerʹs products. This life insurance marketing system is called the A) direct response system B) nonbuilding agency system C) independent agency system D) agency building system Answer: B 19) Which of the following is characteristic of a typical mass merchandising plan? A) higher commission scales for agents and higher administrative expenses B) premiums may be paid through payroll deduction C) group rather than individual underwriting D) employer contributions to the cost of coverage Answer: B 20) David has always been successful in sales. Recently, he was approached by a life insurer interested in hiring him. Initially, David was not interested in the job because he feared it would require a lot of EG Test Insurance.doc 13 administrative work. ʺYouʹre a super salesperson, David,ʺ he was told, ʺWeʹre hiring you to do one thing and one thing only SELL!ʺ David accepted the position. David is a(n) A) exclusive independent agent B) personal-producing general agent C) branch office agent/manager D) direct writing exclusive agent Answer: B 21) Sarah owns a property and liability insurance agency. She is authorized to represent several insurance companies and is compensated by commissions. Sarahʹs agency owns the expiration rights to the business she sells. Sarah is a(n) A) independent agent B) exclusive agent C) direct writer D) insurance broker Answer: A 22) The leaders of a religious group decided to start a life insurance organization to insure members of the religious group. The insurer will operate as a nonprofit organization, thus receiving favorable tax treatment. The insurer formed will be a A) health maintenance organization B) stock insurer. C) fraternal insurer D) reciprocal exchange. Answer: C 23) Scott works in property and liability insurance marketing. He legally represents insurance purchasers, rather than insurance companies. Scott is paid a commission on the insurance placed with insurers. Scott is a(n) A) exclusive agent B) direct writer. C) branch manager D) insurance broker. Answer: D 24) ABC Insurance has always used the exclusive agency system to market coverages. ABC, however, cannot afford full-time agents in sparsely-populated areas. To reach customers in these areas, ABC enters into agreements with local independent agents. Using more than one marketing system is called employing a A) direct response system B) general agency system. C) multiple distribution system D) branch office system. Answer: C 25) Cathy just started a job with XYZ Manufacturing Company. She attended an orientation and was given a packet providing information about the various employee benefits XYZ offers. One item in the packet was a booklet and application form from an auto insurer. The insurer offers lower premiums to XYZ employees. The insurerʹs plan for selling individually-underwritten auto insurance to employees of XYZ Manufacturing Company is called A) direct response B) mass merchandising. C) personal selling D) multiple marketing. Answer: B 26) Brian is a life insurance agent. He is licensed to represent one company and has been assigned a territory. In addition to marketing life insurance products in the territory, Brian is also responsible for recruiting, training, and motivating new agents for the company in his territory. Brian is a(n) A) exclusive agent B) general agent. C) insurance broker D) personal-producing general agent. Answer: B 27) Big Mutual Insurance Company would like to take advantage of financial services deregulation by acquiring a bank and a stock brokerage firm. Big Mutual, however, would have trouble raising the funds needed to make these acquisitions under the mutual form of organization. Big Mutual is planning to switch from the mutual form of organization to the stock form, and to issue shares of common stock to raise capital. This change in organizational structure is called EG Test Insurance.doc 14 A) mutualization C) reinsurance Answer: D B) retrocession. D) demutualization. 28) Jim would like to start a business raising thoroughbred racehorses. The business would be the first of its kind in the state where he lives. Obtaining insurance on the horses is a key concern, and he was dismayed to learn that none of the insurers authorized to operate in his state offer this specialty insurance. What is the name of the intermediary which Jack can use to place this coverage with an insurer not admitted to his state? A) alien insurer B) general agent C) surplus lines broker D) direct writer Answer: C 29) Some investors decided to start an insurance company. Each investor contributed $50,000 to raise the capital required to charter a new company. Each investor received an ownership interest in the company. The company will raise additional capital by selling ownership rights to other investors. Under this type of organization, the customer and owner functions are separate. This type of insurer is called a A) stock company B) reciprocal exchange C) fraternal company D) mutual company Answer: A 30) RST Insurance is an interesting company. It doesnʹt have any agents. Instead, the company sells insurance through radio ads, telemarketers, and newspaper and magazine inserts. This distribution method is called A) reciprocal exchange B) direct response system C) mass merchandising D) multiple distribution system Answer: B 31) One type of insurer is a community-oriented health insurer. In most states, this insurer is set-up as a non-profit organization that provides coverage for hospital services, physiciansʹ and surgeonsʹ fees, and other medical services. This type of insurer is called a A) stock insurer B) captive insurer. C) health maintenance organization (HMO) D) Blue Cross/Blue Shield Plan. Answer: D 32) Which of the following statements is (are) true with respect to the financial services industry? I. The number of firms operating in the industry continues to increase at a high rate. II. The Financial Modernization Act of 1999 permits financial institutions to compete in other financial markets outside their core business area. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 33) The financial services field is currently experiencing consolidation and convergence. If both of these trends continue, in the future we should observe A) fewer financial institutions offering a narrower range of financial services products. B) fewer financial institutions offering a wider range of financial services products. C) more financial institutions offering a narrower range of financial services products. D) more financial institutions offering a wider range of financial services products. Answer: B 34) All of the following are reasons why mutual insurance companies convert to stock insurance companies EXCEPT A) Stock companies can offer stock options to attract and retain key personnel. B) Stock companies can raise new capital more easily. C) Stock companies are exempt from state insurance regulation. EG Test Insurance.doc 15 D) Stock companies offer greater flexibility to expand through acquisitions. Answer: C 35) The demutualization process is expensive and time consuming. As an alternative to demutualization, many states have enacted legislation allowing a mutual company to reorganize as a company that directly or indirectly controls another insurer. The other insurer is a stock company that can issue additional shares of stock to raise capital. The reorganized company is called a A) captive insurance company B) conglomerate C) mutual holding company D) stock holding company Answer: C 36) R.I.P. Company manufactures herbicide and pesticide. The company had difficulty finding affordable liability insurance. R.I.P. established its own insurance company based in Bermuda for the purpose of insuring R.I.P.ʹs loss exposures. The company that R.I.P. formed is called a A) captive insurer B) reciprocal insurer C) fraternal insurer D) holding company Answer: A 37) Which of the following statements is (are) true about savings bank life insurance (SBLI)? I. SBLI is available in every state in the United States. II. The goal of SBLI is to provide low-cost life insurance to consumers. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B Chapter6 - Insurance Company Operations 1) The function of an actuary is to A) adjust claims C) negotiate reinsurance treaties Answer: B B) determine premium rates D) invest insurance company assets 2) Insurers obtain data which can be used to determine rates from A) pricing pools B) insurance advisory organizations C) banks D) reciprocal exchanges. Answer: B 3) Which of the following statements about underwriting policy is (are) true? I. A company must establish an underwriting policy consistent with company objectives. II. Underwriting policy is usually subjective and allows the underwriter considerable flexibility with respect to lines written and forms used. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 4) All of the following statements about underwriting standards are true EXCEPT A) The purpose of underwriting standards is to reduce adverse selection against the insurer. B) The underwriter should select only those insureds who are expected to have no losses. C) The underwriter should select a book of business so that there is a proper balance within each rate classification. D) Equitable rates should be charged so that each group of policyowners pays its own way in terms of losses and expenses. Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 16 5) The underwriting process begins with the A) agent C) inspection report Answer: A B) desk underwriter. D) acceptance of the application. 6) Common sources of underwriting information for life and health insurance include all of the following EXCEPT A) the application B) a physical examination. C) the Medical Information Bureau D) the applicantʹs income tax return. Answer: D 7) If an underwriter suspects moral hazard, the underwriter may ask an outside firm to investigate the applicant and make a detailed report to the insurer. This report is called a(n) A) inspection report B) application. C) M.I.B. report D) agentʹs report. Answer: A 8) One source of life and health insurance underwriting information is an organization that life and health insurance companies can join. As a member, life and health insurance companies report health impairments of applicants, and this information is shared with member companies. Although the information is shared, the underwriting decision of the member company is not disclosed. What is this organization called? A) Fair Isaac Corporation (FICO) B) Medical Information Bureau (MIB) C) National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) D) National Association of Mutual Insurance Companies (NAMIC) Answer: B 9) Factors that may result in more restrictive underwriting decisions include which of the following? I. Inadequate rates; II. The unavailability of reinsurance at favorable terms. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 10) All of the following are functions of the marketing department of an insurance company EXCEPT A) to advertise the insurerʹs products B) to develop new products. C) to identify production goals D) to make final underwriting decisions. Answer: D 11) Which of the following statements about claim settlement is (are) true? I. The fair payment of claims requires an insurer to adopt a very liberal claims policy. II. To prevent lawsuits, an insurer should provide no personal assistance to a claimant other than that which is required by contractual obligations. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 12) All of the following statements about claims settlement are true EXCEPT A) Agents may have the authority to settle claims. B) Independent adjustors may be used in a geographic area where the volume of business is too low for an insurer to have its own adjustors. C) Company adjustors are salaried employees who work for one insurer. D) A public adjustor is usually paid a flat fee that is independent of the size of a claim. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 17 13) Which of the following statements about adjustment bureaus is (are) true? I. They are frequently used to settle claims when a large number of losses occur in a given geographic location as a result of a catastrophic event. II. Their major advantage is low cost because of the use of part-time adjustors. