Unit C Review KEY
advertisement

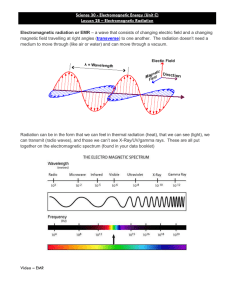
Science 30 Negatively charged Electric potential difference Test body Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Positively charged Coulomb Conductor volt voltage Insulator Field lines Solar wind Gravitational force Electric force Grounded Gravitational field Gravitational field strength Electric current Field lines Mechanical energy armature commutator Transverse wave Parallel connection Resistance Kilowatt-hour Direct current Voltmeter Ohmmeter Transformer Alternating current Ammeter Schematic diagram Primary coil Wavelength (λ) frequency hertz (Hz) Radio wave antenna Black hole Microwaves Ultraviolet radiation Radioactive Nuclear Fusion Infrared radiation Ionizing radiation Gamma radiation Refraction Diffraction Grating Continuous spectrum Spectra Red Shift Nebula Multiwavelength astronomy Spectrometer Red giant Supernova Visible spectrum X-rays Constellation Reflection Absorption (darkline) spectrum Doppler effect Nebula Neutron star Electrical energy Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Series connection Resistor Power Secondary coil electromagnetic spectrum Magnetic resonance imaging Photon Radiation therapy Astronomy Diffraction Emission (bright-line) spectrum Blue shift White dwarf Pulsar V = IR RT = R1 + R2 + R3 Cosmic rays Cosmic rays Resistance Electric potential difference Test body 1 1 1 1 = + + 𝑅𝑇 𝑅𝑇1 𝑅2 𝑅3 Streams of high speed, ionized particles ejected from objects beyond the solar system. They normally consist atomic nuclei. This is the measure of the difficulty electrons have travelling through a component, measured in ohms (Ω). This is the difference in energy per coulomb of charge between two ∆𝑬 points on an electric circuit. It can be found by: 𝑽 = 𝒒 This is a small charge that may for put into an electric field to determine the nature of the charge, the direction of the field and the electric force acting on the test charge. Negatively charged An object has this charge if it has gained electrons. Mechanical energy The energy contained by an object due to its motion or position. It the sum of all of the kinetic and potential energy in a substance. Parallel connection This is a circuit in which the electric current has more than one possible path to flow through. Grounded This is the process where a charged object or circuit is connected to the ground and excess charge can be dissipated. Kilowatt-hour This is a unit of energy that is often used when discussing electrical energy consumption. Diffraction Grating This is an instrument that is used to produce a diffraction pattern of like waves by making them bend due passing by a barrier. Positively charged An object has this charge if it has lost electrons. Series connection This is a circuit in which the electric current has only one possible path to flow through. Radio wave 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + 𝑹𝑻 𝑹𝑻𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝟑 This are very long EMR, they are used in radio communication. Formula to find total resistance in a parallel circuit. Microwaves These are a type of EMR with fairly long waves. They are used in cell phones and for making popcorn. Gravitational field strength This is the quantity of the sphere of influence due to a gravitational field. Wavelength (λ) This is the measure on a wave from one point to the same point on the next wave. (crest to crest, trough to trough … etc.) Nuclear Fusion This is a nuclear reaction in which two nuclei are joined to produce a new daughter nuclei. This is the type of reaction that takes place at the sun to produce solar energy. Ultraviolet radiation RT = R1 + R2 + R3 Spectra Red Shift Nebula volt Gravitational field Transformer Electric current Infrared radiation Direct current This are short waves with higher frequency that visible. It is this element of the sun’s radiation that makes humans susceptible to sunburn and skin cancer. Formula to find total resistance in a series circuit. This is the plural of spectra. This the manifestation of the Doppler Effect that involves a spectral shift because a star is moving away from the observer. This is an interstellar cloud of gas and dust. J This is the SI unit for potential difference. It is equivalent to 1.0 C. This is a sphere of influence that is caused by any object due to its mass. It can apply a force of attraction to any other object with mass within the field. This is a AC device that can step up or step down the voltage between the primary and secondary coils by changing the number of loops. This is the flow of electrons through a conductor. This is EMR that is slightly longer λ than visible. It sends the remote control signal to your TV set. This type of current is present when the charges go directly from the negative electrode to the positive one through the circuit. It is abbreviated as DC. Voltmeter This is an electrical device that measures the potential difference between two points in a circuit. Ammeter This is an electrical device that measures the current flowing through a circuit. armature This is the section of an electric motor that rotates. Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) This is the type of wave that does not require a medium. It is propagated by perpendicular changing electric and magnetic fields. Supernova antenna frequency This is a stellar explosion that produces a very bright cloud of ionized gas that remains very bright object in the sky for week or months. This is an EMR receiver. This is a measure of the number of waves to pass by per second. It is measured in Hz. Ionizing radiation This is the result of radioactive decay. It includes particle and photons (alpha, beta and gamma) that can penetrate living tissue ionize atoms of cells and kill or cause mutation. Gamma radiation This is the shortest λ, higher f waves in the EMR spectrum. They are extremely dangerous. V = IR This is the formula for Ohm’s Law. Refraction This is the bending of light waves due to a change in medium. Moving from a less dense material to a more dense (air to water) will slow the light waves and cause them to bend towards the normal. Field lines These are lines that are drawn around an object to show the direction and strength of the object’s field. They may represent a magnetic field, gravitational field or electric field. Red giant This is a star of great size and age that has a low surface temperature. Continuous spectrum voltage Coulomb commutator This include the complete “ROYGBIV”, it is produced when a glowing solid emits light that passes through a triangular prism. This is also known as potential difference. It represents the difference in energy per coulomb of charge. This is the SI unit for charge. It is equal to 1.0 A.s. One electron has the charge of 1.60 x 10-19 C. This is the part of an electric motor or generator that is found on the armature, that provides the electric current. If found on a DC device it will be the split ring type. Alternating current hertz (Hz) Schematic diagram Primary coil This type of current is present when the charges change direction several times per second while present in the circuit. It is abbreviated as AC. 1 This is the SI unit for frequency. It the equivalent to 𝑠 . This is aka a circuit diagram. It uses symbols to detail the components and nature of a circuit. This is input side of a transformer. Transverse wave This is a wave produced by a disturbance in the medium that is perpendicular to the direction of travel. Doppler effect This is the apparent shift in frequency of waves due to relative motion between the source and the receiver of the wave. X-rays This are fairly short waved, high frequency EMR. They are used to penetrate human tissue to scan for broken bones. Reflection This is when a wave makes contact with a boundary, and bounces off. Visible spectrum This is the part of the EMR spectrum that our human eyes can see. It include the colours: ROYGBIV. Absorption (dark-line) spectrum Multiwavelength astronomy Neutron star Insulator Solar wind This is a spectrum that looks like a continuous spectrum with a series of dark lines on it. It is produced when the white light produced by a glowing solid passes through a cool gas and then a triangular prism. This is the science of studying several different wavelengths of EMR emitted in objects in space. A super-dense star consisting mainly of neutrons formed at the last stage in the star development of intermediate-mass stars. This is a material that will allow not electrons to flow throw it easily. Rubber and glass are examples. Streams of high speed, ionized particles ejected from the sun. They normally consist of electrons, protons and helium nuclei. Conductor This is a material that will allow electrons to flow throw it easily. Metals are examples. Electric force This is a push or pull effect applied to a charged object by the electric field of another charge or by charged plates. Electrical energy This is energy that is available to the movement of electrical charges. Resistor Power Secondary coil Photon electromagnetic spectrum This is a device in a circuit that contains resistance and uses electric energy in a circuit. Is the amount of energy used or work done per unit time. It is measured in watts. This is output side of a transformer. This is a packet of light energy that travels in a wave-like manner. This is the complete band of EMR from Radio to gamma. Magnetic resonance imaging This is a device that uses radio waves and strong magnetic field to obtain internal images of living things. It is abbreviated as MRI. Astronomy This is the scientific study of objects above the earth’s atmosphere. Radiation therapy This is the medical use of ionizing radiation to treat disease like cancer. Blue shift This the manifestation of the Doppler Effect that involves a spectral shift because a star is moving towards the observer. Diffraction This is the wave property that involved the bending of light due passing next to a boundary. With light a spectra can be produced by directing light waves through a diffraction grating. Emission (bright-line) spectrum This is a spectrum that is just a series of bright lines. It is produced when the light produced by a glowing gas passes through a triangular prism. Pulsar White dwarf Magnetic field This is a rotating neutron star that emits radiation in regular pulses. This is a compact star, found as the last stage in the evolution of low-mass stars. This is a sphere of influence that is caused by moving electric charges in a conductor or the magnetic domains within a permanent magnet. It can apply a force to certain metals and to moving charges within the field.