Tesla Turbine as a Compact, Liquid
advertisement
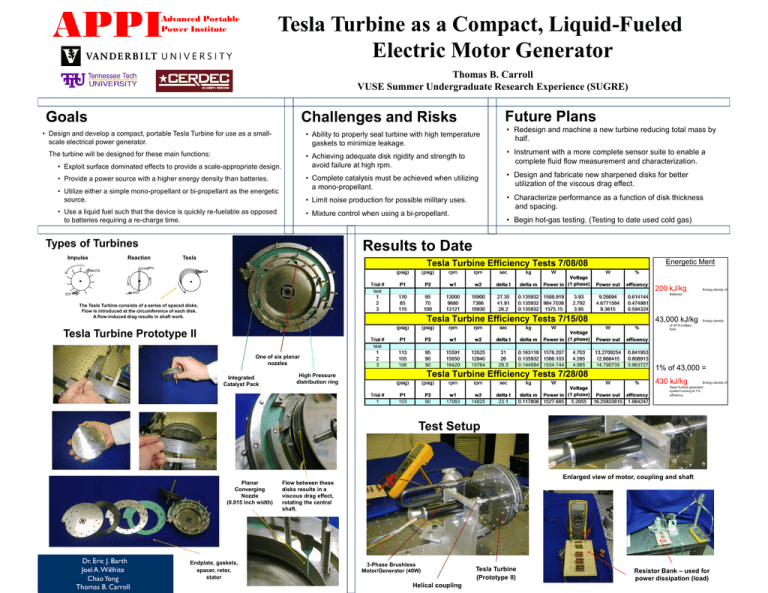
APPI Tesla Turbine as a Compact, Liquid-Fueled Electric Motor Generator Advanced Portable Power Institute Thomas B. Carroll VUSE Summer Undergraduate Research Experience (SUGRE) Goals • Design and develop a compact, portable Tesla Turbine for use as a smallscale electrical power generator. • Ability to properly seal turbine with high temperature gaskets to minimize leakage. The turbine will be designed for these main functions: • Provide a power source with a higher energy density than batteries. • Utilize either a simple mono-propellant or bi-propellant as the energetic source. • Use a liquid fuel such that the device is quickly re-fuelable as opposed to batteries requiring a re-charge time. • Complete catalysis must be achieved when utilizing a mono-propellant. • Design and fabricate new sharpened disks for better utilization of the viscous drag effect. • Limit noise production for possible military uses. • Characterize performance as a function of disk thickness and spacing. • Mixture control when using a bi-propellant. • Begin hot-gas testing. (Testing to date used cold gas) Results to Date Types of Turbines Reaction • Redesign and machine a new turbine reducing total mass by half. • Instrument with a more complete sensor suite to enable a complete fluid flow measurement and characterization. • Achieving adequate disk rigidity and strength to avoid failure at high rpm. • Exploit surface dominated effects to provide a scale-appropriate design. Impulse Future Plans Challenges and Risks Tesla Energetic Merit 200 kJ/kg Energy density of Batteries The Tesla Turbine consists of a series of spaced disks. Flow is introduced at the circumference of each disk. A flow-induced drag results in shaft work. 43,000 kJ/kg Energy density of JP-8 (military fuel) Tesla Turbine Prototype II One of six planar nozzles Integrated Catalyst Pack 1% of 43,000 = High Pressure distribution ring 430 kJ/kg Energy density of Tesla Turbine generator system running at 1% efficiency Test Setup Planar Converging Nozzle (0.015 inch width) Dr. Eric J. Barth Joel A. Willhite Chao Yong Thomas B. Carroll Endplate, gaskets, spacer, rotor, stator Enlarged view of motor, coupling and shaft Flow between these disks results in a viscous drag effect, rotating the central shaft. 3-Phase Brushless Motor/Generator (40W) Helical coupling Tesla Turbine (Prototype II) Resistor Bank – used for power dissipation (load)