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 14) All of the following statements about the settlement of a claim are true EXCEPT A) The insurance policy usually has a provision specifying how a notice of loss is to be made to the insurance company. B) One step in the investigation of a claim is to determine whether the policy was in force when the loss occurred. C) The adjustor must file the proof of loss, which is a sworn statement supporting his or her decision regarding a claim. D) A policy provision may determine how disputes over claim settlements are resolved. Answer: C 15) All of the following statements about reinsurance are true EXCEPT A) A reinsurer may also purchase reinsurance. B) Reinsurance is an arrangement by which the primary insurer that initially writes the insurance transfers to another insurer part or all of the potential losses associated with such insurance. C) The insurer transferring business to a reinsurer is called the ceding insurer. D) The amount of insurance transferred to a reinsurer is called the net retention. Answer: D 16) All of the following are reasons for a primary insurer to use reinsurance EXCEPT A) to increase the unearned premium reserve B) to increase underwriting capacity. C) to protect against catastrophic losses D) to stabilize profits. Answer: A 17) The unearned premium reserve of an insurer is A) an asset representing the investments made with premium income. B) a liability representing the unearned portion of gross premiums on outstanding policies. C) a liability representing claims that have been filed, but not yet paid. D) the portion of the insurerʹs net worth belonging to policyowners. Answer: B 18) A reinsurance contract that is entered into on a case-by-case basis after an application for insurance is received by a primary insurer is called A) a reinsurance pool B) automatic treaty reinsurance. C) retrocession D) facultative reinsurance. Answer: D 19) Which of the following statements about treaty reinsurance is true? A) The reinsurer is required to underwrite each individual applicant that is reinsured. B) The reinsurer must accept all business that falls within the scope of the treaty. C) The ceding insurer can choose which business falling within the scope of the treaty it wishes to reinsure. D) It protects the reinsurer by requiring the ceding insurer to charge adequate premiums. Answer: B 20) Which of the following statements about treaty reinsurance is true? A) Under a surplus-share treaty, 100 percent of the ceding insurerʹs liability must be transferred to the reinsurer. B) Using a quota-share treaty increases the ceding insurerʹs unearned premium reserve. EG Test Insurance.doc 18 C) Under an excess-of-loss treaty, the reinsurer pays losses in full only if they are less than the ceding insurerʹs retention limit. D) Using a reinsurance pool provides financial capacity to write large amounts of insurance. Answer: D 21) Delta Insurance Company has a surplus-share treaty with Eversafe Reinsurance. Delta has a retention limit of $200,000, and nine lines of insurance are ceded to Eversafe. How much will Eversafe pay if a $1,600,000 building insured with Delta suffers an $800,000 loss? A) $600,000 B) $700,000 C) $720,000 D) $800,000 Answer: B 22) Huge Insurance Company is a property insurer that is interested in protecting itself against cumulative losses that exceed $200 million during the year. This protection can best be obtained using A) a quota-share reinsurance treaty B) a surplus-share reinsurance treaty. C) an excess-of-loss reinsurance treaty D) a reinsuance pool. Answer: C 23) All of the following statements about life insurance company investments are true EXCEPT A) Funds for these investments are derived primarily from premium income, investment earnings, and maturing investments that must be reinvested. B) Income from these investments reduces the cost of insurance. C) A primary objective in making these investments is safety of principal. D) The majority of these investments are short-term investments. Answer: D 24) Which of the following statements about the investments of property and liability insurers is (are) true? I. Income from investments is important in offsetting any unfavorable underwriting experience. II. Because premium income is continually being received, the investment objective of liquidity is of little importance. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 25) Functions of an insurance companyʹs legal department include which of the following? I. Lobbying for legislation favorable to the insurance industry. II. Drafting policy provisions. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 26) Jan is employed by an insurance company. She reviews applications to determine whether her company should insure the applicant. If insurable, Jan assigns the applicant to a rating category based on the applicantʹs degree of risk. Jan is a(n) A) underwriter B) actuary. C) loss control engineer D) claims adjustor. Answer: A 27) Mark has been an underwriter for 20 years. An application he recently reviewed looked odd to him. The building value in the application seemed far too high, and Mark suspected the applicant might be planning to destroy the property after it is insured. Mark contacted an outside firm and hired someone to investigate the applicant and to prepare a report about the applicant. This report is called a(n) A) agentʹs report B) binder. C) physical inspection D) inspection report. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 19 28) Antonio is a claims adjustor for LMN Insurance Company. After the insurer is notified that there has been a loss, Antonio meets with the insured. The first step in the claims process that Antonio should follow is to A) determine the amount of the loss. B) attempt to deny the claim regardless of whether he believes the claim is covered. C) verify that a covered loss has occurred. D) delay paying the claim if the claim is covered. Answer: C 29) Beverly lives in a sparsely populated area in northern Idaho. Some insurance companies marketing coverage in northern Idaho cannot afford to have full-time adjustors there. Several insurers hire Beverly to adjust claims for their insureds. Beverly charges the insurers a fee for each claim that she settles. Beverly is a(n) A) public adjustor B) adjustment bureau. C) independent adjustor D) company adjustor. Answer: C 30) New Liability Insurance Company began operations last year and has been very successful. The companyʹs ability to grow is being restricted by an accounting rule that requires insurers to realize acquisition expenses immediately, while not realizing premium income until some time has passed. Reinsurance is often used in such cases for which of the following purposes? A) to stabilize profitability B) to reduce the unearned premium reserve C) to provide protection against catastrophic losses D) to withdraw from a line of business or territory Answer: B 31) Liability Insurance Company (LIC) was approached by a regional airline to see if LIC would write the airlineʹs liability coverage. LIC agreed to write the coverage and entered into an agreement with a reinsurer. Under the agreement, LIC retains 25 percent of the premium and pays 25 percent of the losses, and the reinsurer receives 75 percent of the premium and pays 75 percent of the losses. This reinsurance arrangement is best described as A) excess-of-loss reinsurance B) surplus-share reinsurance. C) quota-share reinsurance D) pool reinsurance. Answer: C 32) Ross studied engineering in college. After graduation, he went to work for an insurance company. Ross visits properties insured by his company. He conducts inspections and makes recommendations about alarm systems, sprinkler systems, and building construction. In what functional area does Ross work? A) underwriting B) loss control C) electronic data processing D) claims adjusting Answer: B 33) Amy heads the legal staff of a large property and liability insurance company. Amyʹs staff is likely involved in all of the following activities EXCEPT A) reviewing policy wording before policies are adopted and marketed. B) recouping subrogation recoveries from third parties who injured individuals insured by Amyʹs company. C) providing legal advice about marketing, taxation, and insurance law. D) reviewing applications to determine if the company should insure the risk. Answer: D 34) Sue double-majored in mathematics and statistics in college. She also enrolled in a number of finance courses. After graduation, she was hired by Econodeath Insurance Company. Her job is to calculate premium rates for life insurance coverages. Sue is a(n) EG Test Insurance.doc 20 A) actuary C) claims adjustor Answer: A B) underwriter. D) producer. 35) Easy Pay Insurance Company may require insureds who suffer a loss to submit a sworn statement to substantiate that a loss occurred and to describe the conditions under which the loss occurred. This sworn statement is called a A) binder B) proof of loss. C) inspection report D) notice of loss. Answer: B 36) All of the following are methods that a property and liability insurance company can use to protect against catastrophic losses EXCEPT A) sale of catastrophe bonds B) purchase of common stock. C) purchase of excess-of-loss reinsurance D) quota share reinsurance with a low retention percentage. Answer: B 37) Which of the following statements is (are) true with respect to catastrophe bonds? I. The bonds are issued by the U.S. Government. II. The bonds pay relatively high interest rates. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 38) Underwriters try to have a proper balance within each risk classification. Much of personal lines underwriting today involves all exposures units with similar loss-producing characteristics being placed in the same category and charged the same rate. This type of underwriting is known as A) class underwriting B) merit underwriting C) line underwriting D) field underwriting Answer: A 39) Pac-Coast Insurance (PCI) concentrates its underwriting activities in California. The company is concerned that if a catastrophic earthquake occurs, it might threaten the solvency of the company. To address this risk, PCI issued some debt securities. If a catastrophic earthquake occurs, PCI does not have to repay the borrowed funds or pay interest. The securities PCI issued are called A) catastrophe futures contracts B) interest rate swaps C) catastrophe bonds D) contingent options contracts Answer: C 40) The process of transferring risk to the capital markets through the use of financial instruments such as bonds, futures contracts, and options is knows as A) consolidation of risk B) avoidance of risk. C) securitization of risk D) compartmentalization of risk. Answer: C 41) Which of the following statements is (are) true about life insurance company investments? I. The majority of life insurance company general account assets are invested in bonds. II. The majority of life insurance company separate account assets are invested in stocks. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 42) One method through which reinsurance is provided is through an organization of insurers that underwrites insurance on a joint basis. Through the organization, financial capacity is available for large commercial risks. This reinsurance arrangement is a(n) A) quota-share treaty B) surplus-share treaty. C) excess-of-loss treaty D) reinsurance pool. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 21 43) Most insurance companies require their marketing representatives to submit an evaluation of the prospective insured. This important source of underwriting information is called the A) application B) agentʹs report. C) inspection report D) physical inspection. Answer: B Chapter7 - Financial Operations of Insurers 1) LMN Mutual Insurance Company has total liabilities of $300 million. The company has total assets of $380 million. What is LMNʹs policyholdersʹ surplus? A) $680 million B) $340 million C) $80 million D) -$80 million Answer: C 2) All of the following would appear in the asset section of an insurance companyʹs balance sheet EXCEPT A) loss reserves B) bonds. C) common stock D) real estate. Answer: A 3) Under one method of estimating a loss reserve, the reserve is based on life expectancy, duration of disability, remarriage of the beneficiary, and similar factors. This method of estimating loss reserves is called the A) judgment method B) tabular value method. C) loss ratio method D) average value method. Answer: B 4) Reasons for the unearned premium reserve include which of the following? I. To pay losses that occur during the policy period. II. To pay premium refunds to policyholders in the event of cancellation. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 5) A property and casualty insurerʹs loss reserve includes estimates for all of the following EXCEPT A) claims anticipated but not yet incurred. B) claims reported and adjusted but not yet paid. C) claims reported and filed but not yet adjusted. D) claims incurred but not yet reported to the company. Answer: A 6) Which of the following statements about methods for estimating loss reserves for property and casualty insurers is (are) true? I. The judgment method involves the use of a statutory formula to estimate the loss reserve. II. The average value method is used when the number of claims is large and the claims are settled quickly. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 7) One item that appears on an insurance companyʹs financial statements is a liability that represents an estimate of the claims reported and adjusted but not yet paid, claims reported and filed but not yet adjusted, and claims incurred but not yet reported to the company. This liability is called the insurerʹs A) net income B) loss reserve. C) admitted assets D) unearned premium reserve. Answer: B 8) A loss reserve established for each individual claim when it is reported to a property and casualty insurance company is call a(n) A) admitted asset B) incurrred-but-not-reported (IBNR) reserve. C) unearned premium reserve D) case reserve. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 22 9) All of the following items would appear in the income section of an insurance companyʹs income and expense statement EXCEPT A) gain on sale of securities B) common stock dividends. C) commissions D) premiums. Answer: C 10) JKL Insurance Company reported the following information on its accounting statements last year: Premiums Written $90,000,000; Loss Adjustment Expenses $5,000,000; Underwriting Expenses $30,000,000; Premiums Earned $100,000,000; Incurred Losses $70,000,000. What was JKLʹs loss ratio last year? A) 70.0 percent B) 75.0 percent C) 83.3 percent D) 90.0 percent Answer: B 11) JKL Insurance Company reported the following information on its accounting statements last year: Premiums Written $90,000,000; Loss Adjustment Expenses $5,000,000; Underwriting Expenses $30,000,000; Premiums Earned $100,000,000; Incurred Losses $70,000,000. What was JKLʹs expense ratio last year? A) 5.0 percent B) 30.0 percent C) 33.3 percent D) 50.0 percent Answer: C 12) JKL Insurance Company reported the following information on its accounting statements last year: Premiums Written $90,000,000; Loss Adjustment Expenses $5,000,000; Underwriting Expenses $30,000,000; Premiums Earned $100,000,000; Incurred Losses $70,000,000. What was JKLʹs combined ratio last year? A) 100.0 B) 103.3 C) 105.0 D) 108.3 Answer: D 13) Which of the following statements about property and casualty insurance company operating results is (are) true? I. An insurance company can have a combined ratio greater than 1 (or 100 percent) and still be required to pay income taxes. II. By all measures, the property and casualty insurance industry is highly profitable when compared to other industries. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I not II Answer: A 14) Life insurance policyowners may borrow the cash value from their life insurance policies. Where are life insurance policy loans shown on a life insurance companyʹs financial statements? A) as an asset B) as a liability C) as income D) as an expense Answer: A 15) MedProf Insurance markets medical malpractice insurance. The companyʹs combined ratio in 2006 was 95.4. Its expense ratio was 25.4. What was the companyʹs loss ratio? A) 60.4 B) 70.0 C) 88.2 D) 120.8 Answer: B 16) To protect policyholders, state laws place limitations on a life insurance companyʹs investments. The assets backing interest-sensitive products, such as variable life insurance and variable annuities, are not subject to these restrictions. Assets backing interest-sensitive products are placed in a special account called the life insurerʹs A) policy reserve account B) asset valuation reserve account C) separate account D) policyholders surplus Answer: C 17) Which of the following statements is (are) true concerning investments of property and casualty insurers and life insurers? I. Property and casualty insurance companies place greater emphasis on liquidity than do life insurers. EG Test Insurance.doc 23 II. Life insurance company investments are, on average, of longer duration than property and casualty insurance company investments. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 18) All of the following are expenses of life insurance companies EXCEPT A) matured endowments B) surrender benefits. C) disability income payments D) realized capital gains. Answer: D 19) All of the following statements about business objectives in designing a rating system are true EXCEPT A) The rating system should encourage loss control activities. B) The rating system should be independent of long-run changes in economic conditions. C) The rating system should be simple to understand. D) The rating system should be stable over short periods so that consumer satisfaction can be maintained. Answer: B 20) All of the following statements about regulatory objectives of insurance rate making are true EXCEPT A) One purpose of rate adequacy is to maintain the solvency of insurers. B) Rates unfairly discriminate if loss exposures that are similar with respect to losses and expenses are charged substantially different rates. C) Insurers know in advance if the coverages marketed will be profitable, so rate regulation is not needed. D) Rates are excessive if policyholders are paying substantially more than the actual value of their protection. Answer: C 21) The unit of measurement used in property and casualty insurance pricing is called the A) unit rate B) premium C) exposure unit D) experience unit Answer: C 22) The portion of an insurance premium allocated to expenses, profit, and a margin for contingencies is called the A) loading B) pure premium. C) gross premium D) experience rate. Answer: A 23) Which of the following statements about judgment rating is true? A) It involves the manual rating of exposures. B) It is used when the loss exposures are so diverse that a class rate cannot be calculated. C) It is a form of experience rating. D) It is only used when credible loss statistics are available. Answer: B 24) Under one type of merit rating, the class or manual rate is adjusted upward or downward based on past loss history. This type of merit rating is called A) schedule rating B) judgment rating. C) experience rating D) retrospective rating. Answer: C 25) All of the following statements about class rating are true EXCEPT A) Exposures with similar characteristics are placed in the same underwriting class. B) The rate charged for each class reflects the average loss experience for that class. C) The complexity of class rating makes it inappropriate for personal lines coverages. D) It is based on the assumption that future losses to insureds will be determined by the same classification factors currently in use. Answer: C EG Test Insurance.doc 24 26) Under the pure premium method of determining class rates, the gross rate is determined by which of the following formulas? A) pure premium/(1 + expense ratio) B) pure premium/(1 - expense ratio) C) (1 + pure premium)/expense ratio D) expense ratio/(1 - pure premium) Answer: B 27) The expected loss ratio for a class of business is 60 percent. What change would be indicated in the level of rates under the loss ratio method if the actual loss ratio turned out to be 68 percent? A) 6.67 percent B) 13.33 percent C) 25.00 percent D) 33.33 percent Answer: B 28) Which of the following statements about schedule rating is (are) true? I. It involves the determination of a basis rate for each exposure, which is then modified by credits or debits. II. It is based on the assumption that certain physical characteristics of the insuredʹs operations will influence the insuredʹs future loss experience. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 29) Which of the following statements about experience rating is (are) true? I. The insuredʹs past loss experience is used to determine the premium for the next policy period. II. Its use is generally limited to small firms whose actual experience lacks credibility. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 30) Which of the following statements about retrospective rating is true? A) The premium for the current period is determined by the loss experience for prior periods. B) The premium for the current period is determined by the loss experience during the current period. C) The premium for future periods is determined by the average loss experience for the current and previous periods. D) The premium for future periods is determined by the loss experience for the current period. Answer: B 31) Monopoly Insurance is the only company marketing a certain line of insurance in a state. After complaints from several consumers, the State Insurance Department investigated Monopolyʹs rates. The regulators determined that Monopoly was taking advantage of being the only insurer offering the line by charging more than double the actuarial cost of the coverage. Which regulatory rating objective was Monopoly violating? A) Rates must be adequate B) Rates should encourage loss control. C) Rates must not be excessive D) Rates must not unfairly discriminate. Answer: C 32) Small Town used to be just that a small town 6 miles from Large City. Over the years, the area between Small Town and Large City was developed, and now Small Town is part of the suburbs surrounding Large City. An auto insurer that operated in the area had a large increase in auto claims from Small Town insureds. The insurer did not adjust its rates, and this year will lose money because of claims attributable to higher population density. Which business rating objective did this insurer fail to meet? A) simplicity B) stability C) responsiveness D) encouragement of loss control Answer: C 33) Nathan was hired as an actuary with ABC Insurance. Nathan was asked to calculate the annual premium for a new product and to explain his calculations to ABCʹs director of ratemaking. Nathan calculated the pure premium and presented this value as the final premium. After Nathanʹs presentation, EG Test Insurance.doc 25 the director of ratemaking said, ʺYou left out something very important. If we sell coverage at the pure premium rate, weʹll be out of business soon.ʺ What did Nathan overlook in his calculations? A) loadings B) the underwriting cycle C) seasonality of claims D) investment income Answer: A 34) XYZ Insurance Company expects $500,000 in claims and loss adjustment expenses for each 1,000 properties that it insures in a certain category of business insurance. What pure premium should XYZ charge for each property insured? A) $69.99 B) $166.67 C) $350.00 D) $500.00 Answer: D 35) XYZ Insurance Company uses class rating to determine the rate to charge for insurance. For one type of insurance, the pure premium XYZ actuaries calculated is $75 per unit. If XYZʹs expense ratio is 25 percent, what is the gross rate for this coverage? A) $37.50 B) $55.25 C) $75.00 D) $100.00 Answer: D 36) RST is a manufacturer. The company does not have a good safety record and pays high workers compensation premiums. RST just hired a new risk manager, and she has instituted several employee safety programs. She has also persuaded the insurer writing RSTʹs workers compensation insurance to base the premium on RSTʹs actual loss experience during the current period rather than on the companyʹs historical performance. This type of plan is called a(n) A) retrospectively rated plan B) class rated plan. C) experience rated plan D) judgment rated plan. Answer: A 37) An Econodeath Insurance Company actuary calculated the present value of the expected death claim the company will pay if it sells whole life insurance to a 30-year-old woman. This value is called the A) net level premium B) gross premium. C) net single premium D) life insurance policy reserve. Answer: C 38) Metro City has six different zip codes. XYZ Insurance Company markets coverages in Metro City. Any applicant who lists one particular zip code is automatically quoted a premium that is three times the average premium for applicants from the other five zip codes. Which regulatory objective is not being met given XYZʹs premium structure? A) Rates must be adequate B) Rates must not unfairly discriminate. C) Rates must be responsive D) Rate must not be excessive. Answer: B 39) All of the following statements about the combined ratio are true EXCEPT A) It is equal to the loss ratio plus the expense ratio. B) A combined ratio greater than 1 (or 100 percent) means an underwriting loss has occurred. C) The combined ratio does not consider investment income. D) A combined ratio less than 1 (or 100 percent) indicates that an underwriting loss has occurred. Answer: D 40) In schedule rating, each building is individually evaluated based on several rating factors. One factor refers to the possibility that the building will be damaged or destroyed by a fire that starts at an adjacent property and spreads to the building. This rating factor is known as A) occupancy B) protection. C) maintenance D) exposure. Answer: D 41) A strip-mall includes eight identical-sized retail units. All of the units were built at the same time and each has an identical sprinkler system. Unit number two is a dry cleaning business. Unit number three is a bar and grill. Unit number four is a dress shop. The owners of these three units are all insured by the same EG Test Insurance.doc 26 insurance company, but the property insurance premiums vary significantly. Which of the following rating factors best explains the difference in premiums? A) exposure B) protection C) construction D) occupancy Answer: D Chapter11 - Life Insurance 1) Which of the following types of families is likely to have the least need for a large amount of life insurance? A) a blended family B) a traditional family C) a single person family D) a sandwiched family Answer: C 2) The human life value is defined as the A) present value of a deceased breadwinnerʹs future gross income. B) future value of a deceased breadwinnerʹs past earnings. C) present value of the familyʹs share of a deceased breadwinnerʹs future earnings. D) future value of the familyʹs share of a deceased breadwinnerʹs future earnings. Answer: C 3) All of the following information is needed to calculate a personʹs human life value EXCEPT A) the personʹs average annual earnings over his or her productive lifetime. B) the personʹs estimated annual Social Security benefits after retirement. C) the personʹs cost of self-maintenance. D) the number of years from the personʹs present age to the expected retirement age. Answer: B 4) To calculate a human life value, it is necessary to deduct certain costs from a personʹs average annual earnings. These costs include A) funeral costs B) income taxes. C) investment income D) pension benefits after retirement. Answer: B 5) All of the following are defects which limit the usefulness of the human life value approach in determining the correct amount of life insurance to purchase EXCEPT A) The effects of inflation are ignored. B) Other sources of income for survivors are ignored. C) Earnings are assumed to remain constant. D) Earnings during the individualʹs productive lifetime are ignored. Answer: D 6) Which of the following statements about the needs approach for estimating the amount of life insurance to purchase is (are) true? I. It involves an analysis of various family needs which must be met if a family breadwinner dies. II. Its use is appropriate only if a person currently has no life insurance protection. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 7) The purpose of an estate clearance fund is to pay all of the following EXCEPT A) burial expenses B) estate administration expenses. C) education costs D) installment debts. Answer: C 8) What is the length of the readjustment period which is considered when the needs approach is used to determine the amount of life insurance to own? A) 3 to 6 months B) 1 to 2 years C) until the youngest child reaches age 18 D) until the surviving spouse reaches age 65 Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 27 9) Under the needs approach, when is the dependency period of a surviving spouse assumed to end? A) 1 or 2 years after the breadwinnerʹs death B) when the youngest child reaches age 18 C) when the surviving spouse reaches age 65 D) when the surviving spouse dies Answer: B 10) The period during which a surviving spouse is ineligible for Social Security benefits is referred to as the A) emergency period B) readjustment period. C) dependency period D) blackout period. Answer: D 11) Which of the following statements about the capital retention approach for determining life insurance needs is (are) true? I. It assumes that life insurance proceeds will be liquidated to provide income to survivors. II. It requires the preparation of a personal balance sheet. