Experiment no 11 Object: To draw the characteristics of PN junction
advertisement

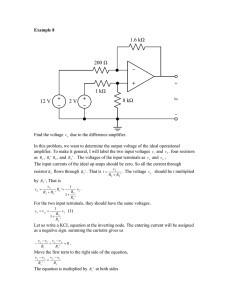
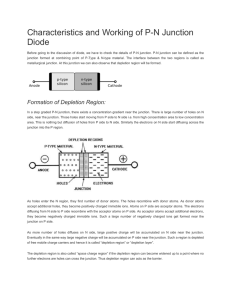
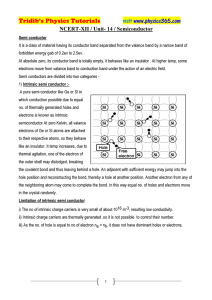
Experiment no 11 Object: To draw the characteristics of PN junction diode. Apparatus Required: transistor, milliammeter and micro ammeter, battery, rheostat, voltmeter and connection wires. Procedure: (A) Forward Biasing: (i) Connections are made as in the fig. (ii) With the help of rheostat, apply different voltages to the PN junction and note the corresponding reading of current in millimeters. (iii) Plot a graph in applied voltages and corresponding currents. (B) Reverse Biasing: (i) Make the connections as in the fig. and proceed exactly in the same way as opted for forward biasing. Result: The characteristic of junction diode ( ) are shown in the graphs. Sources of Error and Precautions: (i) To avoid over heating of the transistor, current should not be passed for long durations. (ii) Voltages applied should be well below the safety limit of the transistor. (iii) Connections should be made carefully. VIVA-VOCE: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is a PN junction diode? What do you mean by P-type germanium and N-type germanium? What property PN junction exhibits? What is the order of currents in the above two cases? Mention the order of voltages with it. What if high voltage is applied in forward bias? Have you heard of turn over voltage? Figure 1: Figure 2: Figure 3: Figure 4: Observations: S.No. Forward Biasing Voltage in Current in mA volts 1 ……… ………. 2 ……… ………. 3 4 5 S.No. 1 2 3 4 5 Reverse Biasing Voltage in Current in mA volts ……. ………. …….. ……… Calculations: (Graph plotting): Plot two graphs- one for forward and other for reverse biasing between voltages applied and the corresponding currents