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 12) When the capital retention approach is used to determine how much life insurance to purchase, all of the following are subtracted from total assets to calculate capital available to produce income EXCEPT A) Social Security benefits B) the amount of any educational funds. C) final expenses D) the value of household property. Answer: A 13) Disadvantages of the capital retention approach include which of the following? I. Assets are often liquidated too quickly. II. It underestimates the amount of life insurance needed. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 14) Tom and Nancy Boyle provide financial support for their two children. In addition, they provide financial support for Tomʹs aged father and Nancyʹs aged mother. The Boyle family can be described as a A) blended family B) single-parent family. C) two-income earner family D) sandwiched family. Answer: D 15) Julian, age 45, would like to determine how much life insurance to purchase using the human life value approach. He assumes his average annual earnings over the next 20 years will be $40,000. Of this amount, $20,000 is available annually for the support of his family. Julian will generate this income for 20 more years and he believes that 5 percent is the appropriate interest (discount) rate. The present value of one dollar payable for 20 years at a discount rate of 5 percent is $12.46. What is Julianʹs human life value? A) $184,600 B) $249,200 C) $360,800 D) $400,000 Answer: B 16) Jessica is an agent for LMN Life Insurance Company. She met with Brad, who was interested in purchasing life insurance. Jessica explained the various uses of life insurance, including income for Bradʹs wife during the 1- or 2-year period following Bradʹs death. This period is known as the A) dependency period B) estate clearance period. C) blackout period D) readjustment period. Answer: D 17) Sarah is using the needs approach to determine how much life insurance to buy. Her cash needs are $30,000; her income needs are $140,000; and special needs are $100,000. Sarah has the following assets: $20,000 in bank accounts, $30,000 in retirement plans, and $40,000 in investment accounts. Sarah owns no individual life insurance. She is covered by a $50,000 group life insurance policy through her employer. Based on this information, how much additional life insurance should Sarah purchase? A) $80,000 B) $130,000 C) $150,000 D) $160,000 Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 28 18) Richard is using the capital retention approach to determine how much life insurance to purchase. Richard would like to provide $35,000 per year to his family, forever, if he dies. The assets that he has today will provide $25,000 in annual income without the liquidation of these assets. If life insurance proceeds can be invested to earn a 5 percent annual return, how much life insurance should Richard purchase to fund the additional income needed to meet the $35,000 annual income goal? A) $10,000 B) $100,000 C) $150,000 D) $200,000 Answer: D 19) Bill is attempting to determine how much life insurance to purchase. He has two dependent children and his wife does not work outside of the home. An advisor suggested that Bill should consider Social Security benefits when doing his life insurance planning. One concern in this regard is the period after Social Security benefits to a widow terminate until they resume again. This period is called the A) blackout period B) dependency period. C) emergency period D) readjustment period. Answer: A 20) When using the needs approach, several ʺspecial needsʺ should be considered. One special need is money to cover unexpected events, such as major car repairs, dental bills, or home repairs. Money set aside for this purpose is called a(n) A) estate clearance fund B) emergency fund. C) readjustment period fund D) mortgage redemption fund. Answer: B 21) Most family heads need substantial amounts of life insurance. However, with limited income, money spent on life insurance reduces the amount of discretionary income available for other high-priority needs. What an insured person gives up when he or she purchases life insurance instead of using the premium dollars for other purposes is called the A) true cost of life insurance B) net cost of life insurance. C) real (inflation-adjusted) cost of life insurance D) opportunity cost of buying life insurance. Answer: D 22) Which of the following statements about yearly renewable term insurance is (are) true? I. It requires evidence of insurability for renewal. II. It is most appropriate when an insured needs lifetime protection. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 23) What happens to the premiums for yearly renewable term insurance as an insured gets older? A) They increase at an increasing rate B) They increase at a decreasing rate. C) They decrease at a constant rate D) They remain level. Answer: A 24) All of the following statements about term insurance are true EXCEPT A) The insurance provides protection for a specified period of time. B) Most policies can be renewed for additional periods without evidence of insurability. C) Most policies can be converted to a permanent life insurance policy. D) Most policies have a cash value that is refunded when coverage ceases. Answer: D 25) All of the following statements about the conversion of a term policy are true EXCEPT A) Under an attained age conversion, the premium is based on the insuredʹs attained age at the time of conversion. B) Under an original age conversion, the policyowner must pay a financial adjustment in addition to the premium for the new policy. C) Most insurers require original age conversion to take place within a specified period (5 years, for example) of the issue of the term policy. D) Evidence of insurability is required before a conversion is permitted. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 29 26) Which of the following statements about a decreasing term insurance policy is true? A) The face amount of the policy decreases during the policy period, and the premium increases. B) The face amount of the policy decreases during the policy period, but the premium remains level. C) The premium decreases during the policy period, but the face amount remains constant. D) Both the premium and the face amount of the policy decrease gradually over the policy period. Answer: B 27) The purchase of term insurance is justified by which of the following circumstances? I. The insured wants to save money through the policy for a specific need. II. The insured has a temporary need for life insurance protection. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 28) A legal reserve in life insurance is a result of A) premium taxes payable by life insurance companies being postponed during the early policy years. B) dividends being paid to policyowners. C) inadequate premiums in the early policy years being subsidized by investment earnings. D) excess premiums in the early policy years being invested at compound interest. Answer: D 29) The net amount at risk for a life insurance policy is the difference between the A) present value of future benefits and the present value of future premiums. B) face amount of the policy and the total premiums that have been paid. C) face amount of the policy and the legal reserve. D) annual premium and the annual policyholder dividend. Answer: C 30) Which of the following statements about life insurance cash values is (are) true? I. Cash values are a result of the level premium method of purchasing life insurance. II. The cash value of a policy must always exceed the policyʹs legal reserve. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 31) All of the following statements about ordinary life insurance are true EXCEPT A) Premiums are level throughout the policy period. B) The face amount of the policy is paid if the insured lives to age 65. C) There is a build-up of cash value that can be borrowed by the policyholder. D) It offers the policyholder the flexibility to meet a wide variety of financial objectives. Answer: B 32) Which of the following statements about limited-payment life insurance is true? A) It is a form of term insurance. B) It matures at the end of the premium-payment period. C) The premium decreases each year during the premium-payment period. D) Its use may be appropriate if a person wants paid-up life insurance during retirement. Answer: D 33) Which of the following statements about endowment insurance policies is (are) true? I. The face amount is paid if the insured dies during the policy period or at the end of the policy period if the insured is still alive. II. The use of endowment insurance has increased in recent years because of its favorable tax treatment. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A EG Test Insurance.doc 30 34) All of the following statements about variable life insurance are true EXCEPT A) The premium is level and guaranteed not to increase. B) The death benefit varies according to investment experience. C) The policyowner has the option of investing the cash value in several investment accounts. D) Cash surrender values are subject to minimum guarantees. Answer: D 35) All of the following statements about universal life insurance are true EXCEPT A) Interest is credited to the policyʹs cash value each month. B) Any withdrawal of a policyʹs cash value reduces the amount of the death benefit. C) Interest credited to a policyʹs cash value is taxable for the policyowner in the year credited. D) The policyowner can add to a policyʹs cash value at any time subject to policy guidelines. Answer: C 36) Which of the following statements about universal life insurance is (are) true? I. The interest rate credited to the cash value at the time the policy is issued remains fixed for the life of the policy. II. A monthly deduction is made from the policyʹs cash value for the cost of insurance protection. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 37) All of the following statements describe the flexibility available to the owner of a universal life insurance policy EXCEPT A) Policy loans are permitted on an interest-free basis. B) The frequency of premium payments can be varied. C) The death benefit can be increased with evidence of insurability. D) Premium payments can be any amount provided there is sufficient cash value to keep the policy in force. Answer: A 38) Which of the following statements about a variable universal life insurance policy is (are) true? I. There is a minimum guaranteed interest rate for the cash value. II. The policyowner has a variety of investment options for the cash value. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 39) All of the following statements about current assumption whole life insurance are true EXCEPT A) It is a form of participating whole life insurance that pays annual dividends. B) An accumulation account is credited with an interest rate based on market conditions and company experience. C) Under the low-premium version, the premium is subject to change after an initial guaranteed period. D) Under the high-premium version, the premium may vanish after a period of time. Answer: A 40) Which of the following statements about an indeterminate-premium whole life insurance policy is (are) true? I. It permits the insurer to adjust premiums based on anticipated future experience. II. It allows policyholder dividends to be used to lower premiums. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 41) A whole life insurance policy in which premiums are reduced for an initial period (e.g. 3 years) and are higher thereafter is an example of a A) level-term policy B) modified life policy C) limited-payment whole life policy D) variable life policy Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 31 42) Which of the following statements about policies sold to preferred risks is (are) true? I. Preferred risks are people whose mortality experience (deaths per thousand at a given age) is expected to be lower than average. II. Insurers require preferred risks to purchase at least a minimum amount of life insurance, such as $100,000. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 43) Which of the following statements about second-to-die life insurance is (are) true? I. The insurance is a form of endowment coverage. II. The premium is lower than the combined cost of purchasing a life insurance policy on each insured. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 44) Which of the following statements about savings bank life insurance is true? A) The maximum amount that a depositor can purchase is $50,000. B) The maximum amount of insurance that a depositor can purchase is limited to the amount of money on deposit in his or her savings account with the savings bank. C) The objective of savings bank life insurance is to provide protection to the bank in case a borrower dies before a loan is repaid. D) The objective of savings bank life insurance is to provide low-cost insurance to consumers by holding down expenses. Answer: D 45) Which of the following statements about industrial life insurance (also called home service life insurance) policies is true? A) Most policies have a face value exceeding $100,000. B) Most industrial life insurance policies are cash value coverage. C) Industrial life insurance is group term insurance coverage marketed to employers. D) This popular product accounts for over 40 percent of the life insurance sold today. Answer: B 46) Michael wants to make sure that life insurance proceeds are available to pay his outstanding mortgage balance if he dies. He purchased a type of life insurance in which the amount of coverage gradually declines, just as his outstanding mortgage balance gradually declines. This type of life insurance is called A) modified life insurance B) decreasing term insurance. C) re-entry term insurance D) current assumption whole life. Answer: B 47) Carl would like to purchase life insurance. He would also like to invest in a mutual fund. An agent told Carl about a form of life insurance in which Carl could select where the saving component is invested. This form of life insurance has fixed premiums and the cash value is not guaranteed. This type of life insurance is called A) universal life insurance B) current assumption whole life. C) variable life insurance D) indeterminate-premium whole life. Answer: C 48) Tamara purchased a term insurance policy when she had high life insurance needs and limited income. Now Tamara can afford whole life insurance. What term life insurance provision will permit Tamara to switch her term insurance to whole life insurance without having to show that she is still insurable? A) renewal provision B) tax-free exchange provision C) conversion provision D) free look provision Answer: C 49) Alex, age 26, purchased a 20-payment whole life insurance policy. After Alex has made 20 premium payments, his life insurance policy is considered A) matured B) reduced. C) expired. D) paid-up. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 32 50) Ann is considering the purchase of a life insurance policy with these characteristics: flexible premium payments, the insurance and savings components are separate, the interest rate credited to the savings is tied to a market interest rate but a minimum rate is guaranteed, and a monthly administrative fee is charged. Ann is considering buying A) whole life insurance B) variable life insurance. C) universal life insurance D) current assumption whole life. Answer: C 51) Dave purchased a life insurance policy. The policy is nonparticipating and the cash values are based on the insurerʹs present mortality, investment, and expense experience. After 2 years, the insurer will recalculate the premium based on the mortality, investment, and expense experience at that time. Dave purchased A) current assumption whole life B) variable life insurance. C) universal life insurance D) variable universal life insurance. Answer: A 52) Which of the following $100,000 whole life insurance policies, issued by the same company to a man age 32, would require the highest first-year premium? A) continuous premium (ordinary) life B) whole life paid-up at 65 C) 10-payment whole life D) 20-payment whole life Answer: C 53) Which of the following statements about variable universal life insurance is (are) true? I Variable universal life insurance has fixed premium payments. II. Variable universal life insurance allows the policyowner to decide where the cash value is invested. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B Chapter 15 - Individual Health Insurance Coverages 1) Problems with the current health care system in the United States include which of the following? I. A large number of people are without health care coverage. II. The administrative costs of delivering health care are high. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 2) The basic benefits provided by individual hospital expense insurance coverage include which of the following? I. Daily hospital benefits II. Miscellaneous hospital expenses, such as X-rays and lab tests A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 3) Which of the following statements about hospital-surgical insurance plans is true? A) Most insurers use a schedule approach to determine reimbursement for surgical procedures. B) Most insurers pay a flat dollar amount per day spent in the hospital. C) Hospital insurance also covers X-rays, inpatient drugs, and lab tests. D) Outpatient care is excluded from coverage. Answer: C 4) Which of the following statements about a schedule of surgical operations found in a surgical expense insurance policy is true? A) Covered surgical procedures are listed, and the surgeon can charge the usual, reasonable, or customary fee for performing the covered procedures. B) It specifies the number of times that surgical procedures must be performed in order to be covered in full. C) It lists the maximum dollar amount that will be paid for each surgical procedure. D) It is a list of the surgical procedures that are excluded. Answer: C EG Test Insurance.doc 33 5) Which of the following statements about surgical expense policies that reimburse physicians on the basis of reasonable and customary charges is (are) true? I. To determine if a fee for a medical procedure is reasonable and customary, it is compared to what other physicians in the same area charge for the procedure. II. A schedule of surgical procedures and dollar amounts payable is included in the policy and all surgeons are paid the scheduled amount for the same procedure. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 6) Which of the following would be covered by the physiciansʹ visits benefit portion of a hospital-surgical insurance plan? A) cost of a minor surgical procedure performed in a doctorʹs office B) cost of a surgical procedure performed at a hospital C) outpatient lab tests and X-rays D) nonsurgical treatment provided by a doctor at a hospital Answer: D 7) Major medical insurance is characterized by which of the following? A) internal limits for all categories of expenses B) high maximum limits C) no exclusions D) no coinsurance Answer: B 8) The length of time major medical benefits will be paid after a deductible is satisfied is called a A) benefit period B) deductible runoff. C) coinsurance period D) stop limit. Answer: A 9) Which of the following statements about a common accident provision in a major medical insurance policy is true? A) It specifies the types of accidents that are covered without deductibles or coinsurance. B) It specifies the method for apportioning insurance coverage among two or more policies covering an accident. C) It specifies that only one deductible has to be satisfied if two or more family members are injured in the same accident. D) It provides disability income benefits if an insured is disabled from an accident that also results in medical expenses. Answer: C 10) Purposes of the coinsurance provision in major medical insurance policies include which of the following? I. To reduce premiums. II. To prevent overutilization of policy benefits. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 11) The effect of a stop-loss limit in a major medical insurance policy is to A) limit the lifetime benefits payable under the policy. B) put a cap on annual benefits that will be paid. C) prevent the insured from receiving duplicate benefits if medical expenses are also covered under workers compensation insurance. D) cover 100 percent of eligible medical expenses after an insured has incurred a specified amount of outof-pocket expenses. Answer: D 12) All the following are common exclusions in a major medical insurance policy EXCEPT A) routine dental care B) surgeonsʹ fees. C) expenses covered by workers compensation laws D) cost of eyeglasses. Answer: B 13) Which of the following statements about long-term care insurance is (are) true? I. It is no longer needed once a person is eligible for Medicare. EG Test Insurance.doc 34 II. Purchasers have a choice of daily benefits and benefit periods. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 14) Which of the following statements is (are) true concerning benefit payments under long-term care insurance? I. Reimbursement policies pay for actual charges up to a specified daily limit. II. Per diem policies pay a specified daily benefit regardless of the charges incurred. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 15) All of the following statements about long-term care insurance are true EXCEPT A) Premiums can be reduced by electing shorter elimination periods. B) A common benefits trigger is the inability to perform a certain number of activities of daily living. C) Protection against inflation is usually made available as an optional benefit. D) Policies currently sold are guaranteed renewable. Answer: A 16) Which of the following statements about disability is (are) true? I. The economic loss to a family from the breadwinnerʹs long-term total and permanent disability is less than the economic loss from the bread-winnerʹs premature death. II. The probability of a working individual, age 25, being disabled at least 3 months before age 65 is less than one percent. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 17) Which of the following statements about individual disability income policies is true? A) Benefits are typically paid only for disabilities resulting from sickness. B) Benefits paid for partial disabilities are usually greater than benefits paid by the same policy for total disabilities. C) Most policies pay a benefit equal to 100 percent of the disabled personʹs lost income. D) Newer policies often provide a residual disability benefit for persons who are able to work but at a reduced income. Answer: D 18) All of the following statements about individual disability income policies are true EXCEPT A) Premiums are often waived while a person is disabled but must be resumed if the insured recovers. B) At the time of purchase, the insured can choose the length of the benefit period from among several available options. C) In order to encourage rehabilitation, benefits may be continued during periods of vocational training. D) Most long-term disability policies contain an elimination period of 15 or fewer days. Answer: D 19) Which of the following statements about the dual definition of total disability typically found in many individual disability income policies is (are) true? I. During the initial period of disability, the insured must be unable to perform the duties of any gainful occupation. II. After the initial period of disability, the insured must be unable to perform the duties of any occupation for which he or she is reasonably fitted by education and training. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 20) Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding the calendar -year deductible used in most major medical policies? I. Once the deductible is satisfied, no additional deductible is payable during the calendar year. II. A carryover provision helps to avoid paying two deductibles in a short period of time. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C EG Test Insurance.doc 35 21) All of the following statements about optional disability income benefits are true EXCEPT A) Under a cost-of-living rider, benefits may be subject to limitations on the size of the annual or aggregate increases. B) A Social Security rider pays additional benefits if the insured is turned down for Social Security disability benefits. C) The election of a return of premium rider results in a lower premium. D) Under an option to purchase additional insurance, the premium for the additional coverage is based on the insuredʹs age at the time the additional coverage is purchased. Answer: C 22) Kevin has an individual major medical policy that his insurer agrees to keep in force until age 65. However, the company has the right to increase the premium each year for the underwriting class in which Kevin has been placed. Which renewal provision is found in Kevinʹs policy? A) noncancellable B) guaranteed renewable C) conditionally renewable D) nonrenewable for stated reasons only Answer: B 23) Which of the following statements about provisions in individual health insurance policies is true? A) If a policy is issued with a ʺguaranteed renewableʺ renewal provision, under no circumstances can the insurer raise the premium when the policy is renewed. B) After a policy is in force for 3 months, the time limit on certain defenses provision prohibits the insurance company from denying a claim based on a fraudulent misstatement in the application. C) The usual length of the grace period is 90 days. D) Under a preexisting conditions provision, a preexisting medical condition is either excluded or not covered until a policy has been in force for a specified period of time. Answer: D 24) Consumer experts generally recommend all of the following when shopping for individual health insurance EXCEPT A) Insure for the large loss B) Avoid limited policies. C) Consider individual insurance before group insurance. D) Use deductibles and elimination periods to reduce premiums. Answer: C 25) Which of the following statements about shopping for health insurance is (are) true? I. Always select the policy with the lowest premium. II. Consider group health insurance first. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 26) Greta purchased a long-term care policy. Gretaʹs eligibility for benefits under the policy will most likely be determined by A) how long premiums have been paid. B) inability to perform activities of daily living. C) continuous hospitalization for at least 60 days. D) eligibility for Medicare benefits. Answer: B 27) The inability of the insured to perform one or more important duties of his or her occupation is called A) sporadic disability B) total disability. C) recurrent disability D) partial disability. Answer: D 28) Ellen purchased an individual hospital-surgical policy. Under the renewal provision in the policy, the insurer has the right to terminate coverage on the policy anniversary date. This renewal provision is A) cancellable. B) optionally renewable. C) guaranteed renewable. D) noncancellable. Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 36 29) Marcus does not have any health insurance. All of the following are guidelines that Marcus should follow when shopping for individual health insurance EXCEPT A) Insure for the large (catastrophic) loss. B) Consider first-dollar coverage. C) Consider group health insurance first. D) Watch out for restrictive provisions and exclusions. Answer: B 30) Brad purchased a major medical insurance policy. All of the following are typical characteristics of major medical insurance EXCEPT A) first-dollar coverage. B) broad coverage. C) high maximum limits. D) coinsurance. Answer: A 31) Barb was injured in an auto accident. She was totally disabled and collected disability income benefits for 8 months. She would like to return to work on a part-time basis to see if her recovery is complete. During this period, her insurer will pay reduced disability income benefits. This type of disability is called A) recurrent disability. B) residual disability. C) permanent disability. D) partial disability. Answer: D 32) An individual health insurance policy provision excluding coverage for impairments that were present or were treated during some specified period prior to the effective date of the policy is called a(n) A) time limit on certain defenses. B) preexisting-conditions clause. C) benefit period provision. D) elimination (waiting) period. Answer: B 33) One long-term care insurance benefit trigger considers whether the insured needs supervision to protect against threats to health or safety due to memory loss or disorientation. This benefit trigger is referred to as a(n) A) activities of daily living trigger. B) medical necessity trigger. C) needs test trigger. D) severe cognitive impairment trigger. Answer: D 34) Bethʹs disability income insurance policy provides benefits for accidental death, dismemberment, and loss of sight. The maximum amount payable under this benefit is known as the A) face value. B) cash value. C) principal sum. D) monthly benefit. Answer: C 35) Jan needed health insurance. She met with an agent who described the provisions of a health insurance policy. Jan purchased the policy. When she got home, she reviewed the policy and noted several provisions were different from what the agent described. She was not satisfied with the policy and immediately sent it back to the agent with a note stating her reasons for returning the policy. Jan is guaranteed a premium refund because of which policy provision? A) waiting period B) time limit on certain defenses C) ten-day right to examine the policy D) waiver-of-premium provision Answer: C 36) One guideline when purchasing individual health insurance is to avoid limited policies. All of the following are examples of limited policies EXCEPT A) hospital indemnity policy. B) surgical policy using reasonable and customary charges. C) cancer policy. D) accident-only disability policy. Answer: B 37) Some physicians, hospitals, and other health care providers agree to make medical services available to insureds at discounted prices. Insureds are not required to use these entities, but if they do, care costs are less than if these entities are not used. Such health care entities are called A) preferred providers. B) high deductible health plans. C) Blue Cross/Blue Shield Plans. D) health savings accounts (HSAs). Answer: A 38) Which of the following statements about eligibility requirements for qualified Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) is (are) true? I. Only individuals who are eligible for Medicare benefits can establish a qualified HSA. EG Test Insurance.doc 37 II. You must be covered by a high deductible health plan and not be covered by any other comprehensive health plan to establish a qualified HSA. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 39) All of the following statements about the tax treatment of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are true EXCEPT A) Contributions to a qualified HSA are tax deductible. B) Distributions from a qualified HSA used to fund medical expenses are taxable. C) Investment income in a qualified HSA accumulates income tax free. D) Distributions from a qualified HSA prior to age 65 for nonmedical purposes are subject to a 10 percent penalty tax. Answer: B 40) Which of the following statements about high deductible health insurance plans is (are) true? I. Coverage under a high deductible health plan is necessary to establish a qualified health savings account (HSA). II. High deductible health plans provide a maximum limit on annual out-of-pocket expenses. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 41) Which of the following statements about health savings accounts (HSAs) is true? A) There are no limits to annual contributions that an individual may make to his or her HSA. B) Once an individual has reached age 65 or is covered by Medicare, no additional contributions to the HSA may be made. C) The health insurance plan covering the HSA account beneficiary is not permitted to use a deductible. D) HSAs offer no tax benefits for the account beneficiary. Answer: B Chapter 20 - Homeowners Insurance, Section I 1) Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding renters insurance? I. Renters insurance is needed if you rent a house, but is not needed if you rent an apartment. II. The ISO renterʹs policy provides ʺall-risksʺ coverage on the insuredʹs personal property. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 2) Which of the following statements about eligibility requirements for homeowners insurance is (are) true? I. A contract can be written on a six-unit apartment complex as long as the tenants are families. II. Separate forms are available for renters and condominium owners. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 3) All of the following statements about the Homeowners 6 (unit-owners form) policy are true EXCEPT A) It includes personal liability coverage. B) It covers personal property on an ʺall-risksʺ basis. C) It provides limited coverage for improvements and alterations. D) It provides limited coverage for loss assessments. Answer: B 4) Which homeowners policy is designed for the tenants of rented premises? A) Homeowners 2 B) Homeowners 4 C) Homeowners 6 D) Homeowners 8 Answer: B 5) Which of the following statements about the Homeowners 8 policy is (are) true? EG Test Insurance.doc 38 I. Losses to the dwelling are settled on a replacement cost basis if the dwelling is insured for its full market value. II. It is designed primarily for expensive, newer, dwellings. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 6) Which of the following statements about the Homeowners 3 policy is (are) true? I. Losses to the dwelling are always settled on an actual cash value basis. II. Coverage on personal property is limited to $5,000. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 7) The major difference between the Homeowners 2 policy and the Homeowners 3 policy is the A) insured perils for the dwelling. B) insured perils for personal property. C) type of liability coverage provided. D) amount of coverage for other structures. Answer: A 8) Persons insureds under Section I of the Homeowners 3 policy include which of the following? I. A spouse of the named insured if living in the same household II. The named insuredʹs children who are under age 24 and who are full-time college students A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 9) Section I of the Homeowners 3 policy provides coverage for all of the following EXCEPT A) loss of use. B) personal property. C) other structures. D) medical payments. Answer: D 10) All of the following are covered under the dwelling coverage (Coverage A) of the Homeowners 3 policy EXCEPT A) any structure attached to the dwelling. B) the land on which the insured dwelling is located. C) materials and supplies intended for alteration or repair of the dwelling. D) materials and supplies intended for construction of a detached garage. Answer: B 11) Which of the following statements about the coverage for other structures (Coverage B) under the Homeowners 3 policy is true? A) The amount of insurance on other structures is equal to a percentage of the coverage on the dwelling. B) Structures attached to the dwelling by a fence or utility line are considered to be part of the dwelling rather than other structures. C) Coverage applies even if the other structure is used for business purposes. D) There is coverage for a private garage only if it is rented to a tenant of the dwelling. Answer: A 12) All of the following losses are subject to special limits of liability under the Homeowners 3 policy EXCEPT the A) theft of firearms. B) destruction by fire of property used for business purposes. C) storm damage to a boat at a marina. D) destruction of jewelry by fire. Answer: D 13) Which of the following statements about the personal property coverage (Coverage C) of the Homeowners 3 policy is (are) true? I. The coverage applies only in the United States and Canada. II. The full amount of coverage applies only if the property is permanently located at any residence of the insured. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 39 14) The Homeowners 3 policy limits the amount of coverage provided on certain personal property (e.g. coin collections and silverware). This personal property can be adequately insured by A) lowering the deductible which applies to personal property losses. B) storing the property away from the home at another location. C) adding a schedule to the policy listing the property with specific amounts of insurance. D) adding an appraisal clause to the policy. Answer: C 15) Which of the following property is covered under the personal property coverage (Coverage C) of the Homeowners 3 policy? A) a pet iguana owned by the named insuredʹs spouse B) a bicycle owned by a foster child living with the named insured C) music CDs located in the named insuredʹs automobile D) a stamp collection insured under a separate policy Answer: B 16) All of the following statements about the coverage for loss of use (Coverage D) under the Homeowners 3 policy are true EXCEPT A) If a covered loss makes the home unfit for living, the insurer pays additional living expenses the insured may incur as a result of the loss. B) The duration of payments for additional living expenses is limited to a maximum of 15 days. C) There is coverage for the fair rental value of any part of the premises rented to others. D) There is coverage if civil authorities prohibit the insured from using the premises because of a loss to a neighboring premises from an insured peril. Answer: B 17) Which of the following statements about the additional coverages under Section I of the Homeowners 3 policy is true? A) There is coverage for the reasonable cost incurred to protect property from further damage after a covered loss occurs. B) There is unlimited coverage for furnishings of the landlord in an apartment on the premises that is rented to others. C) Property removed from the premises because it is endangered by an insured peril is covered on a named-perils basis while it is outside the insured premises. D) Damage caused by the settling of the insured structure is covered as a collapse. Answer: A 18) All of the following are additional coverages under Section I of the Homeowners 3 policy EXCEPT A) the reasonable expenses of removing debris of covered property after an insured loss. B) fire department service charges for which the insured is liable by contract or agreement. C) damage to trees and shrubs caused by a windstorm. D) losses incurred from the unauthorized use of a stolen credit card. Answer: C 19) All of the following are covered perils under the personal property coverage (Coverage C) of an unendorsed Homeowners 3 policy EXCEPT A) earthquake. B) theft. C) windstorm. D) explosion. Answer: A 20) Which of the following losses to a dwelling would be covered under an unendorsed Homeowners 3 policy? A) smoke damage resulting from agricultural operations of a neighboring farmer B) damage to the structure caused by a flash flood C) damage to the structure caused by the weight of heavy snow D) damage to a floor caused by water backing up through a sewer pipe Answer: C EG Test Insurance.doc 40 21) Which of the following statements about covered perils under the personal property coverage (Coverage C) of the Homeowners 3 policy is true? A) Theft losses to boats and watercraft are covered only if they occur at the insuredʹs residence. B) Damage from an explosion is covered only if the explosion is the result of fire or lightning. C) Property damage from vehicles is covered only if it is caused by the insured. D) Smoke damage is covered only if it arises from agricultural or industrial operations. Answer: A 22) Which of the following types of water damage is covered under an unendorsed Homeowners 3 policy? A) damage from flood B) damage from water backing up through a drain C) damage from water below the surface of the ground that seeps into a basement D) damage from water that overflows from a malfunctioning washing machine Answer: D 23) All of the following are general exclusions under Section I of the Homeowners 3 policy EXCEPT A) losses due to earthquake. B) losses due to the failure of the insured to use all reasonable means to save and preserve property after the time of a loss. C) losses resulting from a power failure caused by an insured peril on the residence premises. D) losses due to radiation from a nuclear power plant. Answer: C 24) Which of the following is (are) included among the duties of an insured following a loss covered under the Homeowners 3 policy? I. To file a proof of loss within a specified time period after the insurerʹs request. II. To prepare an inventory of damaged personal property. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 25) Which of the following statements about the replacement cost provision of the Homeowners 3 policy is true? A) It applies to personal property losses only. B) Except for small losses, the insured must repair or replace the damaged property in order to receive full replacement cost. C) The insured is required to carry an amount of insurance equal to 100 percent of the replacement value of the insured property. D) Loss settlements are equal to 50 percent of the value of the loss if the insured is carrying less than the required amount of insurance. Answer: B 26) David has a Homeowners 3 policy that provides $280,000 of insurance on his dwelling, which has a current replacement value of $400,000. Ignoring any deductible, how much will David collect if a kitchen with a replacement value of $24,000 but an actual cash value of $18,000 is destroyed in a fire? A) $18,000 B) $20,000 C) $21,000 D) $24,000 Answer: C 27) Which of the following statements about the appraisal clause in the Homeowners 3 policy is true? A) The appraiser for each party is selected by a judge. B) A binding settlement can be reached only if the umpire agrees with both appraisers. C) Both the insured and the insurer must agree that the appraisal process be used. D) Appraisal expenses are shared by the insured and the insurer. Answer: D 28) Under the Homeowners 3 policy, all of the following are options of the insurer for settling claims EXCEPT A) paying the claim in cash. B) replacing the property. C) repairing the property. D) paying the claim with insurance company stock. Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 41 29) All of the following are duties of the mortgagee under the standard mortgage clause EXCEPT A) to reimburse the insurer for any loss payments. B) to notify the insurer of any change in ownership of the property of which the mortgagee is aware. C) to provide a proof of loss form if the insured fails to do so. D) to pay the premium if the insured fails to do so. Answer: A 30) All of the following statements about the cancellation of a Homeowners 3 policy are true EXCEPT A) The insurer may cancel a new policy for any reason if it has been in force for less than 60 days and is not a renewal policy. B) At least 100 days notice of cancellation must be given if an insurer cancels a policy for nonpayment of premium. C) A policy written for longer than 1 year can be cancelled for any reason on the anniversary date by giving the insured at least 30 days notice of cancellation. D) After a policy has been in force for at least 60 days, it can be cancelled by the insurer if the risk has increased substantially since the policy was issued. Answer: B 31) All of the following statements about conditions under a homeowners policy are true EXCEPT A) If an insurer broadens coverage without an additional premium during the policy period, the broadened coverage applies immediately to the present policy. B) A waiver or change in any policy provision must be approved in writing by the insurer to be valid. C) The insurer must give written consent for an assignment of the policy to be valid. D) If the named insured dies, coverage automatically ceases with respect to any property of the deceased. Answer: D 32) Cal is renting an apartment. Which homeowners policy is specially designed to insure renters? A) HO-2 B) HO-3 C) HO-4 D) HO-6 Answer: C 33) Shauna purchased a condominium unit. Which homeowners policy is specially designed for condominium unit owners? A) HO-2 B) HO-3 C) HO-4 D) HO-6 Answer: D 34) Michelle had four matching end tables in her home. A fire damaged the home, destroying two of the end tables. Michelleʹs home was covered by an unendorsed Homeowners 3 policy. Which of the following is true with regard to the settlement for the end tables in this case? A) Loss to a pair or set is excluded under the policy. B) The insurer will pay the actual cash value of the loss. C) The insurer will pay the replacement cost of the loss. D) If a partial loss to a pair or set occurs, the insurer is liable for replacement of the entire pair or set. Answer: B 35) Bettyʹs personal property is insured for $100,000 under her Homeowners 3 policy. If she usually keeps some personal property at a mountain cabin that she owns, how much coverage for this property is available under her homeowners policy? A) $10,000 B) $20,000 C) $40,000 D) $50,000 Answer: A 36) Linda wants to purchase a homeowners policy, but she has some valuable personal property to which internal policy limits apply. Her agent said that she could obtain coverage under her homeowners policy by attaching a list of this valuable property with specific amounts of insurance. Such a listing is called a(n) A) binder. B) schedule. C) application. D) warranty. Answer: B EG Test Insurance.doc 42 37) All of the following are additional coverages provided under Section I of the Homeowners 3 policy EXCEPT A) reasonable repairs. B) debris removal. C) personal liability. D) property removal. Answer: C 38) Darla purchased an unendorsed Homeowners 3 policy. While the policy was in force, a fire occurred that destroyed a living room set. The living room set cost $4,000 new, but was 25 percent depreciated when the loss occurred. Replacement furniture will cost $4,400. Assuming no deductible, how much will Darla receive from her insurer? A) $3,000 B) $3,300 C) $3,400 D) $4,400 Answer: B 39) A dwelling with a replacement cost of $150,000 was insured under a Homeowners 3 policy for $100,000 at the time the roof was destroyed by a windstorm. The actual cash value of the loss was $9,000, but it will cost $12,000 to replace the roof. Assuming no deductible, what will the insurer pay to settle this loss? A) $8,000 B) $9,000 C) $10,000 D) $12,000 Answer: C 40) Ellen believes the value of the loss to her home is $30,000. The insurer has offered $18,000 to settle the loss. If Ellen and the insurer cannot agree on the value of the loss, which homeowners policy provision specifies how this dispute will be settled? A) insurerʹs option B) appraisal clause C) loss payment clause D) mortgage clause Answer: B 41) Ted purchased a home. To fund the purchase, he borrowed $140,000 from ABC Bank, pledging the home as collateral. Shortly after purchasing the home, Ted lost his job. He could not find another job and could not pay the mortgage each month. Ted set fire to the home. The claims adjuster suspected arson, and an investigation proved that Ted intentionally caused the loss. Under the mortgage clause of the Homeowners 3 policy, how will this loss be settled? A) The insurer has no liability because the loss was intentional. B) The insurer will pay Ted the actual cash value of the loss as intentional loss is not excluded. C) The insurer will pay ABC the value of its insurable interest and pay Ted the value of his insurable interest. D) The insurer will pay ABC the value of its insurable interest and then attempt to recoup the loss payment from Ted. Answer: D 42) Mike and Michelle built their ʺdream home.ʺ They agreed to insure the home for its full value. Their insurer offered a special homeowners policy. Under the policy, if a total loss occurs, the insurer agrees to replace the home exactly as it was before the loss even if the replacement cost exceeds the amount of insurance stated in the policy. What is this type of homeowners policy called? A) waiver of inventory policy B) fair market value policy C) guaranteed replacement cost policy D) actual cash value policy Answer: C 43) Jose and Maria would like ʺall-risksʺ coverage on their home and their personal property. Which unendorsed homeowners form provides this coverage? A) Homeowners 2 B) Homeowners 3 C) Homeowners 4 D) Homeowners 5 Answer: D 44) All of the following statements about covered perils and loss settlements under an unendorsed Homeowners 3 policy are true EXCEPT A) The dwelling is covered on an all-risk basis. B) Personal property losses are settled on a replacement cost basis. C) Losses to the dwelling may be settled on an actual cash value basis. EG Test Insurance.doc 43 D) Personal property is covered on a named-perils basis. Answer: B 45) Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding how the Homeowners 3 policy handles the peril of collapse? I. Collapse is specifically excluded, and there are no exceptions to the exclusion. II. Collapse that is caused by a Coverage C peril is covered. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 46) Following catastrophic hurricane losses, South Coast Insurance Company changed its deductible provision. Rather than using a specified dollar value, $250 for example; the dollar value of the deductible increases with the size of the loss. The type of deductible that South Coast changed to is called a(n) A) aggregate deductible. B) franchise deductible. C) straight deductible. D) percentage deductible. Answer: D Chapter 22 - Auto Insurance 1) Which of the following statements about the liability limits of the PAP is (are) true? I. The policy is written with split limits of liability. II. Prejudgment interest is considered part of the damage award and is subject to the policy limit of liability. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 2) Which of the following statements about the payment of defense costs by the PAP is (are) true? I. They are paid in addition to the policy limits. II. They are payable even after the limit of liability is exhausted. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 3) All of the following are covered autos under the liability section of the PAP EXCEPT A) a nonowned van which is driven by the insured on a regular basis. B) a trailer owned by the named insured. C) a borrowed auto used by the insured as a substitute for a stolen covered auto. D) a newly acquired auto which replaces a vehicle previously described in the policy. Answer: A 4) All of the following are insured persons under the liability coverage of the PAP EXCEPT A) a friend to whom the named insured loans a covered auto. B) the employer of the named insured for actions resulting from the named insuredʹs use of a covered auto. C) the former spouse of the named insured who moved out of the home 2 years ago when the divorce was finalized. D) a relative of the named insured if a member of the same household. Answer: C 5) Which of the following persons is (are) covered for liability insurance under the PAP? I. A family member who drives a covered auto. II. A family member who occasionally drives a friendʹs auto. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 6) All of the following are covered as supplementary payments under the liability section of the PAP EXCEPT A) the cost of an appeal bond in a lawsuit. B) the cost of a bail bond for a traffic violation when no accident is involved. C) interest which accrues on a liability judgment covered by the policy. EG Test Insurance.doc 44 D) reasonable expenses incurred by the insured to testify at a trial involving a lawsuit covered by the policy. Answer: B 7) Which of the following situations would be covered by the liability section of an unendorsed PAP if the insured is legally liable? A) The insured injures a pedestrian while operating a friendʹs new motorcycle. B) The insured backs into and damages the garage door of his rented house. C) A friendʹs suitcase and laptop computer were damaged in an auto accident while the insured and the friend were vacationing together. D) The insured damages a parked car while driving a dump truck for his or her employer. Answer: B 8) What is the purpose of the extended nonowned liability coverage endorsement to the PAP? A) to provide liability coverage for an insuredʹs employer when an insured uses his or her auto for business purposes B) to provide liability coverage for an insured who occasionally operates a nonowned auto C) to provide liability coverage for anyone who loans a covered auto to another driver D) to provide liability coverage for an insured who operates a nonowned auto on a regular basis Answer: D 9) Which of the following situations would be covered under the liability section of the PAP? I. A mechanic is sued by a pedestrian who is injured when the mechanic has an accident while road testing the insuredʹs auto. II. The daughter of the named insured is sued after she has an accident when a new friend she just met at a campus hangout lets her drive his car. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 10) Larry has $25,000 of bodily injury liability coverage under his PAP. This limit is the minimum amount required by his state to be considered financially responsible. While on a vacation, Larry visited a neighboring state which has a minimum financial responsibility limit of $50,000 for bodily injury. Which of the following statements describes the situation for Larry while he was in the neighboring state? A) Larryʹs policy was suspended while he was in the neighboring state. B) Larry had only $25,000 of liability coverage. C) Larryʹs policy automatically provided $50,000 of liability coverage. D) Larryʹs policy automatically provided $100,000 of liability coverage. Answer: C 11) John occasionally borrows the car of his friend, Sophie. Sophie has a PAP with liability limits of 100/300/50. John also has a PAP, and his liability limits 250/500/50. John had an accident while using Sophieʹs car and was found to be legally liable for $300,000 in bodily injury liability. How much will be paid by each policy? A) Sophieʹs policy will pay $150,000, Johnʹs policy will pay $150,000. B) Sophieʹs policy will pay $50,000, Johnʹs policy will pay $250,000. C) Sophieʹs policy will pay $100,000, Johnʹs policy will pay $200,000. D) Johnʹs policy will pay the entire amount. Answer: C 12) Which of the following statements about the medical payments coverage of the PAP is true? A) The amount of the benefit typically is $100,000. B) Covered expenses must be incurred within 6 months of the accident. C) Covered expenses include the cost of funeral services. D) The benefit limit applies on a per-accident basis rather than on a per-person basis. Answer: C 13) All of the following are covered persons under the medical payments coverage of the PAP EXCEPT A) a family member of the named insured if struck by an auto while crossing the street. B) a pedestrian struck by the named insuredʹs auto. EG Test Insurance.doc 45 C) the named insured who is injured while occupying a friendʹs auto. D) a friend who is injured while occupying the named insuredʹs auto. Answer: B 14) Tony has a PAP which provides medical payments coverage. Under which of the following circumstances would the injured person be eligible for benefits under Tonyʹs policy? I. A friend is injured while Tony is driving a nonowned auto. II. A hitchhiker riding with Tonyʹs son is injured when the son wrecks Tonyʹs auto. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 15) All of the following are exclusions under the medical payments coverage of the PAP EXCEPT A) injuries incurred while riding a motorcycle. B) injuries incurred while an auto is being used without the presumption that permission would have been granted to use the auto. C) injuries incurred in an auto while it is used in a share-the-expense car pool. D) injuries incurred during the course of employment if workers compensation benefits are available. Answer: C 16) Which of the following statements about the uninsured motorists coverage of the PAP is true? A) The coverage usually applies only to property damage. B) The coverage applies only if the uninsured motorist is legally liable. C) Unless higher amounts are purchased, the maximum benefit is normally limited to $1,000. D) A covered personʹs only recourse is to sue the insurer if there is a disagreement over the amount of damages. Answer: B 17) Which of the following persons is (are) insured under the uninsured motorists coverage of the PAP? I. A pedestrian struck by a covered auto if he or she has no insurance to pay medical expenses II. The spouse of a named insured who is killed by an uninsured motorist A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 18) All of the following are considered to be uninsured vehicles for purposes of the uninsured motorists coverage of the PAP EXCEPT A) a vehicle owned by an individual who is insured, but for less than the amount required by the stateʹs financial responsibility law. B) a hit-and-run vehicle, the ownership of which cannot be determined. C) a vehicle upon which just enough liability insurance has been purchased to satisfy the stateʹs financial responsibility law. D) a vehicle insured by a company which becomes insolvent before a claim can be paid. Answer: C 19) Joyce was injured by an uninsured drunk driver while she was riding in a friendʹs car. Joyce and her friend each have a PAP with an uninsured motorists limit of $50,000. How much will be paid by each policy if it is determined that Joyce has $70,000 of bodily injuries? A) Each policy will pay $35,000. B) Joyceʹs policy will pay $50,000, and the friendʹs policy will pay nothing. C) Joyceʹs policy will pay $50,000, and the friendʹs policy will pay $20,000. D) The friendʹs policy will pay $50,000, and Joyceʹs policy will pay $20,000. Answer: D 20) All of the following statements about Part D (coverage for damage to your auto) of the PAP are true EXCEPT A) Coverage may be purchased with or without collision insurance. B) Losses are paid regardless of fault. C) Coverage applies to a nonowned auto occasionally driven by an insured. EG Test Insurance.doc 46 D) A newly acquired auto is covered only if the named insured asks the company to insure it within 24 hours of acquisition. Answer: D 21) Which of the following is considered to be a collision loss under Part D (coverage for damage to your auto) of the PAP? A) The covered auto hits a deer. B) The covered auto is vandalized by a thief after it is stolen. C) The covered auto is damaged when it slid off an icy road and hit a fence. D) The covered auto is damaged when struck by a rock thrown by a child. Answer: C 22) John has an auto which is covered for collision losses subject to a $250 deductible. Kateʹs auto also has collision coverage but her deductible is $500. Which of the following statements describes how a $2,000 collision loss will be paid if it occurs when John borrows Kateʹs car because his car is in the shop for repairs? A) Johnʹs policy will pay $1,500, and Kateʹs policy will pay nothing. B) Johnʹs policy will pay $1,750, and Kateʹs policy will pay nothing. C) Kateʹs policy will pay $1,750, and Johnʹs policy will pay nothing. D) Kateʹs policy will pay $1,500, and Johnʹs policy will pay $250. Answer: D 23) All of the following losses are excluded under Part D (coverage for damage to your auto) of an unendorsed PAP EXCEPT A) vandals damages a portable cell phone kept in the car. B) theft of a compact disc player which was permanently installed in the auto. C) damage caused to a carʹs engine because the named insured never changed the oil. D) destruction of a radar detector which overheated and caught on fire. Answer: B 24) The insurance companyʹs options for settling a collision loss to a covered auto under the PAP include which of the following? I. Pay the loss in money. II. Repair or replace the damaged auto. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: C 25) Duties of an insured after a collision loss covered under the PAP include which of the following? I. Take reasonable steps to protect the vehicle from further damage. II. Admit fault if the insured believes he or she caused the collision. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: A 26) In addition to providing coverage in the United States, its territories and possessions, and Puerto Rico, where else does the PAP provide coverage? A) in Mexico B) in Canada C) in both Mexico and Canada D) anywhere in the world Answer: B 27) All of the following statements about the termination provisions of the PAP are true EXCEPT A) The insured can cancel the policy for any reason. B) The insurer can cancel a newly-written policy if it has been in force for fewer than 60 days. C) The insurer can cancel the policy after it has been in force for 60 days only if the insured has three or more traffic violations. D) The insurer can refuse to renew the policy at its annual anniversary date as long as proper notice is given prior to the end of the policy period. Answer: C 28) The Miscellaneous-Type Vehicle Endorsement to the PAP can be used to insure all of the following vehicles EXCEPT EG Test Insurance.doc 47 A) motor homes. C) snowmobiles. B) golf carts. D) motorcycles. Answer: C 29) Which of the following statements about the Miscellaneous-Type Vehicle Endorsement to the PAP is (are) true? I. It provides bodily injury liability coverage for any vehicle rented by the insured. II. To lower premiums when a motorcycle is insured, bodily injury to passengers can be excluded. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: B 30) Ken fell asleep while driving late at night. He crossed the center line and hit a car approaching from the other direction. The following losses occurred: • The driver of the other car suffered $30,000 in bodily injuries. • Kenʹs car sustained $5,000 in damages. • Ken incurred $5,000 in medical expenses. • The car that Ken hit was a total loss. Which of Kenʹs Personal Auto Policy (PAP) coverages will cover the other driverʹs medical expenses? A) bodily injury liability B) collision coverage C) medical payments coverage D) property damage liability Answer: A 31) Ken fell asleep while driving late at night. He crossed the center line and hit a car approaching from the other direction. The following losses occurred: • The driver of the other car suffered $30,000 in bodily injuries. • Kenʹs car sustained $5,000 in damages. • Ken incurred $5,000 in medical expenses. The car that Ken hit was a total loss. Which of Kenʹs Personal Auto Policy (PAP) coverages will cover the damage to Kenʹs car? A) bodily injury liability B) collision coverage C) medical payments coverage D) property damage liability Answer: B 32) Ken fell asleep while driving late at night. He crossed the center line and hit a car approaching from the other direction. The following losses occurred: • The driver of the other car suffered $30,000 in bodily injuries. • Kenʹs car sustained $5,000 in damages. • Ken incurred $5,000 in medical expenses. • The car that Ken hit was a total loss. Which of Kenʹs Personal Auto Policy (PAP) coverages will cover Kenʹs medical expenses? A) bodily injury liability B) collision coverage C) medical payments coverage D) property damage liability Answer: C 33) Ken fell asleep while driving late at night. He crossed the center line and hit a car approaching from the other direction. The following losses occurred: • The driver of the other car suffered $30,000 in bodily injuries. • Kenʹs car sustained $5,000 in damages. • Ken incurred $5,000 in medical expenses. • The car that Ken hit was a total loss. Which of Kenʹs Personal Auto Policy (PAP) coverages will cover the damage to the car that Ken hit? A) bodily injury liability B) collision coverage C) medical payments coverage D) property damage liability Answer: D 34) Sarah purchased a Personal Auto Policy with liability limits of 50/100/25. Sarah ran a stop sign and hit a van. The van sustained $15,000 in damages. The following bodily injuries were suffered by passengers in the van: Passenger #1, $15,000; Passenger #2, $60,000; and Passenger #3, $10,000. Sarah sustained $5,000 in medical expenses, and Sarahʹs car sustained $10,000 in damages. How much will Sarahʹs insurer pay under Part A: Liability Coverage? A) $90,000 B) $100,000 C) $115,000 D) $125,000 Answer: A EG Test Insurance.doc 48 35) Patricia purchased a Personal Auto Policy (PAP). Her car was rear-ended by a driver who fled the scene. Patricia suffered whiplash, migraine headaches, and she was unable to work. Which of the following coverages will cover her lost work earnings? A) medical payments B) uninsured motorists C) underinsured motorists D) bodily injury liability Answer: B 36) Rob purchased a Personal Auto Policy (PAP) with collision and other-than-collision coverage. All of the following losses are excluded under this physical damage coverage EXCEPT A) Rob wrecked his car while using it as a taxi cab. B) Thieves took Robʹs radar detector from his car. C) A flash flood washed Robʹs car off the road and damaged it. D) The new tires Rob had on the car were defective and wore out after 2 months. Answer: C 37) Angie was injured when her car was struck by a driver who ran a red light. The other driver carried the minimum liability coverage necessary to be considered financially responsible. Angieʹs injuries were $15,000 above the minimum bodily injury limit. There is a coverage that can be added to the PAP that applies when a negligent driver carries the minimum liability insurance required by the state, but less than the insuredʹs actual damages for bodily injury. This coverage is called A) medical payments coverage B) underinsured motorists coverage. C) bodily injury liability coverage. D) uninsured motorists coverage. Answer: B 38) Dennis was involved in an accident. He believes the damage to his auto is $6,000. His insurer believes the damage is only $3,500. Which PAP provision is designed to handle disputes between the insurer and the insured over the amount of the loss? A) other insurance provision B) agreed amount endorsement C) coinsurance provision D) appraisal provision Answer: D 39) The purpose of the collision damage waiver when renting an auto is to A) relieve the renter of financial responsibility if the rented car is damaged or stolen. B) relieve the renter of legal liability to third parties arising out of operation of the rented car. C) relieve the renterʹs insurer of legal liability to third parties arising out of operation of the rented car. D) waive the insuredʹs deductible if the rented car is damaged or stolen. Answer: A 40) Which of the following statements is (are) true with respect to the collision damage waiver on rented cars? I. It is inexpensive and is provided at no charge by most rental car companies. II. It waives renterʹs liability for bodily injury liability arising out of the use of the rented auto. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D 41) The purpose of gap insurance is to A) pay the difference between the bodily injury liability limit purchased and the actual amount of bodily injury liability if it exceeds the limit. B) pay the difference between the amount the insurer pays if a car is a total loss and the amount owed on a lease or car loan. C) pay the difference between the medical payments coverage limit and the actual medical expenses of injured family members or passengers in the insured auto. D) pay the difference between the uninsured motorists coverage limit and the actual amount of the medical expenses incurred by the insured. Answer: B 42) A car damaged in an auto accident may have reduced market or resale value after it is repaired. Some insureds sought to recover this reduction in market or resale value. This loss in value is called: A) gap coverage B) betterment. EG Test Insurance.doc 49 C) diminution D) subrogation. Answer: C 43) If the value of a vehicle is increased after repairs, such as repainting an entire auto when only one fender or door is damaged, the insurer will not pay for the increase in value. Another name for the increase in value is A) diminution B) betterment. C) appraisal D) subrogation. Answer: B 44) The 2005 PAP states that the insurer has no duty to provide coverage if the insured fails to comply with certain listed duties. In practice, however, the insurer is only relieved of its duty to provide coverage if A) the insured was unaware of the listed duties. B) failure to comply with the duties is prejudicial to the insurer. C) the claim involves bodily injuries of more than $50,000. D) the claim occurred in another state. Answer: B 45) Which statement concerning towing and labor coverage under the PAP is (are) true? I. If the insured purchases collision coverage, towing and labor coverage is provided automatically. II. Towing and labor coverage pays for repairs at a service station or garage. A) I only B) II only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II Answer: D EG Test Insurance.doc 50